DR
AHMED JASIM MOHAMMED
ASS, PROF
Early pregnancy
disorderDisorders of early pregnancy Early pregnancy loss:
More pregnancies are lost in the early weeks than at any other stages of pregnancy.Three of the main categories of early pregnancy loss are:
abortion (spontaneous abortion, induced abortion)
ectopic pregnancy
hydatidiform mole
Abortion
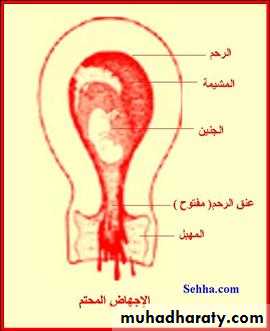
Abortion MisscariageIs the termination of pregnancy before time of viability which is the 24th weeks of pregnancy .
Viability mean the time where fetus is capable of surviving outside uterus.
(Some consider time of viability as 24th weeks and others considered it as 20th weeks or 22nd weeks)(in our locality 24th weeks).
The most common time for abortion is 7-13 weeks of gestation.
Abortion types:
SpontaneousInduced
Incidence:
it is expulsion of the products of conception without medical or surgical intervention.Incidence:
15-20% in early pregnancy. The rate of abortion is known to decrease with increasing gestational age from 25% at 5-6 weeks to 2% after 14 weeks.
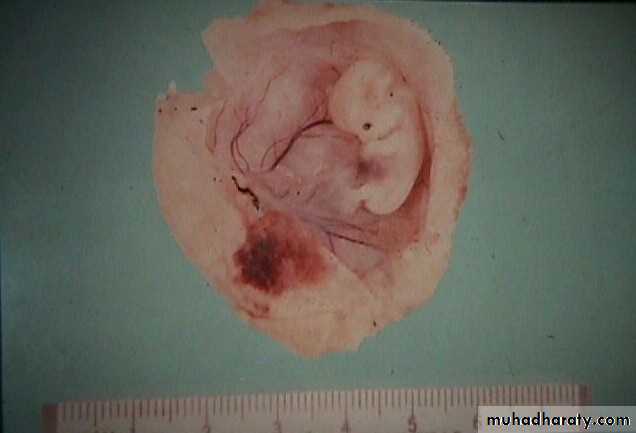
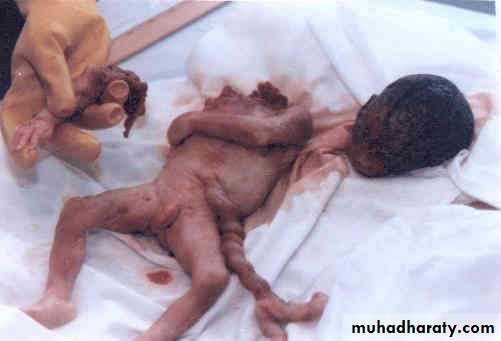
Blighted Ovum (Anembryonic pregnancy):
Those early pregnancy loss in which fetal development is not observed with ultrasound and fetal tissue is absent on the histologic examination of product of conception. It is caused by genetic cause.
Causes of spontaneous miscarriage:
Maternal causes:General:
• Acute febrile illness.• b. infection (bacterial vaginosis, syphilis, rubella). Any severe infection that leads to bacteraemia or viraemia can cause sporadic miscarriage.
• c. Severe hypertension
• Severe renal disease.
• Badly controlled Diabetes mellitus.
• Hypothyrodisim.
• Severe malnutrition.
1. Maternal causes:A. General:
Trauma.1.direct penetrating injury.
2.surgery (abdominal, pelvic)
3.amnicentesis.
4.chorionic villous samplling
Poisons (cytotoxic drug, lead, quinine, ergot, smoking, alcohol).
Local cause
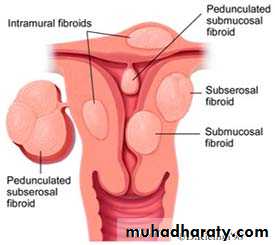
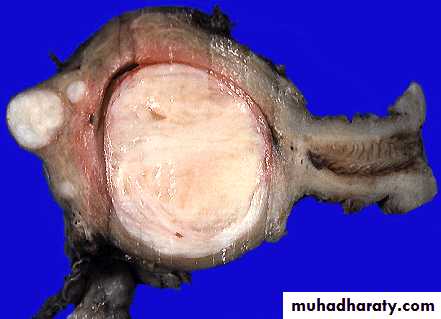
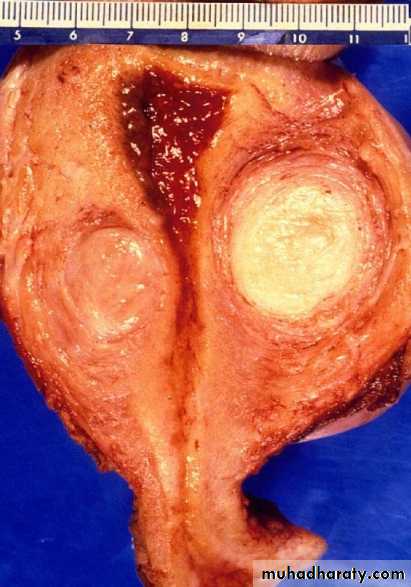
• Uterine fibroids. (submucous fibroid related to uterine cavity).
• Congenital abnormalities (double, septate uterus).
• Cervical incompetence/ weakness.
• Incarcerated retroverted uterus in pelvis (Fixed).
• Asherman's syndrome (intrauterine adhesion).
• Presence of intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD).
• g. Abnormalities of implantation (low implantation of placenta).
Uterine fibroid
Fetal causes:
Fetal abnormalities.multiple pregnancy.
immunological causes factors:
a. autoimmune disease (antiphospholipid antibody, thrombophilia, any persistent and identifiable hypercougulable state either acquired or inhertant).b. Rh incompatibility (occasionally).
4. Endocrine abnormalities:
a. luteal phase inadequacy.b. hypersecration of LH.
Pathological anatomy: First trimester of pregnancy:
The attachment of chorion to deciduas is so delicate that separation may follow strong uterine contractions produced by any cause. The resulting hemorrhage into the chorio-decidual space leads to further separation.In other cases fetal death precedes uterine contractions.
The deciduas basalis remains in the uterus, and membranes and most of deciduas capsularis is expelled.
In some cases the gestation sac is retained in uterus for days or weeks as a missed abortion
Pathological anatomy:Second trimester:
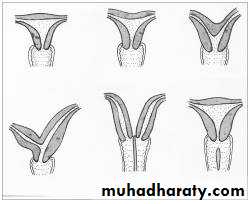
the placenta is a definite structures, and if happen after this time the process of abortion is similar to that of labour. Bleeding and painful contractions are followed by dilatation of cervix, rupture of membranes and expulsion of fetus and placenta. If a conceptus is expelled, normal uterine involuation follows, but frequently part of placenta is retained with some blood clots.Clinical varieties of miscarriage (spontaneous abortion):
Threatened abortionInevitable abortion:
Incomplete abortion:
Complete abortion:
Missed abortion:
Septic abortion:
Recurrent abortion (Habitual):
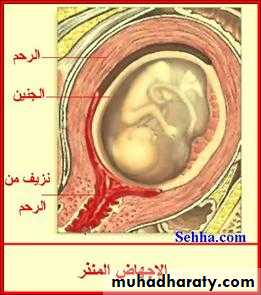
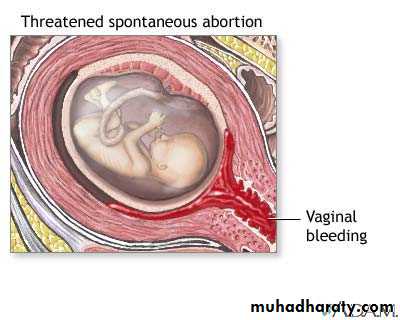
Threatened abortion
symptoms:
1.scanty uterine bleeding preceded by symptoms of pregnancy.
2.pain is usually absent but may be backache or mild lower abdominal pain.
Threatened abortion
Signs (Examination):1.uterus is enlarged corresponding with date of amenorrhoea.
2.cervix is closed.
3.no pelvic tenderness.
Threatened abortion
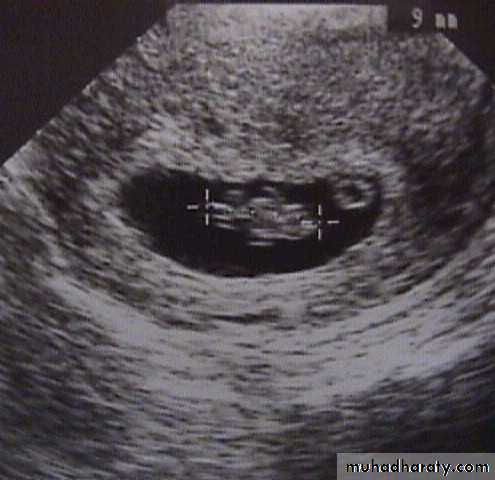
Investigations:Ultrasound :confirm intrauterine gestation (IUG) and fetal heart (FH).
Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (hCG) increase in serial measurement.
Threatened abortionTreatment:
No specific treatment needed. only need reassurance and rest until bleeding stopped.Progesterone, hCG it's benefit is not confirmed yet???
Anti D (250unite) should be given to non sensitized Rh negative women.
Threatened abortionPrognosis:
50% of pregnancy have successful outcome and increase risk of:Preterm labour
Low birth weight
Perinatal death.
Antepartum hemorrhage
Manual removal of the placenta
Cesarean delivery.
Risk of a malformed surviving infant does not appear to be increased.
Inevitable abortion:
Means that it is impossible for the pregnancy to continue and the process is now irreversible.Symptoms:
1.severe vaginal bleeding because a large area of the placenta has detached from the uterine wall.
2. It is accompanied by acute abdominal pain which is similar to the pattern of uterine contractions in labour (intermittent).
3. No products of conception expelled yet.----------
Inevitable abortion:
Signs:Uterus is enlarged.
Internal os is dilated (open).
Inevitable abortion:
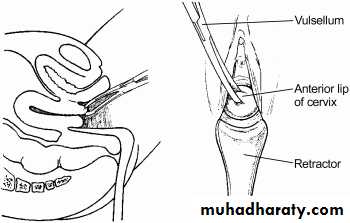
Treatment:Once the diagnosis is made, uterus should be evacuated
in first trimester
Evacuate uterus under general anesthesia by curettage or suction curettage (without cervical dilatation because cervix is already dilated).
Inevitable abortion:
• in second trimester :• Allow miscarriage to take place spontaneously and the process can be expedited and bleeding controlled with ergometrine 0.5mg and oxytocin 5unit or prostaglandin in addition to supportive therapy (correction of blood loss, analgesia, antibiotic is given as necessary).
• Uterus need evacuation if patient not abort all the product of conception and severe bleeding was associated.
• Anti D (250unite) should be given to non sensitized Rh negative women
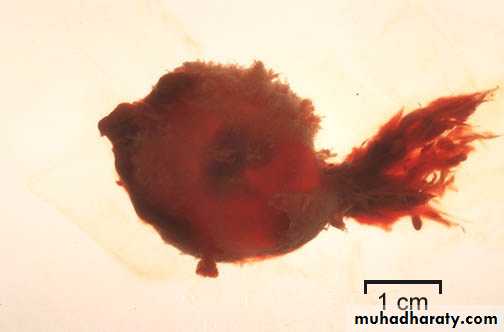
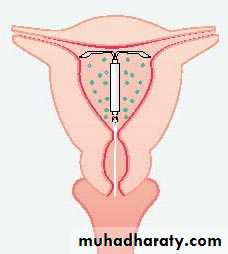
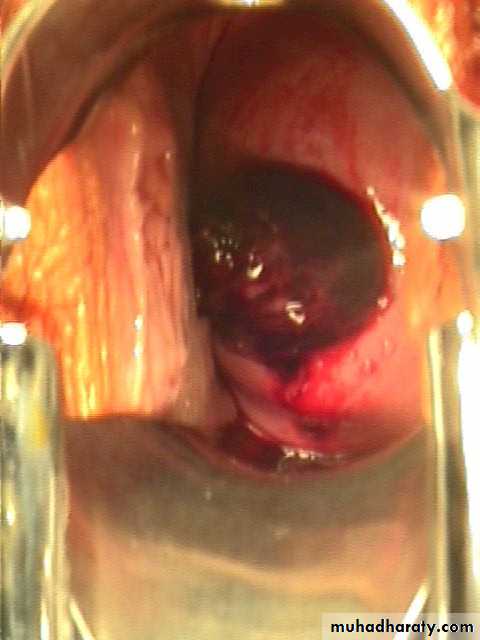
Incomplete abortion:
Symptoms are the same as for inevitable abortion but some products of conception are passing from uterus and part of product of conception retained in the uterus or cervical canal, a situation that causes ongoing cramping and excessive bleeding with danger of shock and sepsis.
Incomplete abortion
Symptoms:1. uterine bleeding which is varies may be severe to cause hypovolemia or mild
2.history of passing part of conception (Women describe the product of conception as looking like pieces of skin or liver).
Incomplete abortion:
Sign:1.Uterus may be smaller than expected for period of amenorrhea.
2.Cervix is open.
3.Speculum examination reveals dilated internal os and tissue within the endocervical canal or vagina.
4.Bleeding may be heavy.
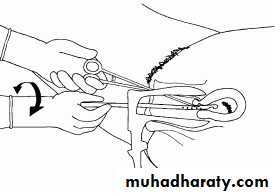
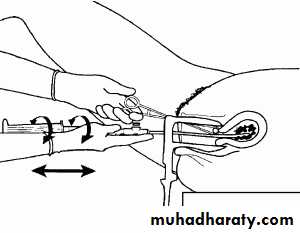
Incomplete abortion with products of conception passing through the dilated cervical os
Incomplete abortion:
Treatment:Severe vaginal bleeding
Need admission to hospital and resuscitation with intravenous fluid (IV) fluid and blood transfusion(if needed) and give analgesia and evacuation of uterus by curettage with out need of dilatation under oxytoxic drugs.
Anti D (250unite) should be given to non sensitized Rh negative women.
Digital removing of product of conception which are in cervical canal is advised as this help to relieve the discomfort.
Digital removing of product of conception which are in cervical canal as much tissue as possible as this help to relieve the discomfort.
Incomplete abortion
B. Mild vaginal bleeding:Ultrasound examination done to confirm presence of retained product of conception which need surgical evacuation by curettage.
Anti D (250unite) should be given to non sensitized Rh negative women.
Complete abortion:
All product of conception have been expelled and uterus is empty without need for medical or surgical intervention.
Symptoms:
Scanty blood loss and cessation of abdominal pain after history of severe abdominal pain and severe vaginal bleeding with passing product of conception.
Complete abortion:
Signs1.uterus is smaller than period of amenorrhea and firmly contracted.
2. cervix is closed or patulous in multiparous women.
Complete abortion:
Investigations:Ultrasound to confirm empty cavity.
Complete abortion:
No further treatment is needed but patient warned to report at once if bleeding recur or develop fever.Anti D (250unite) should be given to non sensitized Rh negative women.
Missed abortion:
fetus dies in uterus and is retained inside uterus.
Symptoms:
1.May be preceded by sign and symptom of threatened abortion.
2.Disappearance of symptoms of pregnancy.
3.Dark brown vaginal discharge.
4.Diagnosed incidentally by ultrasound(sometimes).
Missed abortion:
examination:uterus is smaller than expected.
Cervix is closed.
Missed abortion:
Signs:1.Uterus is smaller than period of amenorrhea (small for date uterus).
2.Cervix is closed.
Investigations:
hCG drops in 7-10 days. Positive test dose not exclude missed although negative test support diagnosis of dead fetus.
Missed abortion:
Ultrasound showed: no fetal heart and gestational sac may collapse.If there is any doubt about diagnosis, it is wise to wait for a few days and repeat scan to see if sac is growing.
If ultrasound is not available, abdominal x-ray after 16 weeks show collapse of fetal skeleton
Missed abortion:Complications:
1.infection.
2.coagulation disorder (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy-DIC-). It is rare if less than one month from death of fetus.
3. psychological distress to mother.
Missed abortion:
Treatment:Once diagnosis established, evacuation of uterus without delay after investigation (mainly for fibrinogen level).
First trimester:
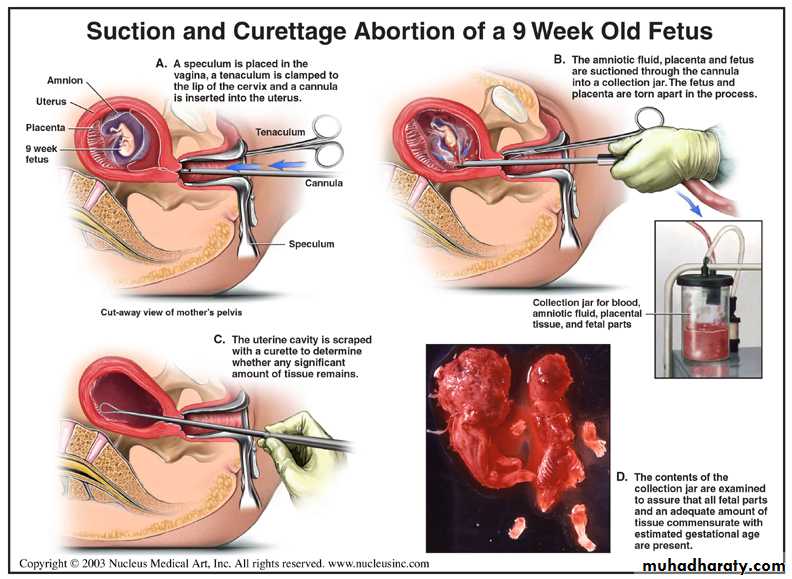
Suction curettage is preferred.
Second trimester:
Induction of abortion and uterine activity is stimulated by oxytocin infusion after pre treatment with mifepristone or vaginal prostaglandin E2 or prostaglandin extra-amniotically by foly catheter introduced through cervix.
Anti D (250unite) should be given to non sensitized Rh negative women.
Septic abortion:
Infection of the uterine cavity may occur following any kind of abortion but is more common followingmissed abortion.
incomplete abortion.
induced abortion (criminal).
Infection will first occur in the uterus but will rapidly spread to the fallopian tubes, pelvic organs and peritoneum and will cause septicemia if not promptly treated.
The commonest microorganism are Escherichia coli (E coli), streptococcus, staphylococcus aureus, clostridium Welchii
Symptoms:
History of abortion (often criminal).Maternal fever.
Lower abdominal pain.
Persistent vaginal bleeding.
Offensive vaginal discharge.
Septic abortion:
Symptoms:
history of abortion (often criminal).
maternal pyrexia.
Lower abdominal pain.
persistant vaginal bleeding.
offensive vaginal discharge.
Septic abortion:
Signs:patient is ill, toxic.
Raise temperature and tachycardia.
Suprapubic tenderness with guarding.
Uterus is very tender.
Cervix remained patulous.
Offensive vaginal discharge.
Septic abortion:
Investigations:Ultrasound.
Vaginal and cervical swab, blood and urine culture.
Septic abortion:
1.admission to hospital.
2.antibiotic therapy parentral wide-spectrum antibiotic continuo for at least 5 days after fever subside.
If no response, change according to result of culture and sensitivity
If the product of conception are retained, the uterus should be evacuated by curettage.
Septic abortion
• If there is mild bleeding• curettage postponed until 24 hours after starting antibiotic therapy .
• b. if there is Severe bleeding
• Curettage under general anesthesia done without delay with antibiotic and oxytoxic drugs.
• Anti D (250unite) should be given to non sensitized Rh negative women.
Complications of septic abortion:
bacteramic shock.renal failure.
hepatic failure.
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy (DIC).
more liable for perforation during curettage.
gangrenous uterus if clostridia infection.
maternal death.
long term squeal after treatment (infertility, chronic pelvic infection and pain).
Tissue obtained at the time of miscarriage should be examined histologically to confirm pregnancy and to exclude ectopic pregnancy or unsuspected gestational trophoblastic disease.
Recurrent miscarriage (recurrent abortion)(Habitual abortion):
It is three or more consecutive (successive) spontaneous abortions.Incidence: 1-2 % of pregnancy.
Risk of further abortion after 3 abortion estimated as 30-70%.
Causes of recurrent abortion:
A. idiopathic (chance phenomena).B. causes which are:
1.Genetic
Parental chromosome abnormalities (in 3 - 5% of couples with RM).
Fetal aneuploidy ((trisomy or monosomy)).
2.Endocrinopathies
Badly controlled diabetes mellitus (well-controlled diabetes mellitus is not a risk factor for recurrent miscarriage).
thyroid auto-antibodies are increased among women with RM (treated thyroid
dysfunction is not a risk factor for recurrent miscarriage).
polycystic ovaries (PCO) ???
Causes of recurrent abortion:
3.antiphospholipid syndrome (apl)lupus anticoagulant (LA) and the anticardiolipin antibodies (aCL) have been shown to be of reproductive significance.
4. thrombophilic defects.
5. Immune dysfunction.
6. Structural uterine abnormalities. (congenital anomalies, submucous and intramural leiomyomas, polyps, intrauterine adhesions).
Recurrent abortion (Habitual):Evaluation of wife and husband with recurrent abortion includes:
a. full history (past obstetric history, past gynaecological history, past medical history, family history, previous investigation and treatment) and history about husband.
b. physical examination.
c. investigations required in recurrent abortion are:
1.Maternal and paternal chromosome analysis (karyotype) and fetal chromosome analysis to exclude translocations.2.Thrombophilia screen.
3. Anticardiolipin antibody, lupus anticoagulant.
To diagnose APS it is mandatory that the patient should have two positive tests at least six weeks apart for either lupus anticoagulant or anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies of IgG and/or IgM class present in medium or high titre.
4.Pelvic ultrasound.
5.Hysterosalpingogram/ hysteroscopy (to evaluate uterine cavity).
Recurrent abortion (Habitual):
Mid- follicular serum LH/FSH.High vaginal swab.
After evaluation , cause can be identified in 50% of cases.
6.Mid- follicular serum LH/FSH.(LH=lutinizing hormone, FSH = follicular
stimulating hormone)
7.High vaginal swab.
A significant proportion of cases of recurrent miscarriage remain unexplained, despite detailed investigation.
TORCH (Toxoplasmosis, Other [congenital syphilis and viruses], Rubella, Cytomegalovirus and Herpes simplex virus) screening is unhelpful in the investigation of recurrent miscarriage, outside an acute infectious episode .
Recurrent abortion (Habitual):
• Treatment:• if the cause can be identified , treat the cause as:
• *cervical incompetence – cerclage.
• *Uterine abnormalities -Surgical treatment, excision of septum, myomectomy.
• *Antiphospholipid Ab can be treated with aspirin and heparin.
• *serum immunological factors can be treated by immune therapy under study?.
Recurrent abortion (Habitual):
• Idiopathic (no identified cause):• These women can be reassured that the prognosis for a successful future pregnancy is good in subsequent pregnancy. with supportive care alone , the success pregnancy is 75%.
• The patient need:
• *Supportive care alone.
• *Weekly assessment by ultrasound.
• *Screen for antiphospholipd Ab
• *Screen for bacterial vaginosis.
• *Aspirin 75mg/ day peri-coceptional till 36 weeks of gestation.(may be used).
• *hCG 10000unit/ week intra muscular.(may be used).
• *IV immunoglobulin not proved.
Idiopathic recurrent pregnancy loss has successful pregnancy in 67% of pregnancy even without treatment.
Induced abortion: (termination of pregnancy)
Abortion which occurs as a result of interference which may be medical, surgical or result from the use of herbal preparations or other traditional practices which cause the uterus to expel or partly expel its contents.Legal induced abortion (therapeutic abortion)
Induced abortion may be:A. Legal induced abortion (therapeutic abortion)
Is the termination of pregnancy before time of viability for purpose of saving mother's life.
In our locality it is done for medical indication (only) as in :
Malignant disease (breast carcinoma, cervical carcinoma).
severe cardiac disease.
Severe renal problem.
Severe Pulmonary disease.
Severe gastrointestinal disease.
In other part of world , it done for fetal abnormalities and for mental health of mother and welfare of existing children in family.
B. Illegal induced abortion (criminal abortion):
Strange method are sometimes used as well as instrument not sterile and mostly done by unskilled person.It is dangerous because of:
drug used may cause poisoning.
infection easily introduced.
risk of severe hemorrhage.
embolism may occur.
perforation of uterus.
Management of miscarriage:
The treatment option should take into account :The patient’s symptoms.
type of miscarriage.
volume of retained tissue .
patient's choice.
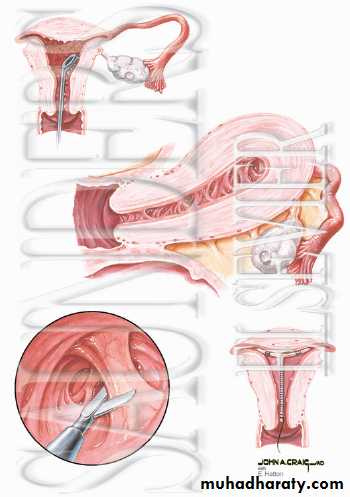
Surgical evacuation
Surgical evacuation remains the treatment of choice if:
bleeding is excessive.
vital signs are unstable.
infected tissue is retained.
Surgical evacuation technique determined by duration of pregnancy and skill of obstetricians and include:
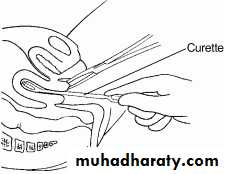
1.Curttage.
2.Suction curettage.
3.Dilatation and curettage (D&C).
4.Dilatation and evacuation.
5.Menstrual aspiration (pregnancy below 6 weeks).
6.Hysterotomy (second trimester rarely).main removal of product of conception after opening uterus in laprotomy before fetal viability).
7.Hysterectomy (special cases as in cervical carcinoma).(main removal of uterus).
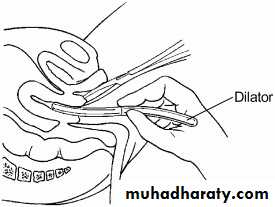
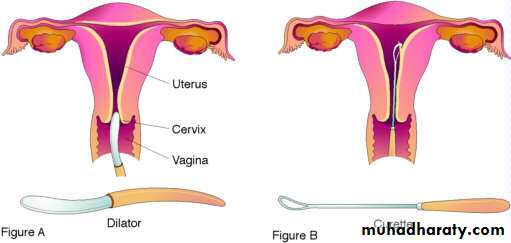
1. cervical dilatation followed by uterine evacuation (first trimester):
CurttageSuction curettage
Dilatation and evacuation ???D&C.
The cervical dilatation can be achieved by:
Mechanical dilatation (Hegar dilator).
Laminaria
Prostaglandin pessaries.
Laprotomy:
Hysterotomy (second trimester rarly).
Hysterectomy (special cases as in cervical carcinoma).
Menstrual aspiration (below 6 weeks)???.
Manual vacuum aspiration
MVA syringe and cannulae
In all cases where surgical evacuation by curettage is the treatment option consideration should be given to the use of a cervical priming agent and method which are:.Mechanical dilatation (Hegar dilator).
b.Laminaria
c. Prostaglandin pessaries.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
• oxytocin infusion intravenously (IV).• prostaglandin E2, F2α and PG analogue (second trimester). Route of administration either:
• vaginal insertion.
• oral ingestion.
• Parentral injection.
• Extra amniotic through foly catheter which pass the cervix.
• Intra amniotic injection.
• antiprogestrone (mifepristone Ru 486).
• intra amniotic hyperosmotic fluid (urea).
• various combination of the above.
Complications of curettage:
Immediate :
haemorrhage.
uterine perforation.
cervical injury.
acute haematometra.
intra-abdominal organ injury.
increase maternal mortality.
Delayed:
infection.retained tissue.
Late
1.Asherman's syndrome (intrauterine adhesions).2.Future pregnancy adverse outcome (as cervical incompetence)
3.Rh sensitization if mother Rh negative and not receive prophylactic treatment.
POST-PROCEDURE CARE
After abortion, patient should know the condition which necessitate immediate medical care which are:prolonged bleeding (more than two weeks).
prolonged cramping (more than a few days).
bleeding more than normal menstrual bleeding.
severe or increased pain.
fever, chills, or malaise.
syncope (fainting).
Contraception:
Patient after abortion can get pregnancy even before next menses. All hormonal methods can be safely initiated immediately following abortion and intrauterine device (IUD) can be safely inserted.