1
4th stage
Surgery
Lec -
Dr.mohamaad
fawzi
11/29/2015
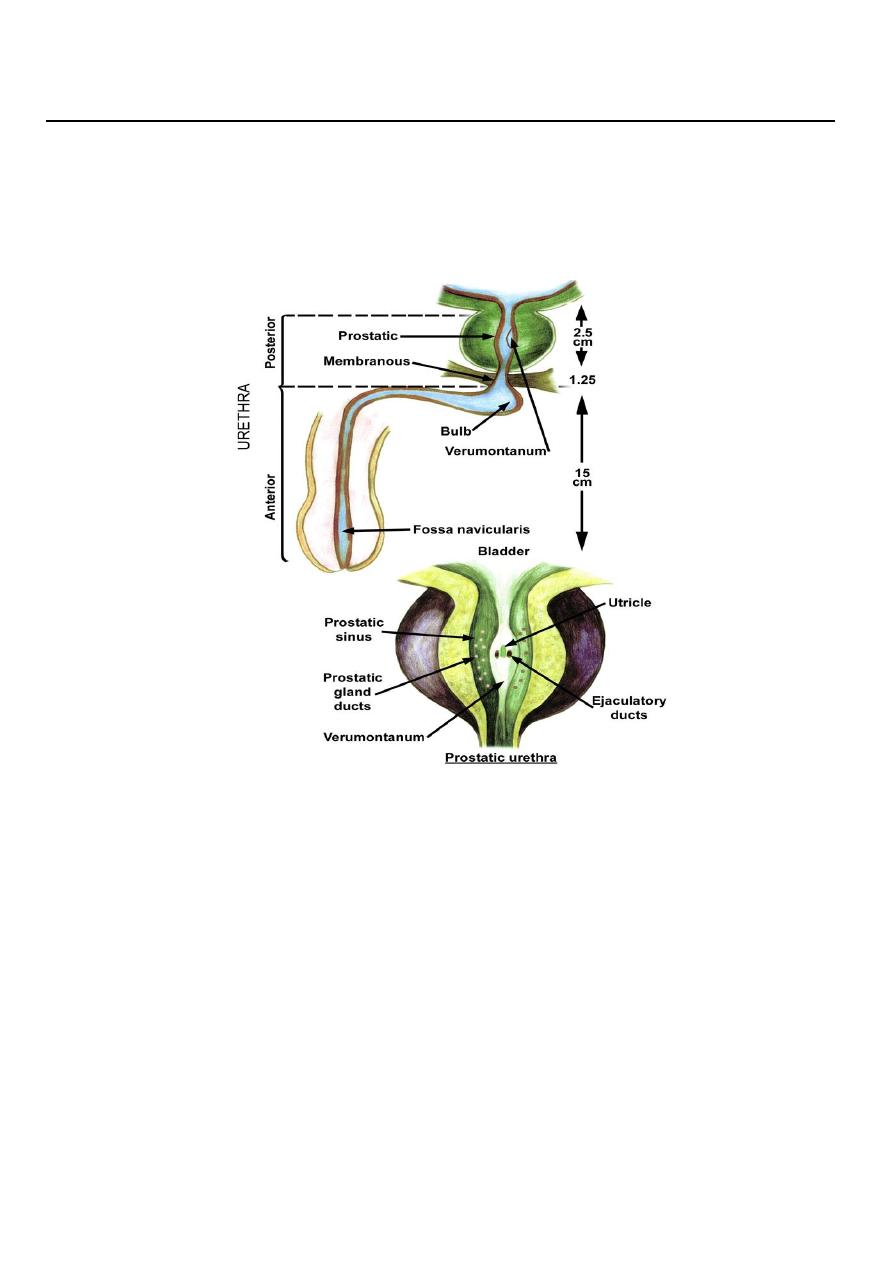
Urethral stricture
Causes
o Inflammatory
post gonorrheal
o Congenital
o Traumatic (ant.and post .urethral injury )
o Instrumental
indwelling catheter
urethral endoscopy
o Post operative
open prostatectomy
amputation of penis
2
Clinical features
Obstructive symptoms : straining, weak stream, terminal dribbling, & in severe cases
retention of urine
Irritative symptoms : increasing frequency day and night due to incomplete evacuation or
infection
diagnosis
History of infection,trauma,folleys catheter or endoscopy
obstructive symptoms
Uroflowmetry
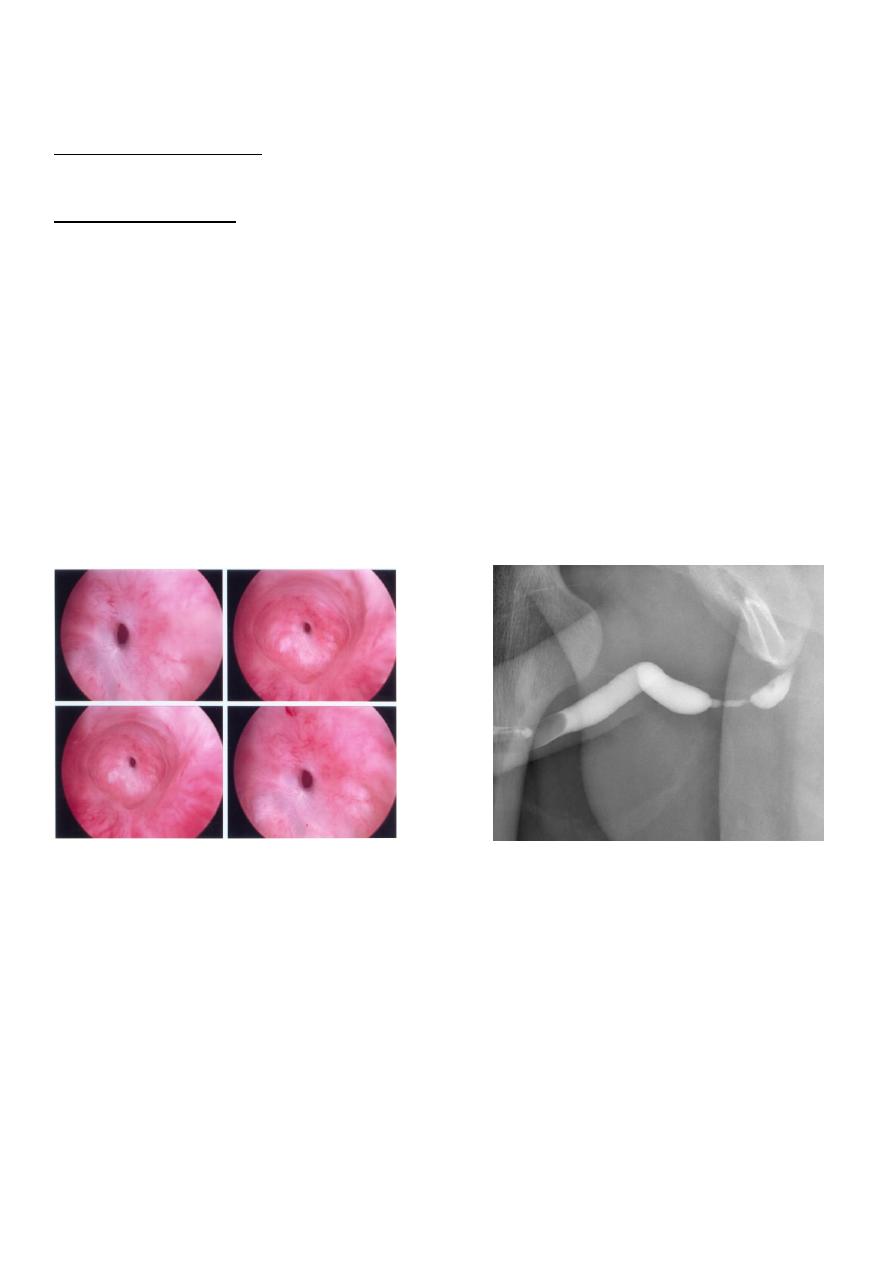
Urethrography
urethroscopy
Urethroscopy retrograde urethrography
Complication
Retention of urine
Urethral diverticulum
Periurethral abscess
Urethral fistula
Hernia,hemorrhoids,rectal prolaps due to straining during voiding
3
Treatment
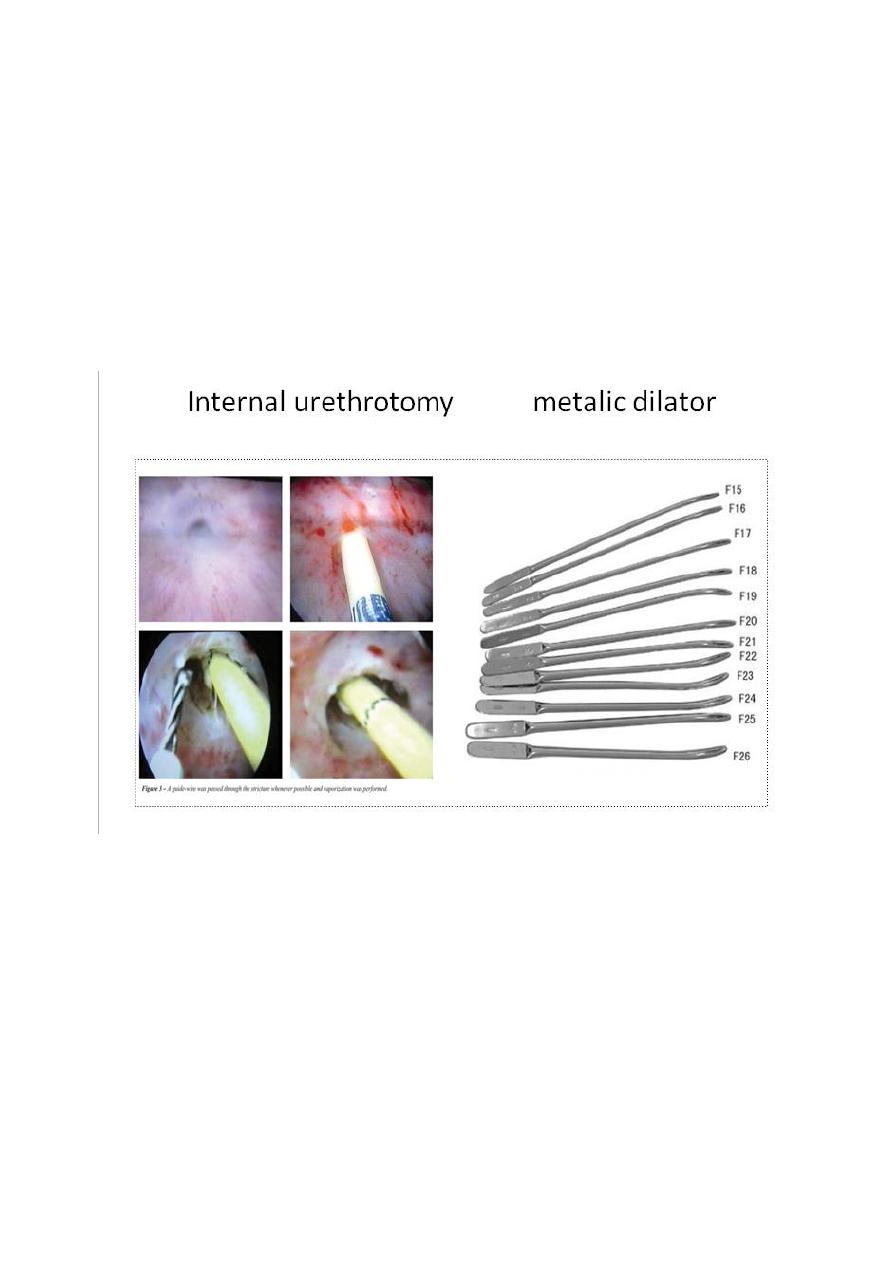
Urethral dilatation
metal dilators (sounds)
Filiforms&followers
Endoscopic incision
by cold knife or laser
it seem to cure 50% of simple stricture
may be supplemented by intermittent dilatation to improve success rate
infection and bleeding are rare comlication
Urethroplasty
Should be considered when more simple means fail to give lasting relief of symptoms
Short stricture……excision with end to end anastomosis
other wise different types of flaps or graft uses for more complicated stricture
4
Urinary diversion
Temporary : to relieve distal obstruction
Permanent : after removal of the bladder
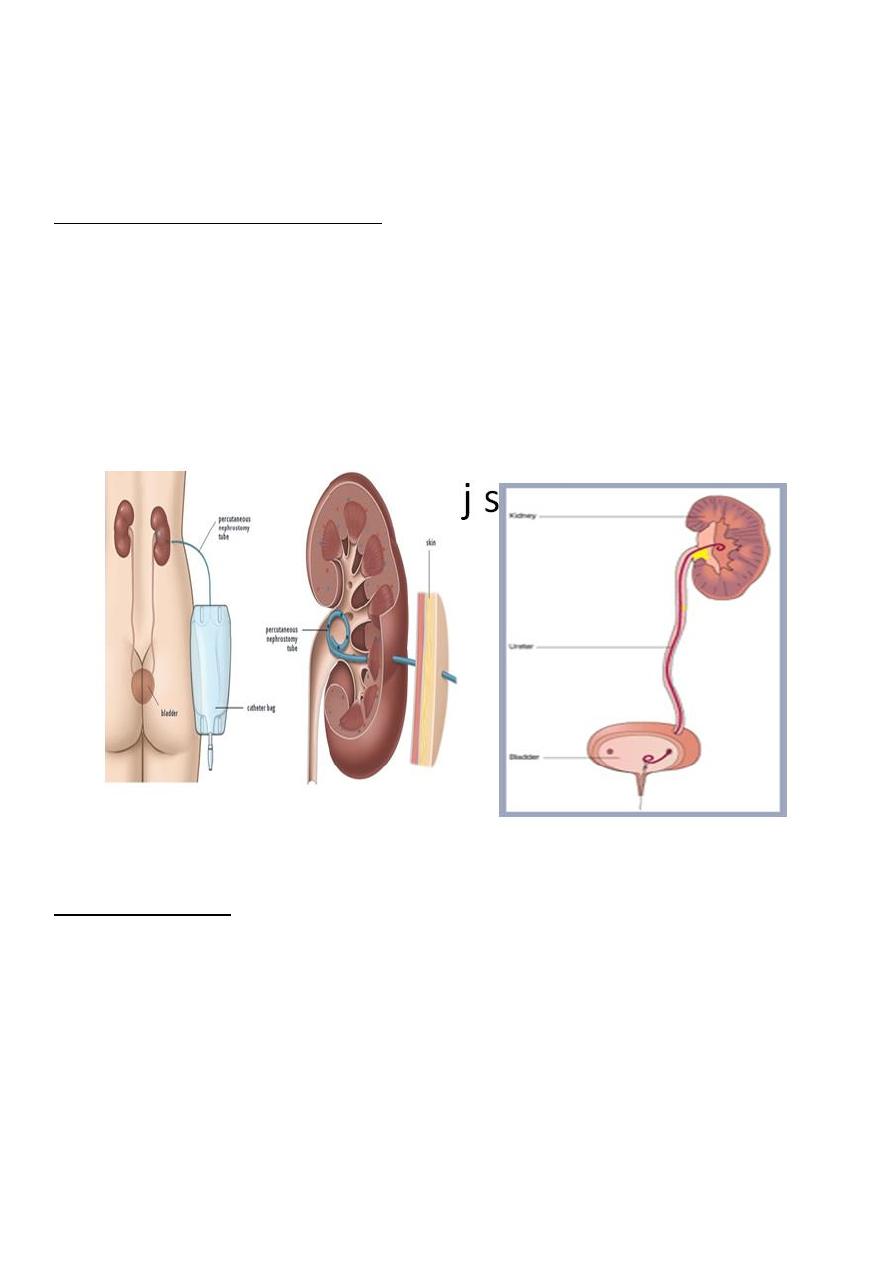
Temporary (for the obstructed kidney)
Double j ureteric stent (change every three monthes)
nephrostomy (if jj not possible)
percutaneous
formal
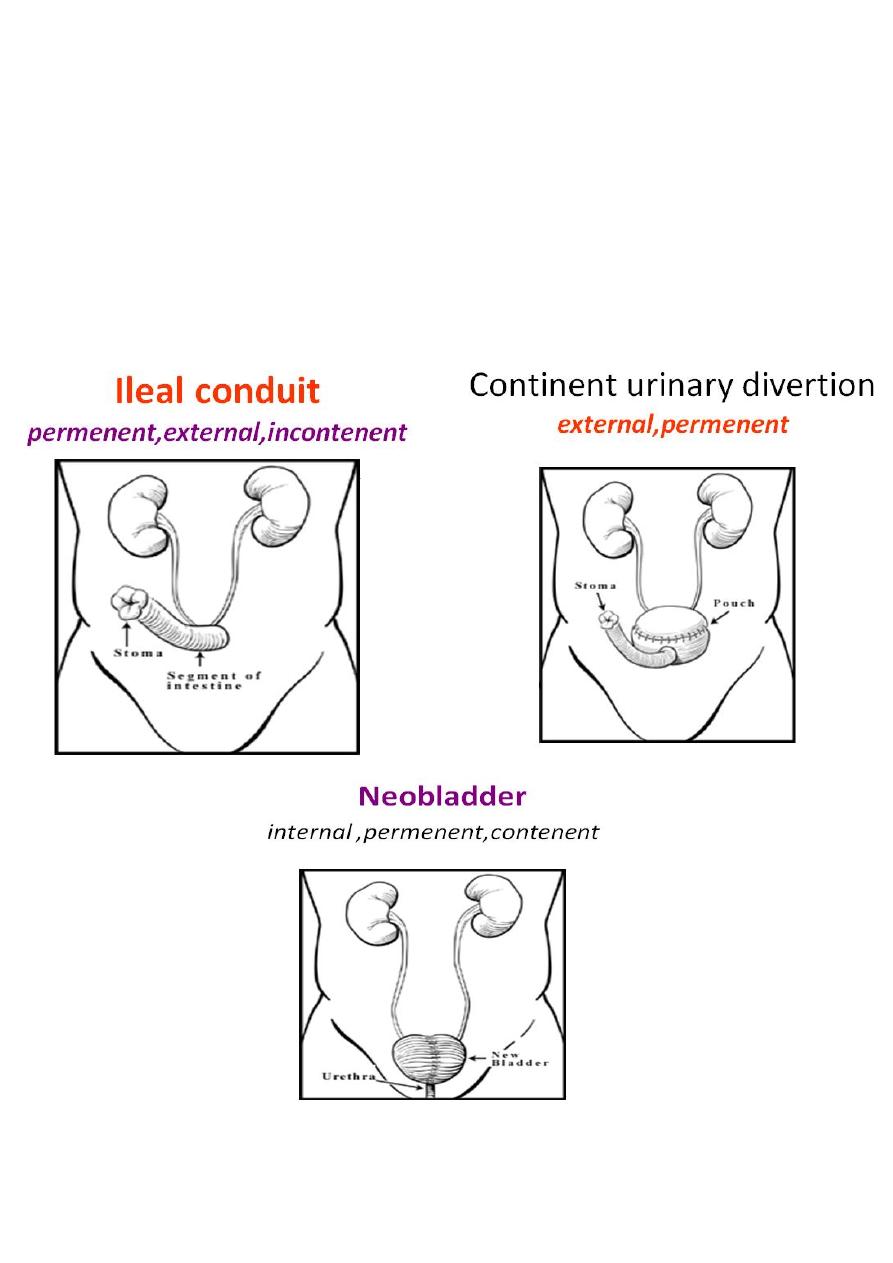
Permanent divertion
External
ileal conduit (external stoma)
Internal divertion
ureterosigmoidostomy
neobladder
•
.
5
Indications of permenent divertion:
• 1- After simple or radical cystectomy.
• 2- severe neuropathic bladder dysfunction.
• 3- uncorrectable urinary fistula .
• 4- severe intractable interstitial cystitis .
• 5- prior to renal transplantation in patient with lower tract dysfunction.
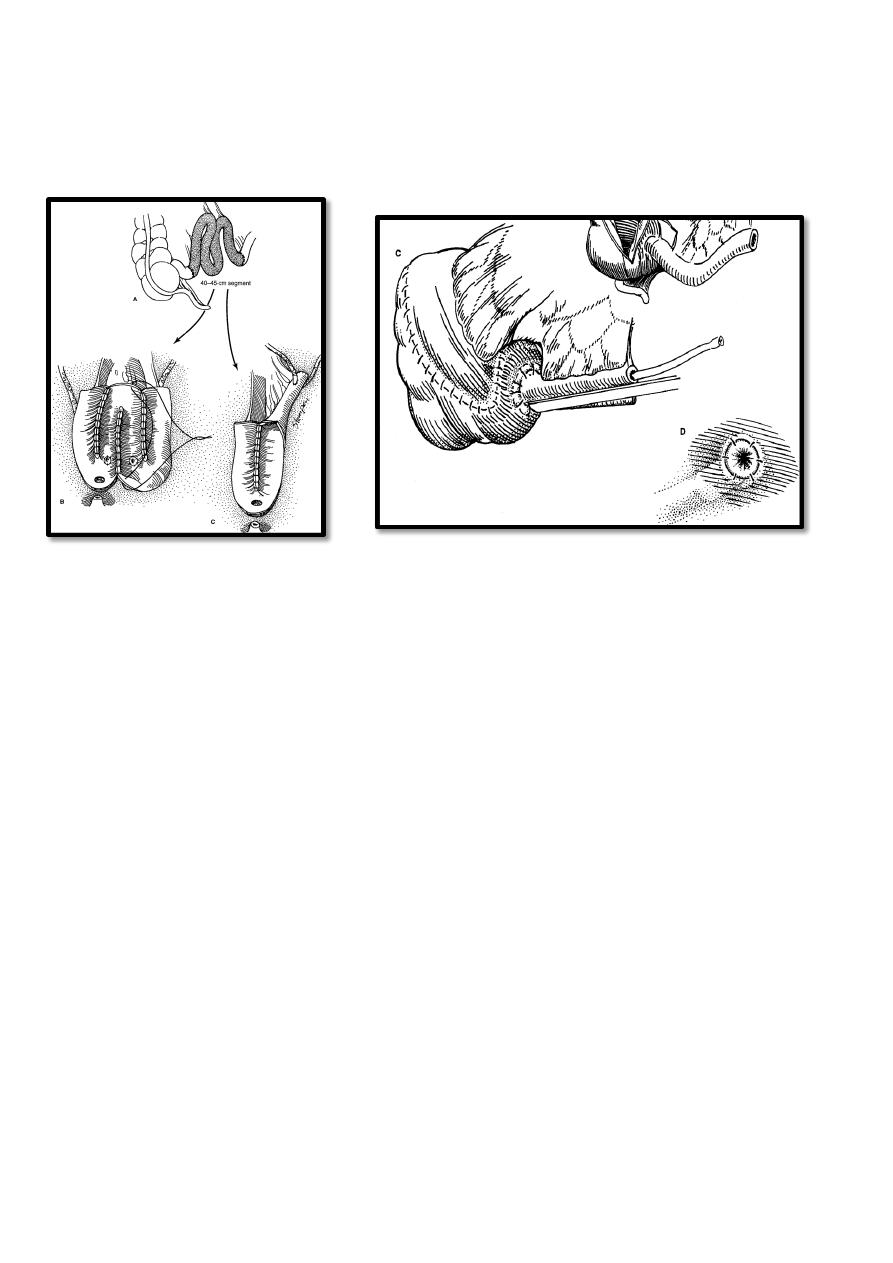

6
ilial pouch
