1
Forth Stage
Surgery
(Urology)
Lec-9
د.محمد فوزي
12/20/2015
Congenital Anomalies Of The Lower Urinary System
Hypospadias
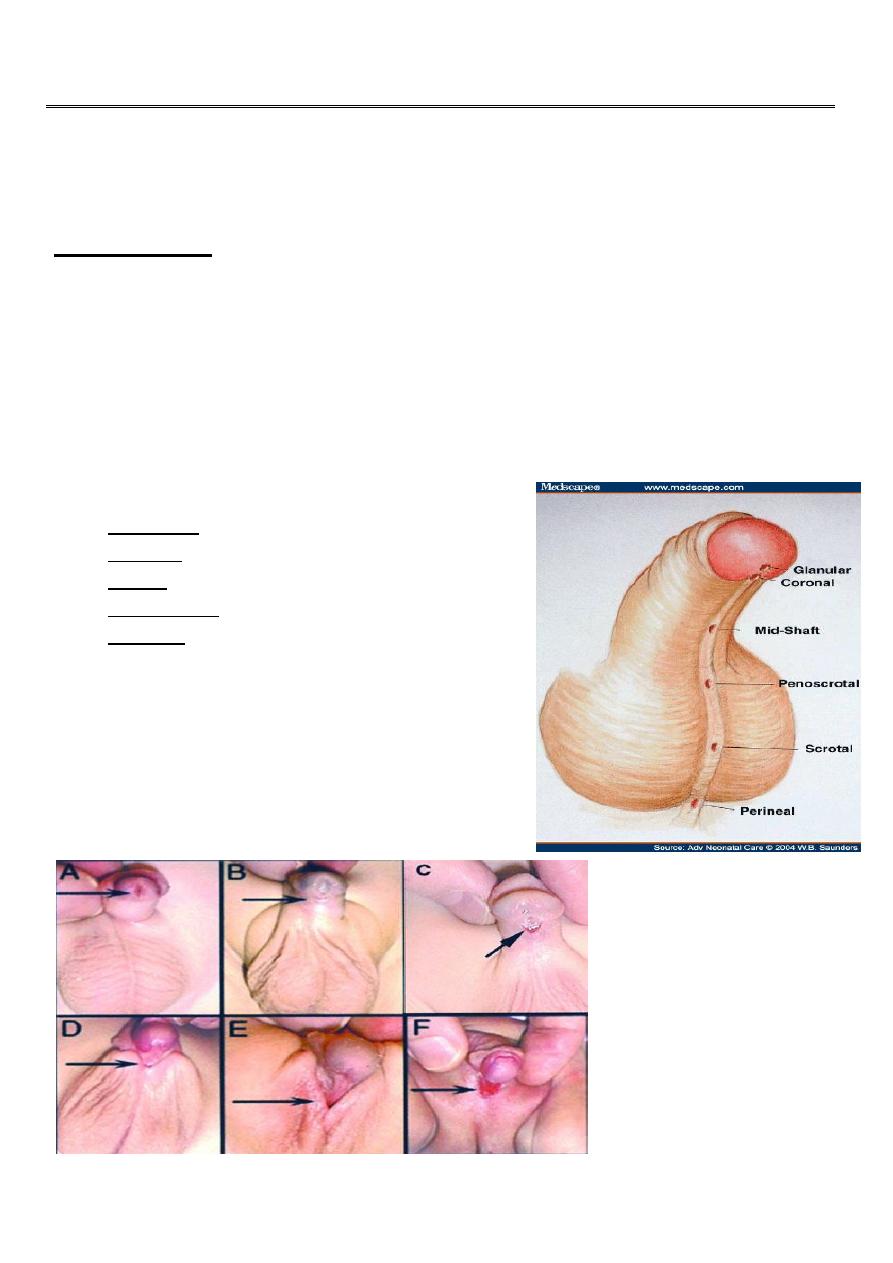
Urethra normally opens at the tip of the glans penis, & the penis is straight during
erection.
In hypospadias the external urethral meatus opens on the under surface of the
penis proximal to the tip of the glans penis. The missing part of the urethra is
replaced by a fibrous band causing ventral curvature(cordee).
Types
According to the position of the opening :
Glandular.
Coronal.
Penile: distal, penile shaft or proximal.
Penoscrotal.
Perineal. The scrotum is bifid (inter sex).
"Hypospadias is due to failure of fusion
of urethral folds"
2
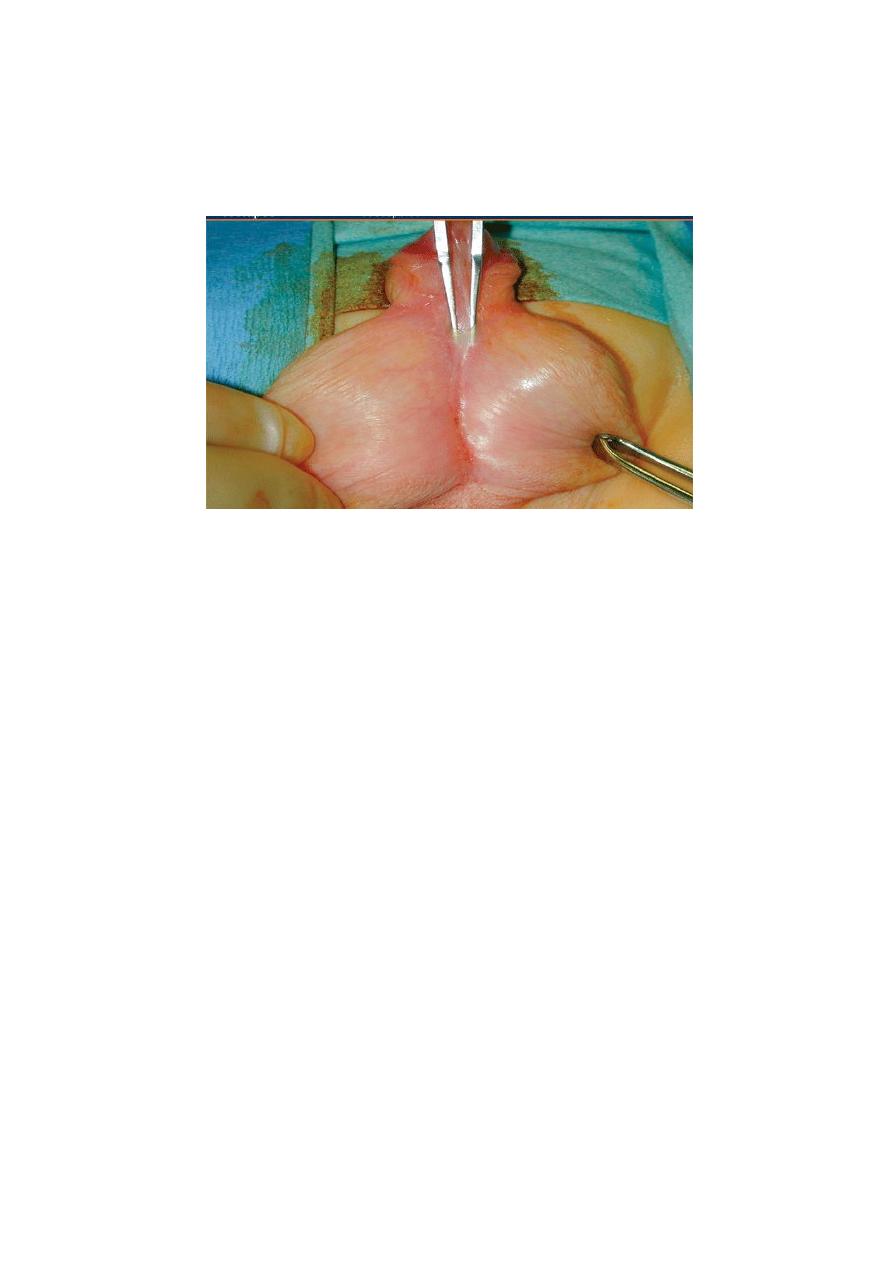
Important clinical points
The abnormal hooded prepuce
shouldn’t be circumcised to be used for
later reconstruction.
Increased incidence of undescended testes.
Meatal stenosis usually present may result in repeated UTI.
"
HYPOSPADIAS: meatal stenosis"
Treatment
-For psychological reasons hypospadias should be repaired before school age.
-Repair traditionally in the first 2 years
Stages of operations:
-Orthoplasty: straitening of the penis.
-Urethroplasty: formation of neourethra
MAGPI.
Flip-flap.
Mathieu.
Complications
1. Stricture.
2. Fistula.
3. Failure of operations.
3
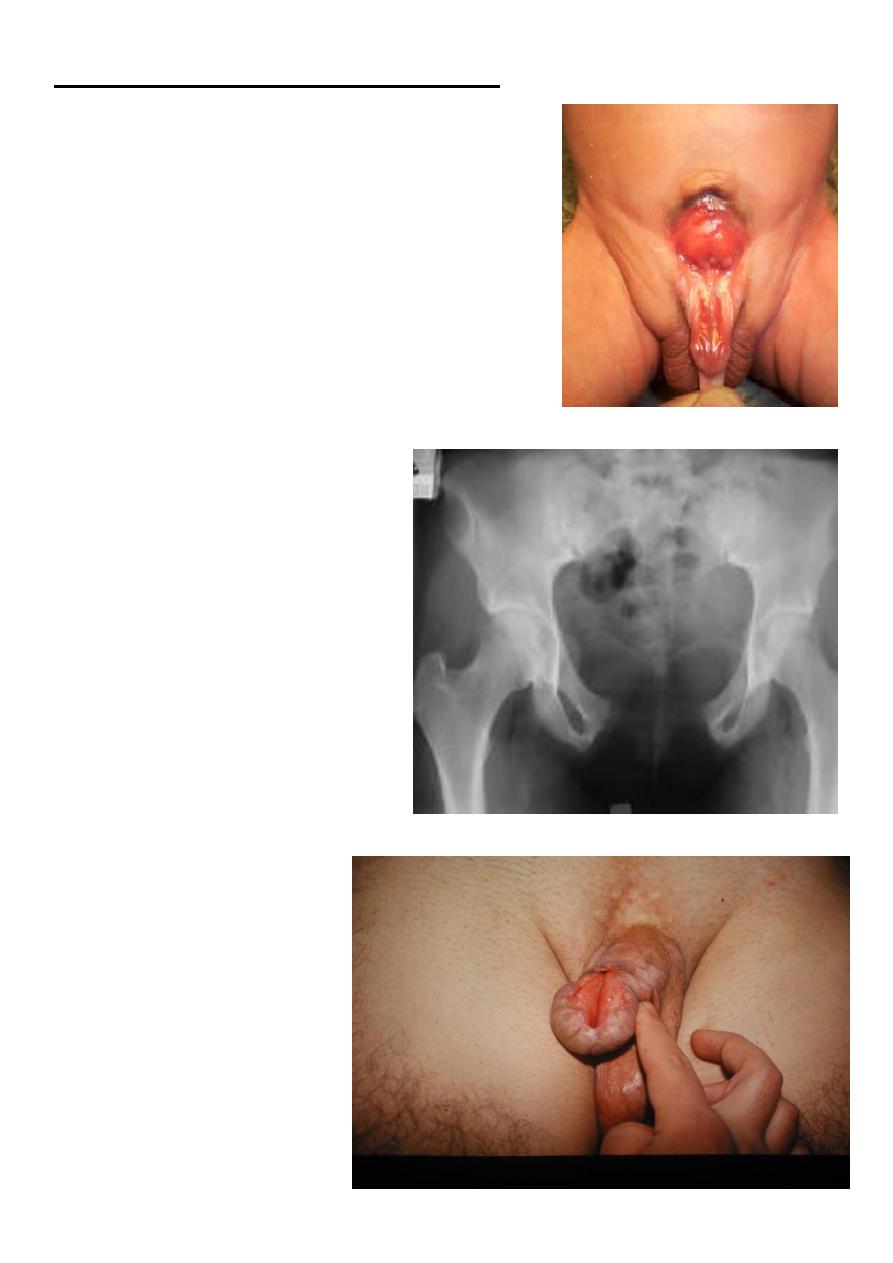
Bladder Extrophy (Ectopia Vesicae)
-Rare anomaly 1:50,000. affects males more.
-Absent anterior wall of the bladder.
-Absent anterior abdominal wall from the umbilicus
downward.
-Widening of symphysis pubis causing waddling gait.
-Associated epispadias with short & wide penis.
"Pelvic X ray: pubic diastasis"
"EPISPADIAS"
4
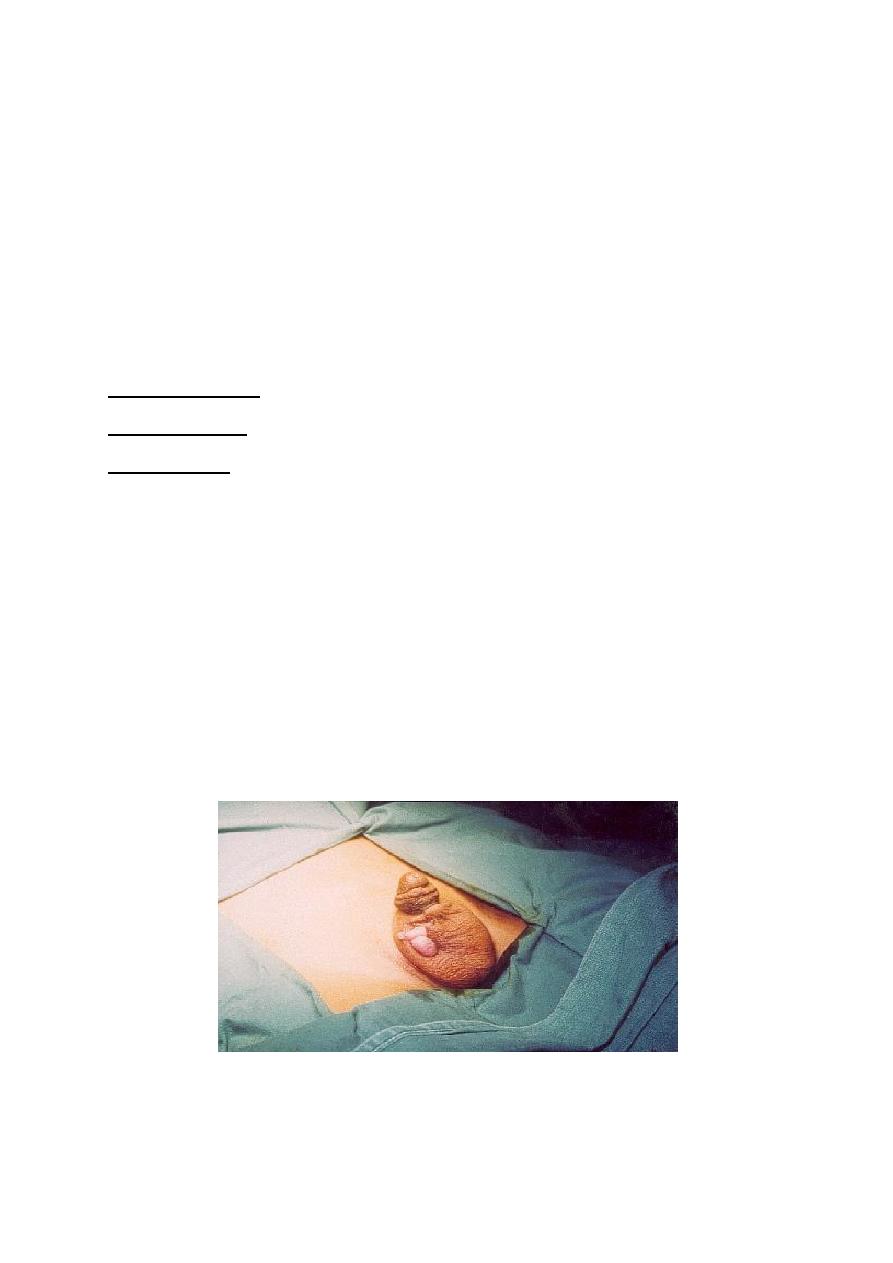
Undescended testis
-Normally the testis developed in the abdomen under the kidney, then descends
down to the scrotum through inguinal canal just before birth, guided by
gubernaculum under hormonal control.
-Undescended testis referred to testicular arrest during descent in its path to the
scrotum.
Facts
1. It affects 1% of all males.
2. In 20% bilateral.
3. Right side more than left side.
4. Incidence is higher in premature infants.
5. Associated with inguinal hernia in 75%.
6. Testicular descent may be completed at first year of life.
Types
1. Intra abdominal.
2. Intra-canalicular.
3. At external ring.
4. At scrotal neck.
Pathophysiology
-Lower temp is required for spermatogenesis.
-Hormonal function remains normal (secondary sex characters develop normally).
Differential diagnosis: of absent testis
1-Anorchia: testicular vanishing syndrom.
2-Retractile testis: normal phenomenon in young
children due to strong cremasteric reflex, the scrotum is
well developed & the testicle can be brought down to
the bottom of the scrotum, examin at squatting
position. no treatment is required.
3-Orchedectomy
4-Ectopic testis
5-Undescended testis
5
Complications
1. Sterility in bilateral cases.
2. Torsion of the spermatic cord.
3. High liability for malignancy.
4. Liability for trauma and infection.
5. Associated hernia complications.
6. Psychologic disturbance.
Investigations
1. Hormonal assay to exclude anorchia.
2. U/S & CT scan for localization.
3. Laparoscope.
Treatment
1-Hormonal:
2-Surgical: ( orchidopexy):
Beter to be done befor two years old.
Staged orchiopexy.
Laparoscopic orchiopexy.
For intra abdominal
Orchiectomy: Specially in adulthood.
"Sub dartous pouch fixation"

6
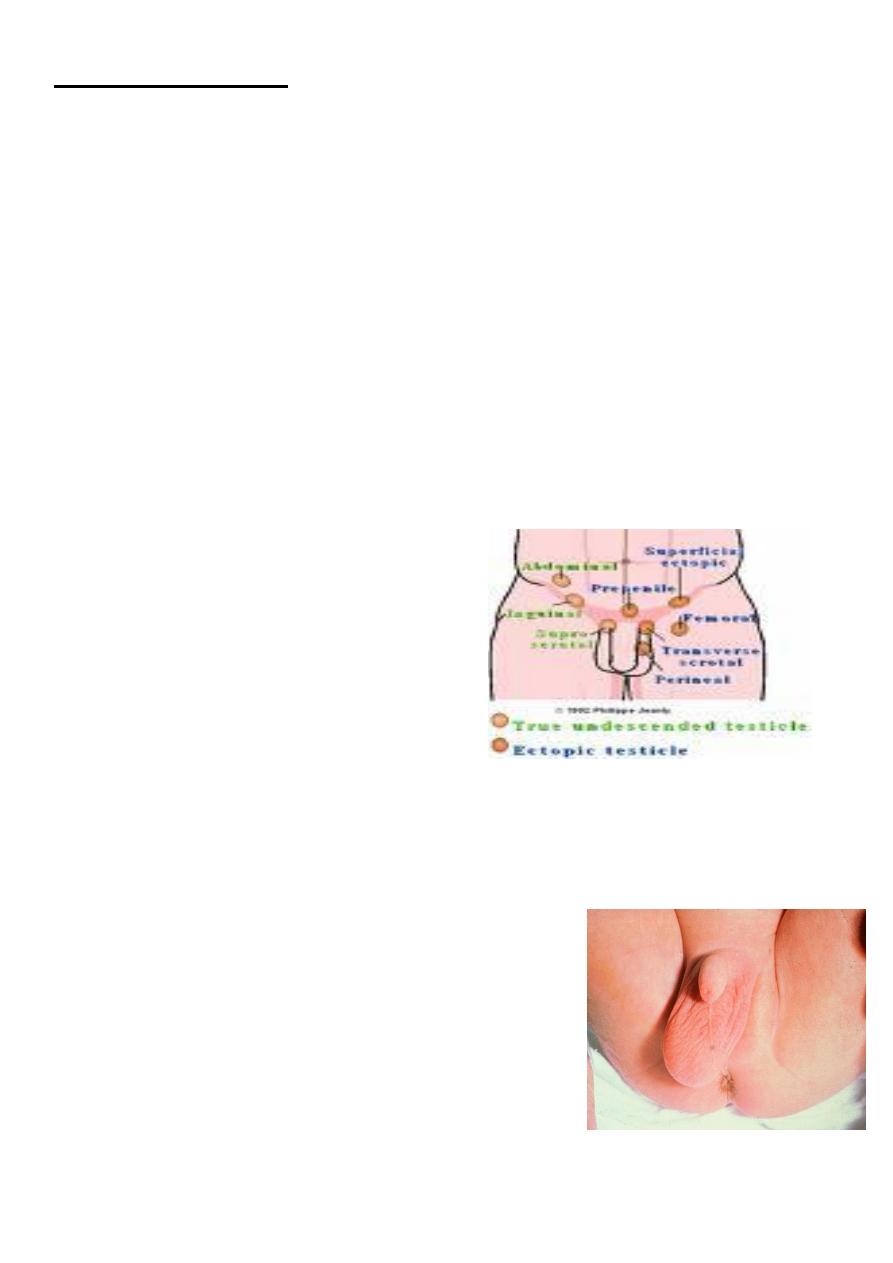
Ectopic testis
The position of the testis is outside the normal pathway of the testicular descent.
Penile root.
Femoral triangle.
Crossed ectopia.
Perineal.
treatment :Replacement the testicle to the scrotal sac for proper development.
Posterior urethral valve
-The most common obstructive urethral lesion in infants and newborns, occures
only in males and are found at the distal prostatic urethra.
-The valves are mucosal folds (thin membrane).
-PUV may cause varying degrees of obstruction when the child attempts to void
(mild, moderate or severe).
-BOO result in retention and variable degrees of hydronephrosis.
"MCUG"
"Cystoscope" is diagnostic by direct visualization of the valve and therapeutic to
destruct the valve by electrocautary.
