
1
Forth stage
Surgery
Lec-7
د.محمد فوزي
1/11/2015
Urinary tract infection
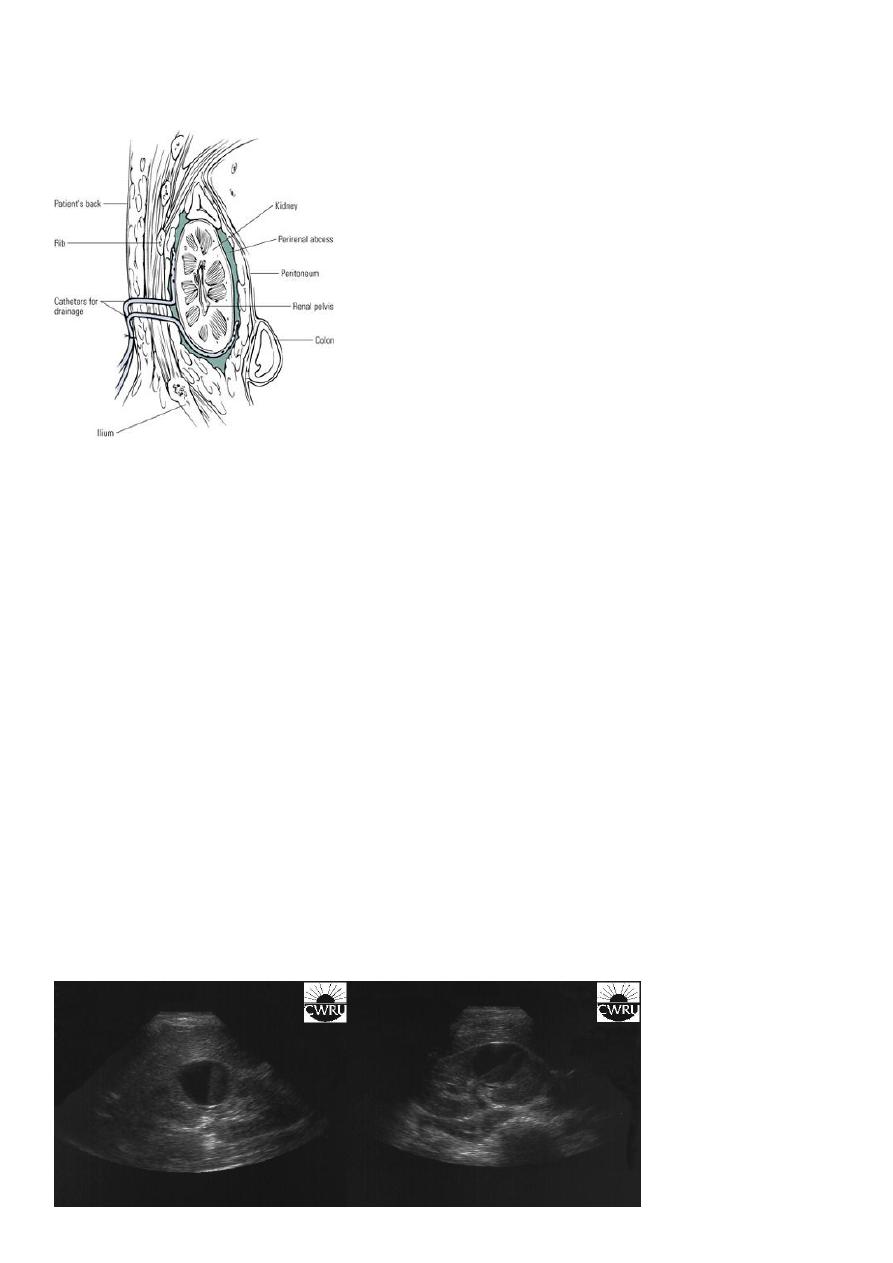
Perinephric abscess :
Infection and pus collection in the perinephric space within Gerota’s fascia
Source of infection :
1. Hematogenous,
2. lymphatic
3. infected peri renal hematoma or urinoma,
4. extension from a nearby infected focus like appendicitis
5. untreated pyonephrosis or renal abscess.
6. Rarely mycobacterial perinephric abscess may occur.
Clinical features :
1-High swinging pyrexia 2-tenderness and fullness in the loin.
The symptoms are marked if the infection started at lower pole because the upper pole is
hidden by thoracic cage .
Investigations :
1. GUE: normal unless the abscess is extended from renal pathology.
2. WBC: neutrophil leukocytosis.
3. U/S: pus collection around the kidney with or without hydronephrosis.
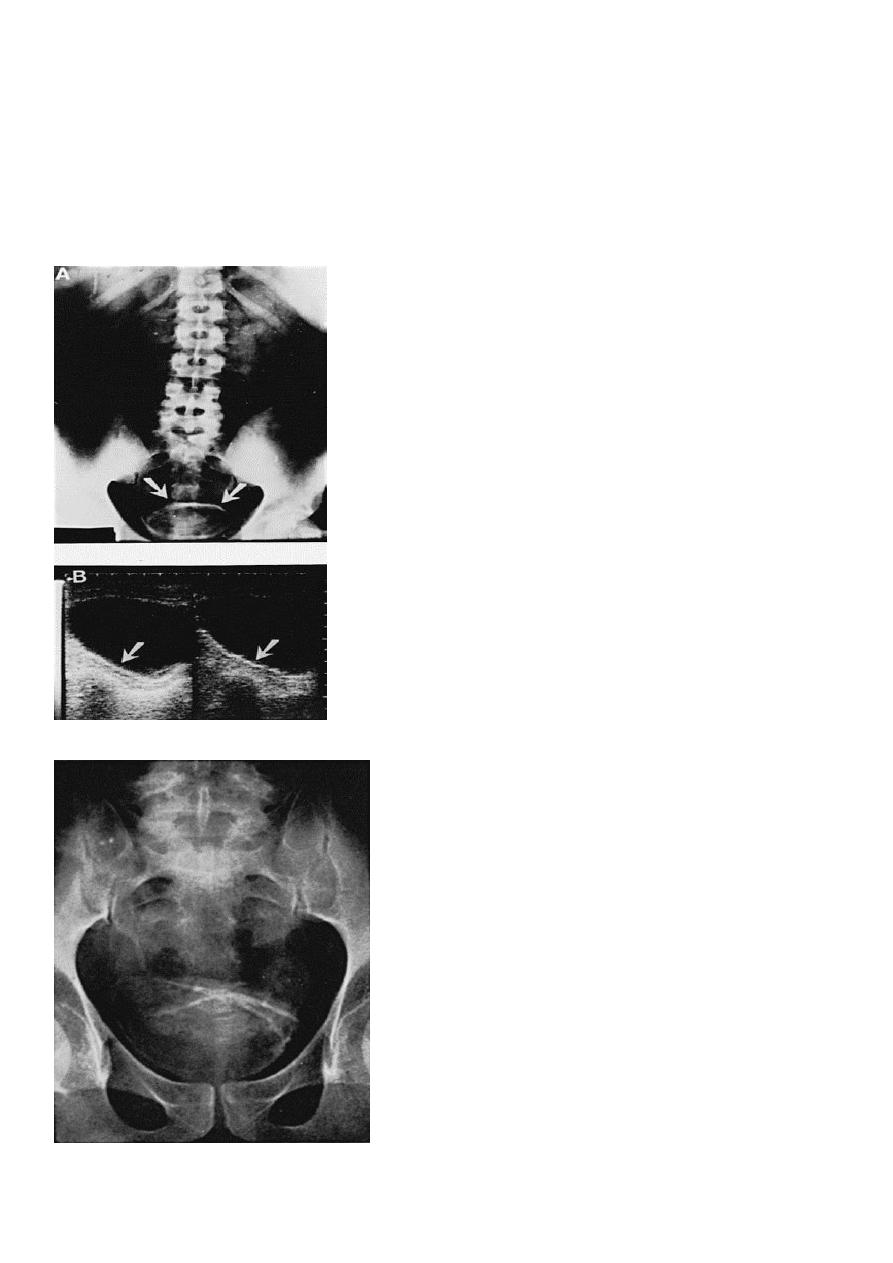
4. KUB: obscured psoas shadow, spine scoliosis,.
5. CT scan & MRI: diagnostic
Treatment :
Drainage is the principle treatment of pus collection anywhere in the body.
Under antibiotic cover lumber incision is made, all loculi destructed, pus drained and wound
closed over a tube drain.
2
Drinage of perinephric abscess
Renal carbuncle(renal cortical abscess):
It arises as a result of blood born micro-organism especially staphylococcus aureus from a
skin lesion in debilitated or immune compromised patient like diabetics. Rarely the abscess
arises from infected cortical hematoma or cyst.
Clinical picture :
Ill defined tender renal mass
persistent pyrexia
leukocytosis.
Investigations :
1. GUE: normal or pyuria.
2. U/S: cystic cortical lesion with internal echoes.
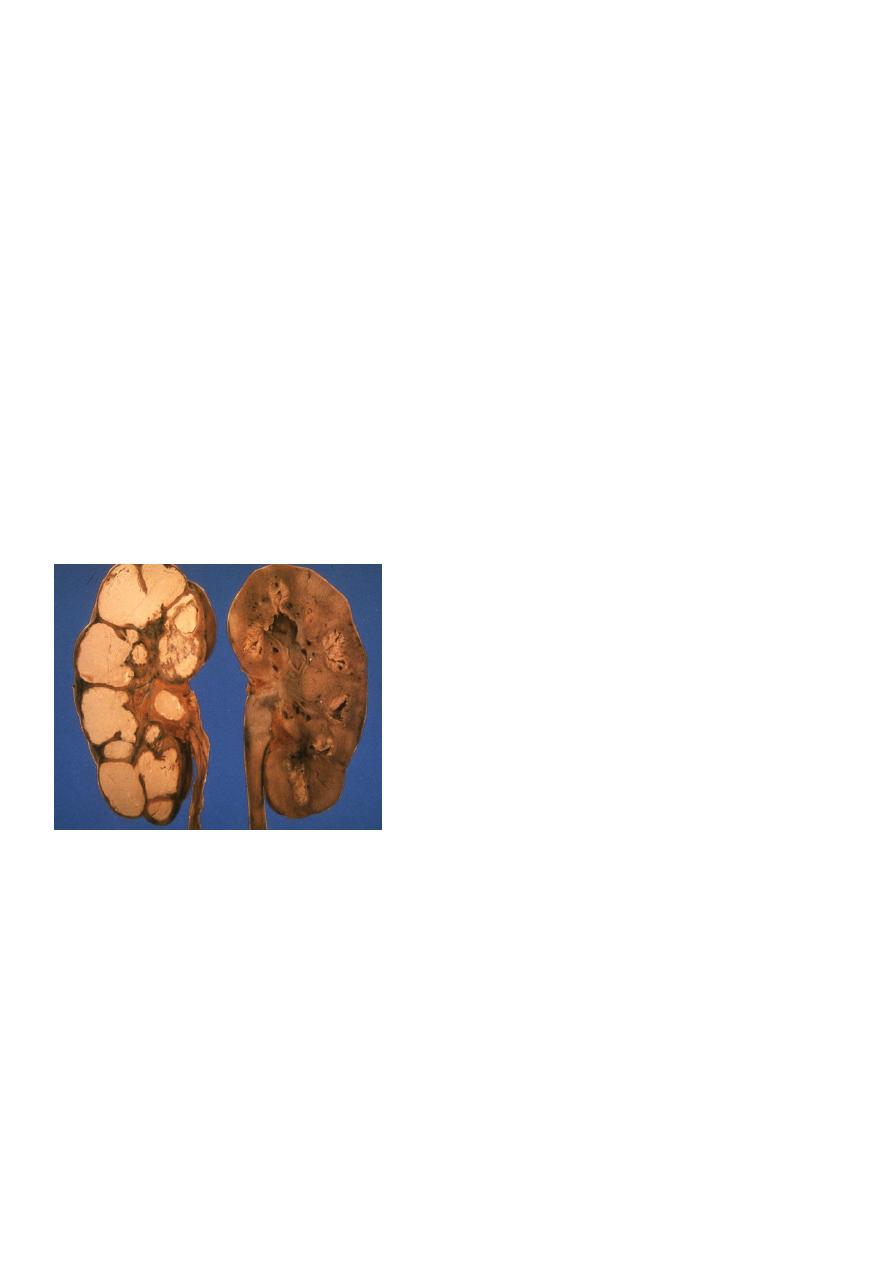
3. IVU: space occupying lesion, which may be confused with renal tumor.
4. CT scan & MRI: diagnostic.
U/S cystic lesion with internal echoes (renal abscess)
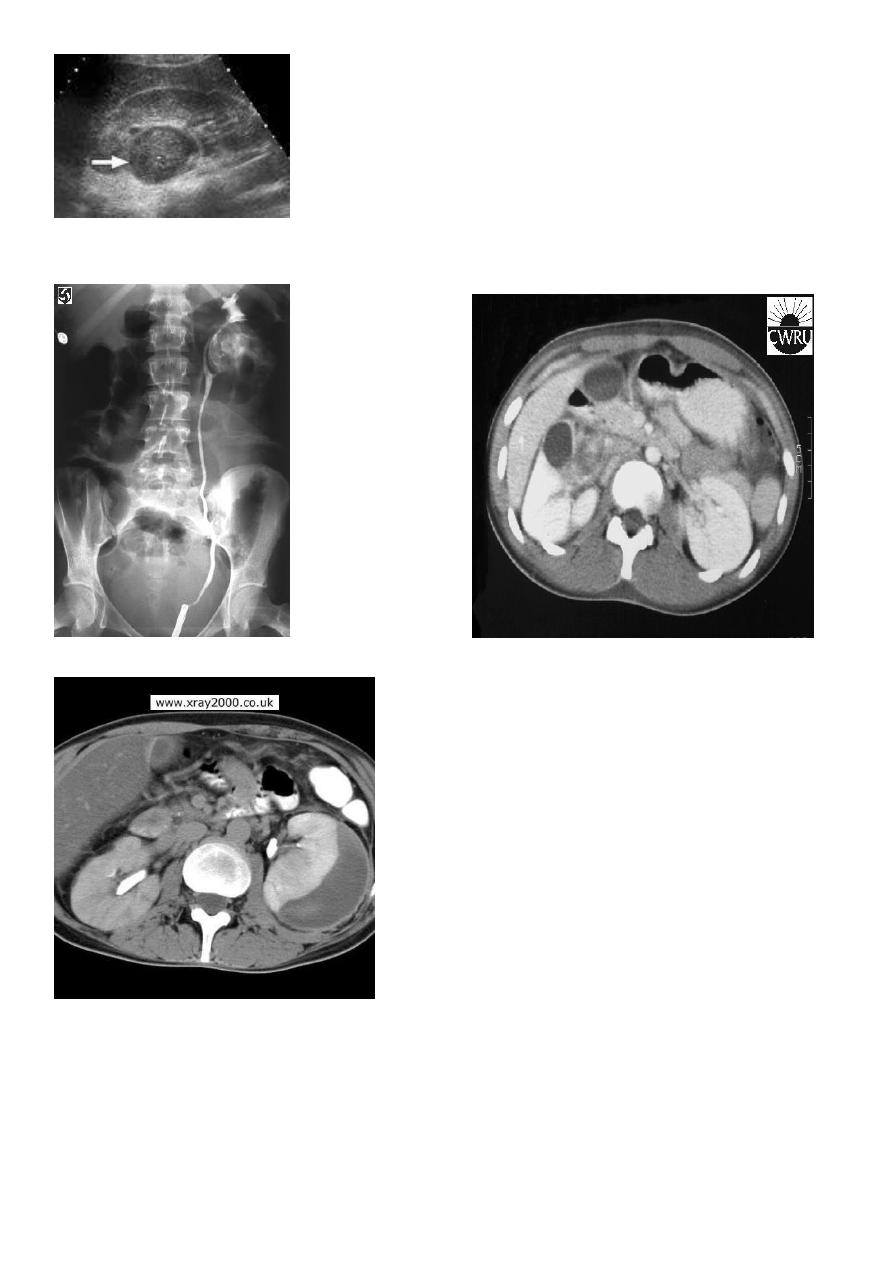
3
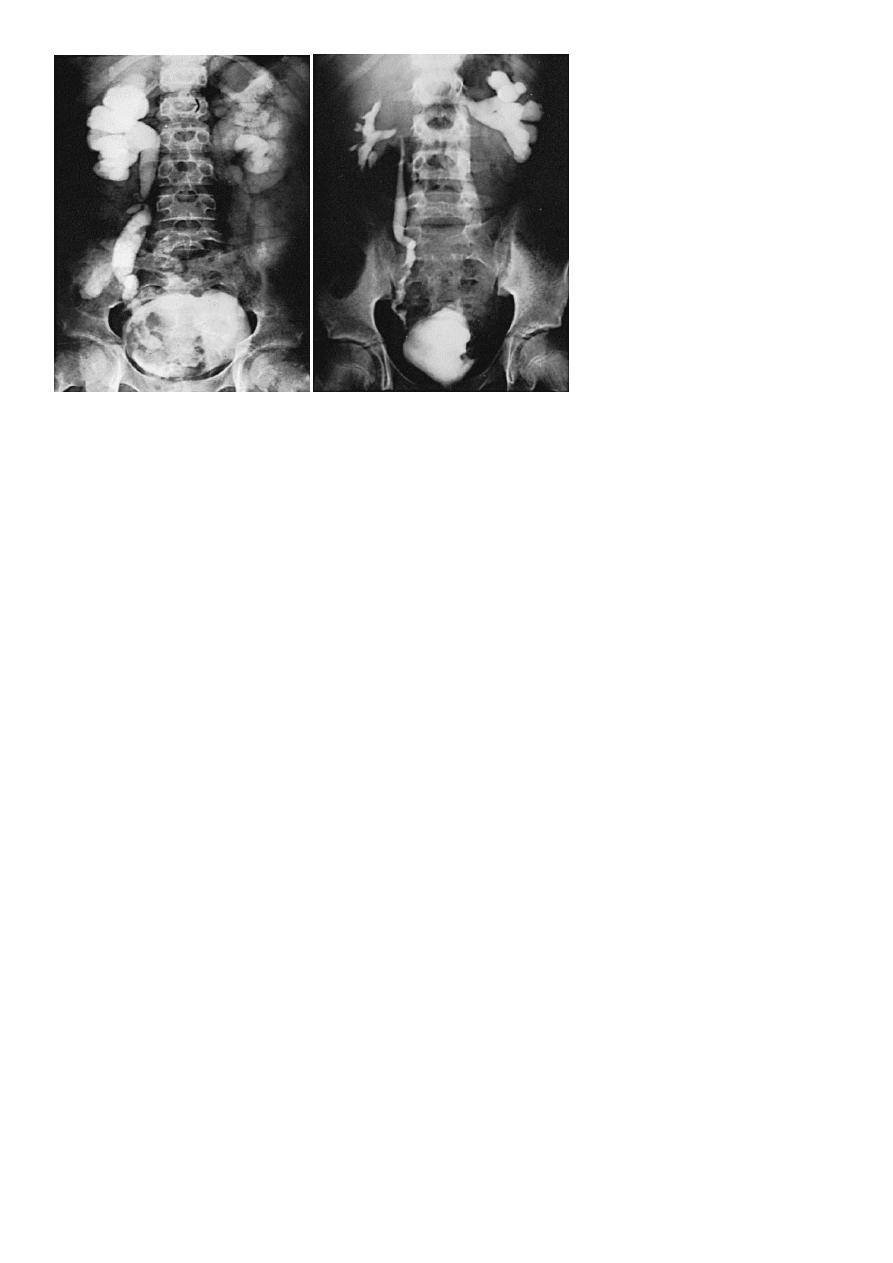
Retrograde pyelography: Left renal abscess CT scan: right renal abscess
CT scan: Left renal abscess
Treatment :
-Drainage is the principle treatment of pus collection anywhere in the body.
-If pus is too thick to be drained by percutaneous needle aspiration under antibiotic cover
lumber incision is made , all loculi destructed , pus drained and wound closed over a tube
drain
4
Specific infection of the kidney :
Renal Tuberculosis:
Bacteria: Mycobacterium TB
-
-Pathogenesis: Hematogenic
-Start unilateral , late bilateral affection.
-The 1
st
lesion starts usually in the pyramids
-Chronic: Asymptomatic until late stage
-TB granuloma, caseation, open to the calyces.
-Renal destruction, calcification.
-The ureteric upper & lower 1/3
rd
is affected
-Ureteral & bladder involvement is commonly secondary
RENAL TB
Clinical picture : Always suspect if
:
Endemic area
-
-Age : 20----30 year
-Chronic symptoms
-Non responsive UTI to adequate therapy
Unexplained hematuria
-
-Night sweating Wt loss
Chronic renal sinuses
-
TB is the most common opportunistic infection in AIDS patients
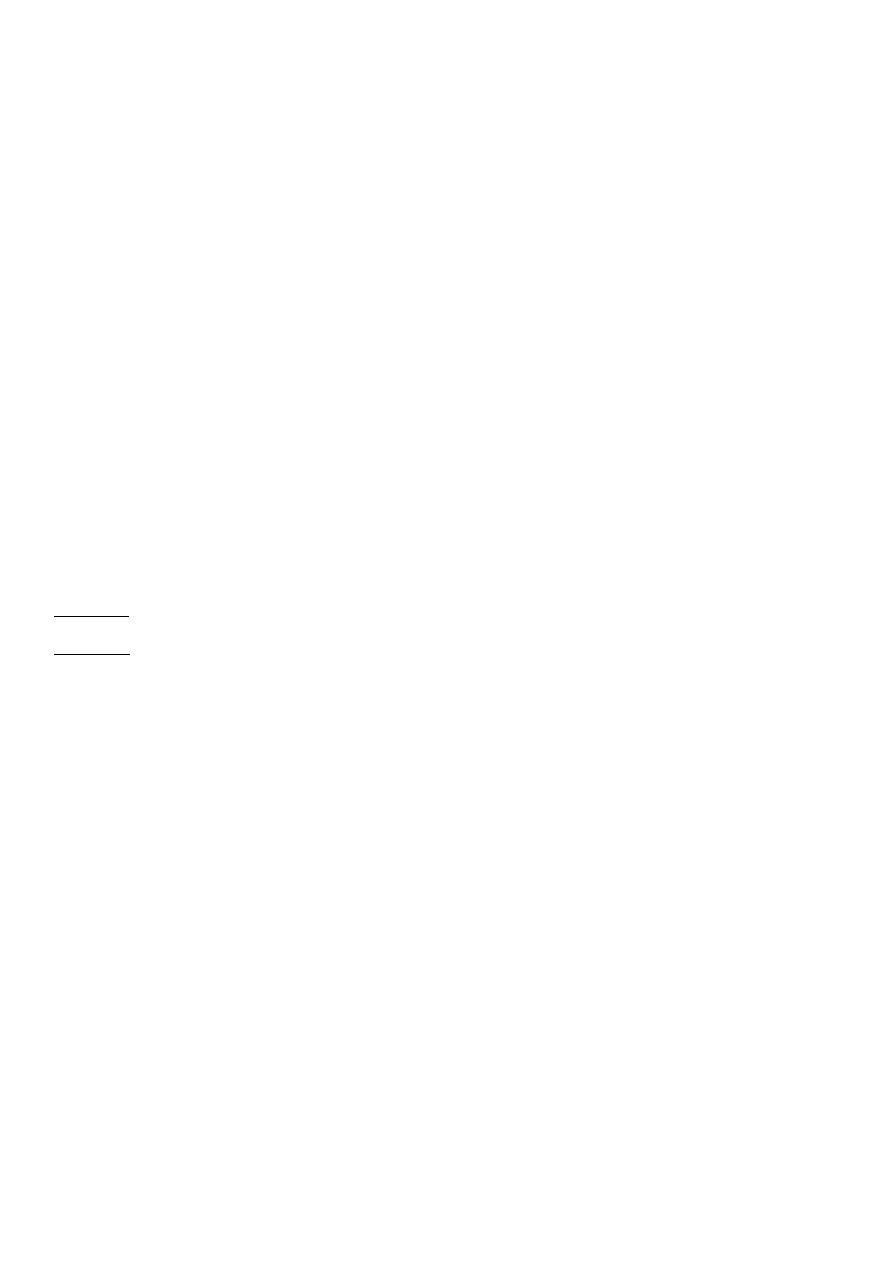
5
Investigation :
GUE : RBC , Sterile acid pyurea.
-ve urine C&Ss
Three successive morning urine samples for AFB.
24 hours urine collection for AFB.
TB culture & sensitivity.
ESR increased
WBC total & differential.
KUB: Renal calcification
IVU
CXR
Cystoscopy: for lower tract involvement.
Treatment :
Medical:
Surgical:
If complicated
No clinical control
Correct obstruction
Nephrectomy.
Bilhariziasis :
-Trematode: schistosoma haematobium
-Male: female 3:1
-Endemic in Nile valley, Iraq, & middle east in general.
-Marshes & slow running fresh water is the habitat of the fresh water snail ( bulinus
truncatus ) which is the intermediate host.
Clinical features :
-Urticaria ( swimming itch )
-Fever , sweating
-Hematuria: intermittent, terminal
-Lymphadenopathy & splenomegaly
6
Investigations :
-GUE : early morning samples for several consecutive days – ovae with terminal spines
-Leukocytosis – eosinophilia
-Cystoscopy
-Bilharzial pseudotubercles , nodules, sandy patches, ulceration, fibrosis,
-granulomas, papillomas, carcinoma (SCC).
Imaging study :
7
Treatment :
-Antimony e.g. praziquantel & metriphonate
-Papilloma : endoscopic removal
Carcinoma : radical cystectomy
-
