
1
Forth stage
Medicine
Lec-1
د.فاخر
1/1/6112
PITUITARY DISEASES
Hyperprolactinemia
Prolactinoma
Acromegaly
Craniopharyngioma
Diabetes insipidus
HYPERPROLACTINEMIA
• Common
• Present with hypogonadism and/or galactorrhea
Causes of hyperprolactinemia
Physiological :
stress
pregnancy
lactation
nipple stimulation
sleep
coitus
exercise
baby crying
drug induced :
dopamine antagonist
• antipsychotic , antidepressant , antiemetic
• dopamine – depleting
• reserpine , methyldopa
estrogens (occp)
pathological
common : prolactinoma , primary hypothyroidism , polycystic ovary , macroprolactinemia
uncommon : hypothalamic dis , renal failure , pit tumor secreting prolactin & GH
rare : Chest wall reflex (herpes zoster) , Ectopic source
Clinical assessment :
• In women
galactorrhea (lactation in the absence of breast feeding)
hypogonadism : secondary hypogonadism, anovulation, infertility
• In men
decrease libido
2
reduce shaving
lethargy
rarly galactorrhea if associated with gyenicomastia
• Other features of hypopituit, local complication and hormone excess
Investigations
• Exclude pregnancy
• Measure serum prolactin
-upper limit 500mU/L
-500-1000mU/L in non pregnant and lactating indicate stress and drugs, repeat test
-1000-5000mU/L either due to drugs, microprolactinoma or dissconnection
->5000mU/L highly suggestive of macroprolactinoma
• Test for gonadal functions (testosterone, LH, FSH)
• TSH & T4 (to exclud primary hypothyroidism)
• MRI or CT scan if prolactin >1000mU/L
• Test for hypopituitarism
Management:
• Correct underlying cause(cessation of drug, thyroxin replacment for prim
hypothyroidism)
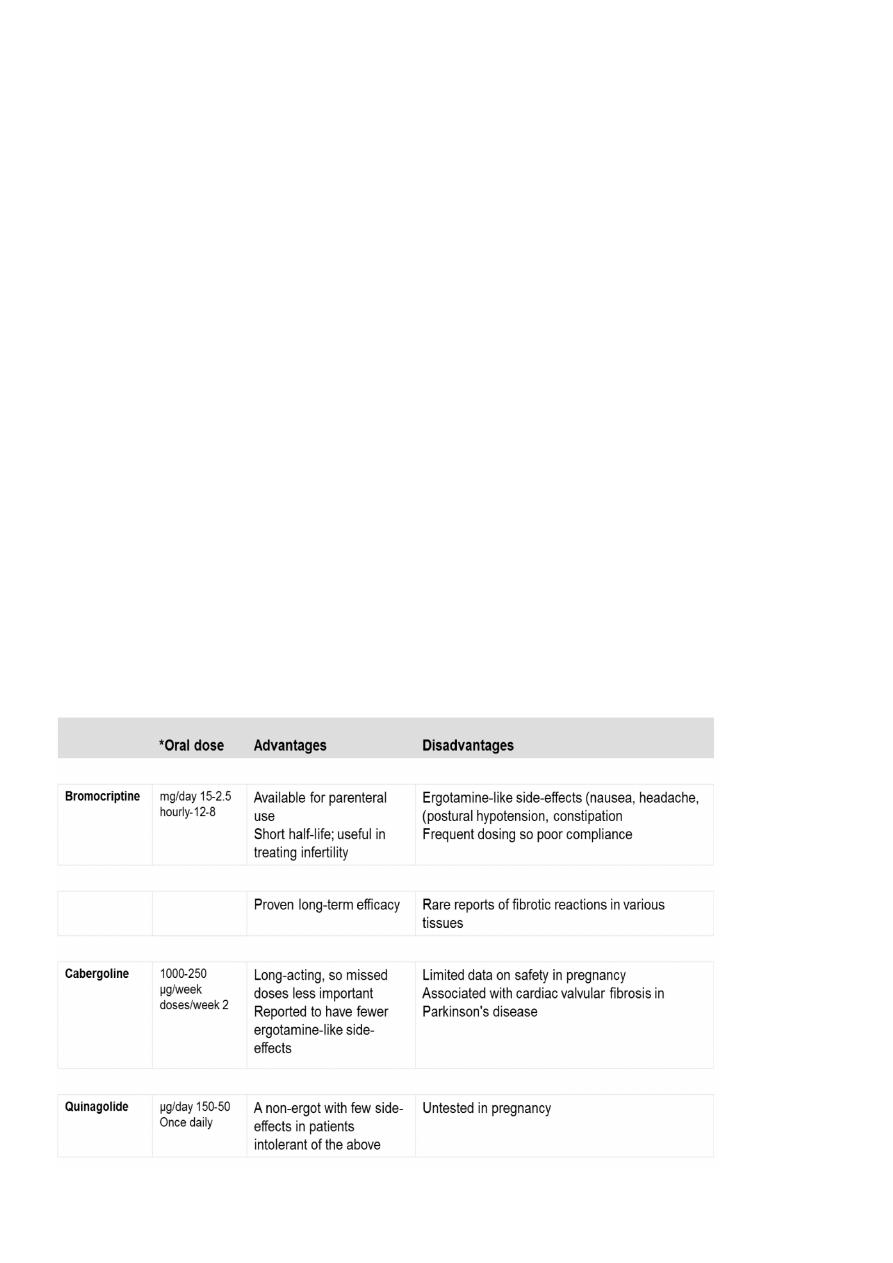
• Dopamine agonist (bromocriptin, cabergoline, quinagolide)
• Treat prolactinoma
dopamine agonist therapy: drugs used to treat prolactinomas
3
PROLACTINOMA
• In premaenopausal women - mostly microadenoma, and present as hyperprolactinemia.
• In men and postmenopausal women – almost macroadenomas and present insidiously
with mass effect.
• Occasionally can secrete excess GH and cause acromegaly.
• There is relation between prolactin conc and tumor size.
• Investigated like other pit tumors.
Management
Medical
Dopamin agonist drugs (reduce s prolactine and cause tumor shrinkage),
can be withdrawn after few years in some patients with microadenoma.
In macroadenomas only withdraw drugs after curative surgery or radiotherapy and under
supervision.
Bromocriptin and cabergoline (ergot derived) associated with fibrosis reaction in heart
causing tricusped regurgitation
Surgery and radiotherapy
only for macroadenomas that fail to shrunk with dopamine agonists
if patients intolerant for dopamine agonists
trans-sphenoidal surgery for microadenomas with 80% cure rate ( lower rate for
macroadenoma)
radiotherapy for some macroadenoma to stop dopamine agonists
To achieve pregnancy
dopamine agonist may be followed by pregnancy
if microadenoma withdraw dopamine agonist if get pregnant
if macroadenoma continue dopamine agonist during pregnancy with follow up for visual
field and prolactin
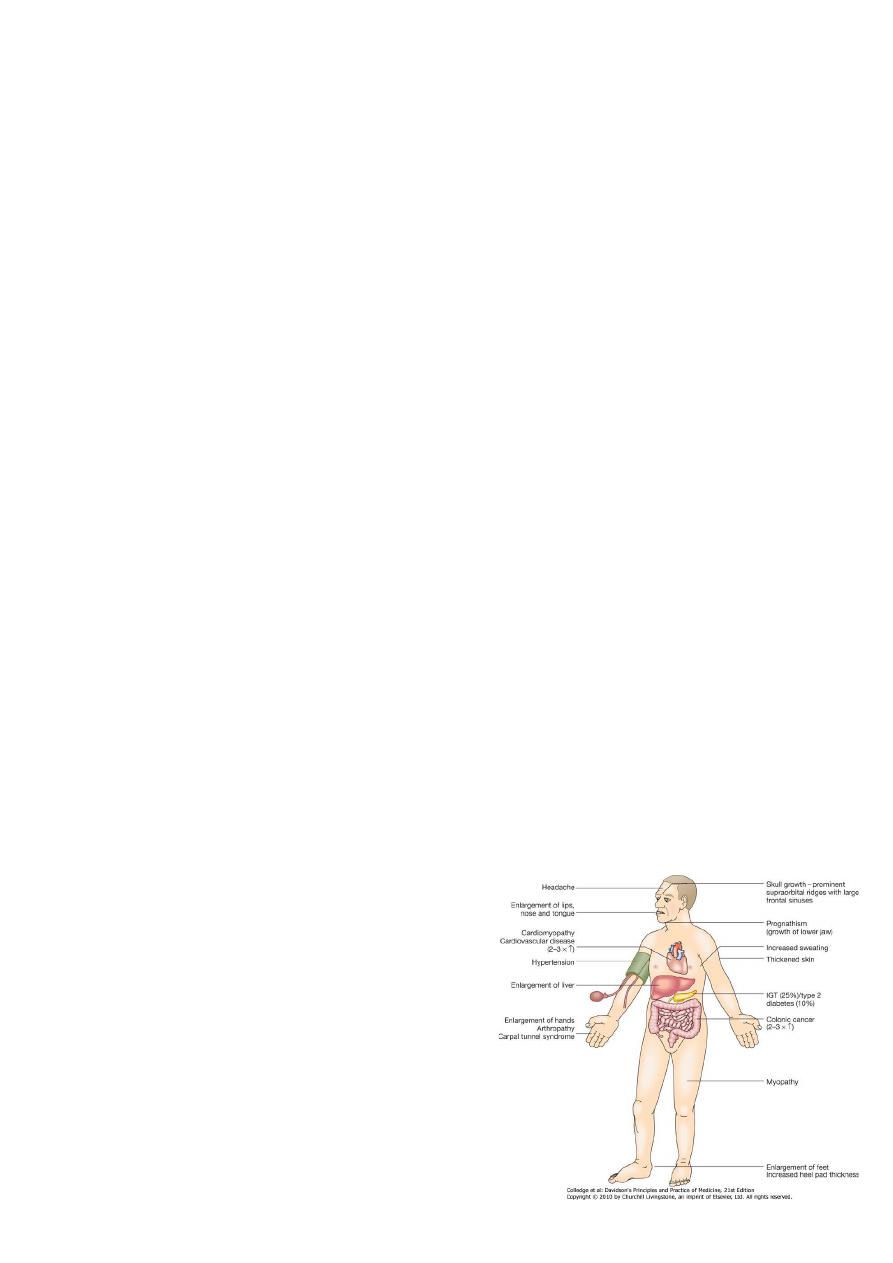
ACROMEGALY
GH secretion from pituitary tumor usually
macroadenoma
Clinical features
• Before puberty –gigantism
• In adults—acromegaly
• In adolescent and persist ---combined
• Headache and sweating are most common
complaint.
• Other features of hypopituitarism

4
Investigations
• Measure GH during oral GTT---in acromegaly failure to suppress GH with paradoxical rise
in 50%
• Prolactine elevated in 30%
• Other pit function tests
• In diabetics difficult to diagnose by GTT
-measure IGF-1 *if only DM, IGF-1 is low
*if DM with acromegaly, IGF-1 is high
• Colonoscopy to screen for colonic cancer
Management
Surgical
– Trans-sphinoidal surgery as first line and to debulk the tumor
– Second line therapy with radiotherapy or medical according to post operative
imaging and GTT results
Radiotherapy
– Second line if acromegaly persist after surgery
– Risk of hypopituitarism
Medical therapy
– second line treatment following surgery may be stopped years following radiotherapy
– somatostatines analogues octeriotides and lanreotide as slow release injections every few
wks
– Somatostatines can be used as first line as alternative to surgery
– Dopamine agonists are less potent
– GH receptor antagonist pegvisomant as daily self injection for some patients not
responding to somatostatin
CRANIOPHARYNGIOMA
• Benign tumors develop in cell rest of Rathke’s pouch
• Located in sella tursica or commonly in suprasellar space
• Cystic with solid component that may be calcified
• More common than adenomas in young
• Present as pressure symptoms, hypopituitarism or cranial DI. Also
features of hypothalamic damage
• Treated surgically by craniotomy
• Radiotherapy usually needed
• Often recur, causing morbidity of obesity, visual failure and water
balance problems

5
DIABETES INSIPIDUS
• Uncommon.
• Persistent excretion of excessive quantities of dilute urine and thirst.
• Types 1. cranial DI (deficient ADH secretion by hypothalamus
2. nephrogenic DI (renal tubules are not responding to ADH)
Causes of diabetes insipidus
1. Cranial
2. Structural hypothalamic or high stalk lesion
3. Idiopathic
4. Genetic (dominant and recessive).
5. Nephrogenic
6. Genetic
7. Metabolic (hypokalemia, hypocalcaemia)
8. Drugs (lithium, demeclocycline)
9. Poisoning (heavy metals)
10. Chronic kidney disease (polycystic kidney ,sickle cell, infiltrative dis.
Clinical features
• Polyuria and polydipsia (5-20 L /day urine of low specific gravity and osmolality
• Potentially lethal condition if unconscious pt or hypothalamic damage
• Differntial d is primary polydipsia
Investigations
• low serum ADH
• Urine <600 mOsm /kg + increase plasma osmolality >300mOsm/kg
• Water depreviation test
• 5% hypertonic saline infusion to inc plasma osmolality then measure ADH
• Pituitary function test and imaging
water deprivation test
To establish a diagnosis of diabetes insipidus, and differentiate cranial from nephrogenic
causes) protocol
• No coffee, tea or smoking on the test day
• Free fluids until 0730 hrs on the morning of the test, but discourage patients from 'stocking
up' with extra fluid in anticipation of fluid deprivation
• No fluids from 0730 hrs
• Attend at 0830 hrs for body weight, plasma and urine osmolality
• Record body weight, urine volume, urine and plasma osmolality and thirst score on a visual
analogue scale every 2 hrs for up to 8 hrs
• Stop the test if the patient loses 3% of body weight
• If plasma osmolality reaches > 300 mOsm/kg and urine osmolality < 600 mOsm/kg, then
administer DDAVP 2 μg IM

6
Interpretation of water deprivation test
• Diabetes insipidus is confirmed by a plasma osmolality > 300 mOsm/kg with a urine
osmolality < 600 mOsm/kg
• Cranial diabetes insipidus is confirmed if urine osmolality rises by at least 50% after
DDAVP
• Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is confirmed if DDAVP does not concentrate the urine
• Primary polydipsia is suggested by low plasma osmolality at the start of the test
Management
• For cranial DI
– DDAVP (des-amino-des- aspartate-arginine vasopressin/ desmopressin.
– Long half life analogue of ADH
– Administered intranasally ,(5 ug morning and 10 ug evening). given IM in sick pts
– Adjust the dose according to s. level of Na&/or osmolality
– Excessive treatment cause water intoxication & hyponatremia
• For nephrogenic DI
– treated by thiazide diuretics and NSAID
