Dr. Muwaffaq Mezeil Telfah
MBChB, MSC, MRCS/EngPeritoneum and Intra-abdominal Sepsis
Learning objectives
To recognize and understand:The concept of peritonitis.
The clinical features of localized and generalized peritonitis.The common causes and complications of peritonitis.
The principles of surgical management in patients with peritonitis.
Basic facts about peritoneum
The peritoneal membrane is a thin layer lining the peritoneal cavity.Network of lymphatic vessels and rich plexus of capillary blood vessels.
It consist of two layers.
The parietal peritoneum is richly supplied with nerves.
Clinical implications:
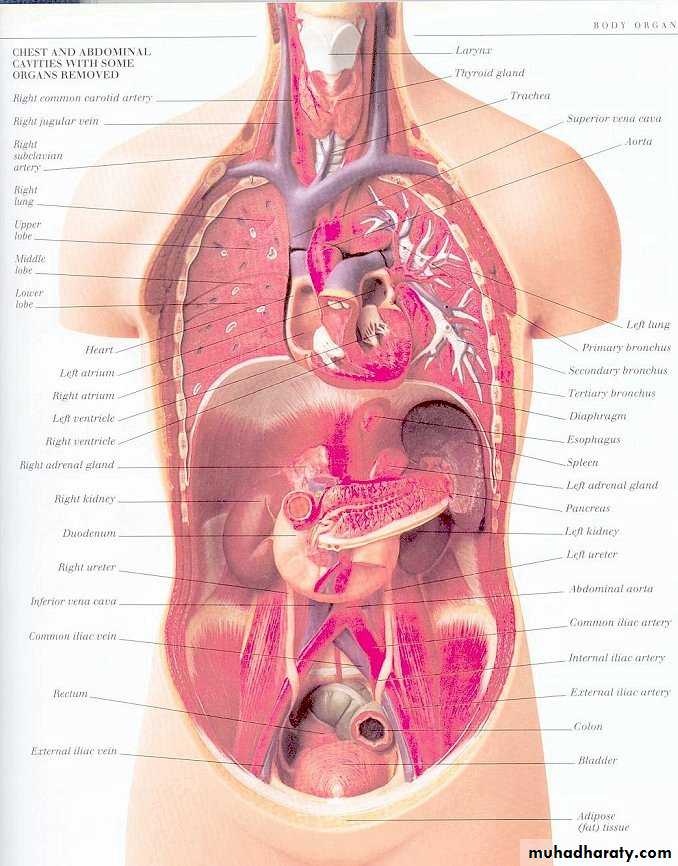
The largest cavity in the body= peritoneal cavity = skin surface area.
Somatic and visceral pain.
All absorption and exudation occur.
Exudation from inflamed peritoneum….. fluid loss.
Absorptive ability…….Peritoneal dialysis.
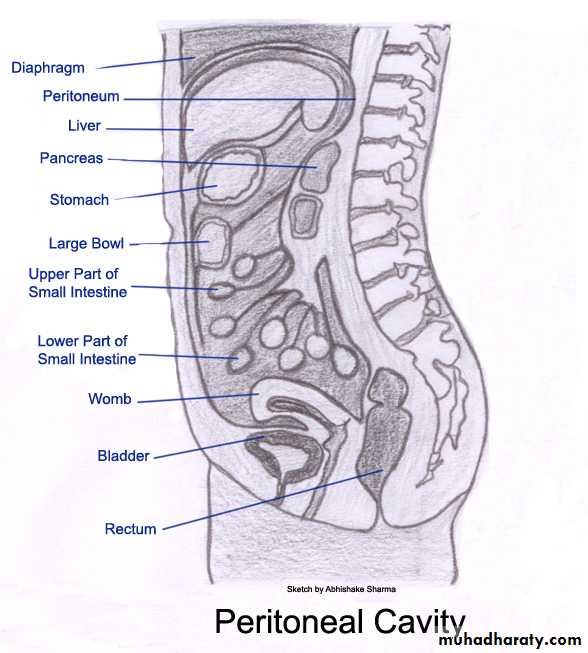
Peritoneal cavity
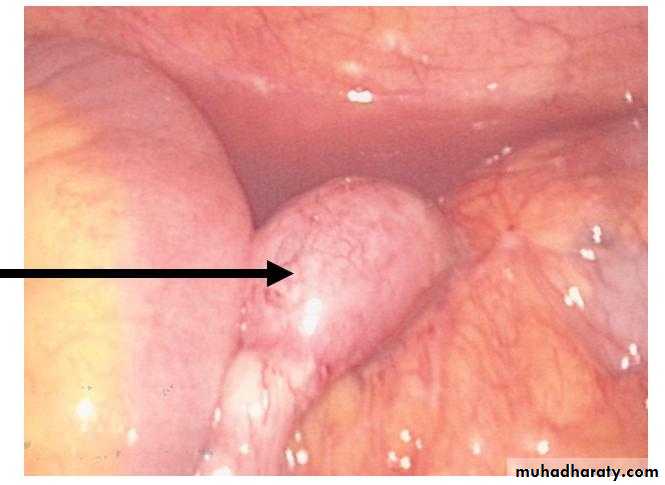
Peritonitis
Bacterial infection, e.g. appendicitis, perforated viscus ,tuberculosis.Chemical injury, e.g. bile peritonitis.
Ischemic injury, e.g. strangulated bowel, vascular occlusion.
Direct trauma, e.g. operation.
Allergic reaction, e.g. starch peritonitis.
Bacterial peritonitis
Poly-microbial in origin:Gastrointestinal tract e.g. E.Coli, Bacteroids, clostridia, Klebseilla and streptococci.
Non-Gastrointestinal: Chlamydia, Gonococcus, and Mycobacteria.
Mono-microbial e.g. primary spontaneous peritonitis.
Paths to peritoneal infection
Gastrointestinal perforation.Transmural bacterial translocation (no perforation).
Exogenous contamination.
Female genital tract infection.
Haematogenous spread (rare).
Peritonitis
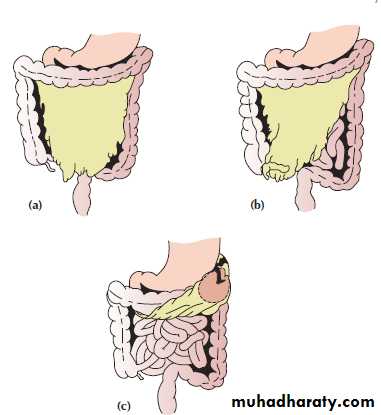
Localized or generalizedWhy ?
Factors which favor the localizationAnatomical factors.
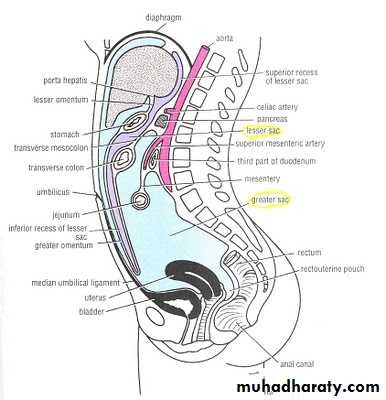
Compartments
Greater sac and lesser sacSupracolic and infracolic
Peritoneal cavity
Pathological process (localization)
The inflamed peritoneum permeability inflammatory exudates fibrin deposition.Adherence of loops of intestine .
The peristalsis of the affected bowel will be retarded .
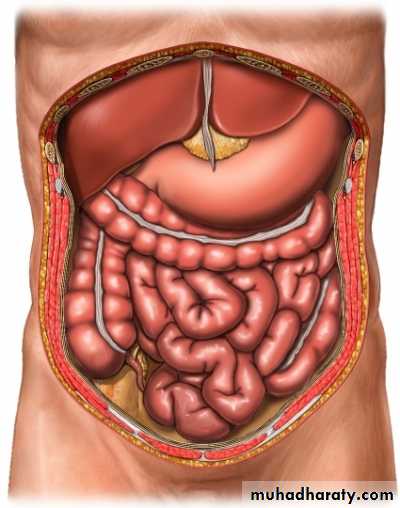
Greater omentum
By enveloping the inflamed structure
Abdominal policeman
Greater omentum = Abdominal policemanSurgical factors
Drainsproviding an exit for the intra-abdominal collections.
Source of exogenous infection.
Factors which favor development of generalized peritonitis
Spread of the peritoneal contamination = perforation of obstructed system.Stimulation of the peristalsis by food or purgatives or an enema.
The virulence of the infecting micro-organism.
The age of patient: children elderly.
Deficient natural resistance i.e. decreased immunity
Clinical picture:
Severe abdominal pain, referred pain to shoulder.
vomiting.
On examination:
in pain, ill looking.
rising pulse with elevated temperature
Local examination:
reveals localized or generalized tenderness depending on the extent of peritonitis.
Guarding and rigidity.
The abdomen is "silent" i.e. no bowel sounds.
Rectal/ vaginal exam may reveal tenderness.
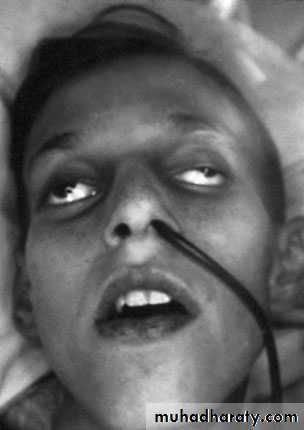
Hippocratic facies
In advanced cases,
The abdomen becomes distended and tympanitic. The patient become increasingly toxic with rapid thread pulse and cold extremities with cyanosis " circulatory failure“.Investigation:
Blood tests:WBC count
Amylase level in pancreatitis.
Imaging studies:
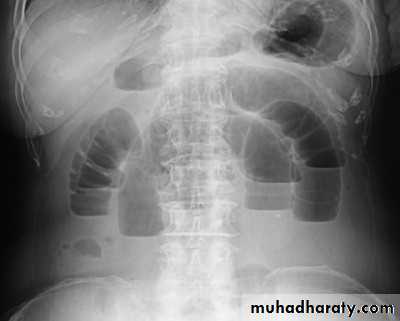
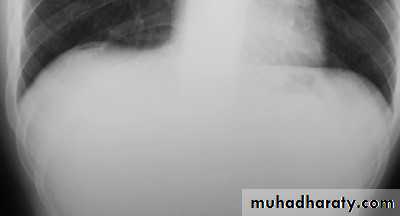
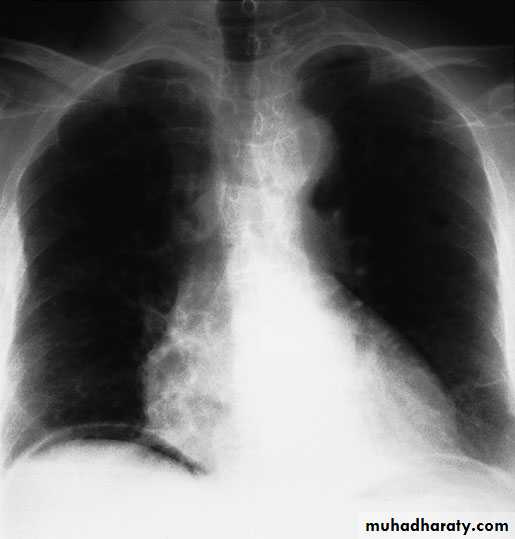
plain X ray of the abdomen
CXR in erect position.
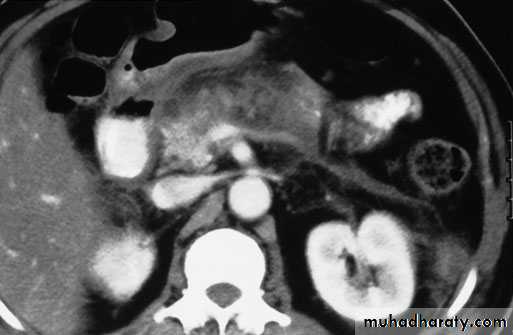
U/S and/or CT Scan.
Treatment:
In case of doubt: early surgical intervention is to be preferred to "wait and see policy" !1. General care of patient (supportive treatment).
2. Definitive treatment.
Supportive treatment :
Correction of fluid and electrolytes imbalance:Gastrointestinal decompression:
Antibiotics:
Analgesics:
Vital systems support:
Definitive treatment :
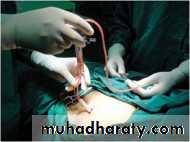
Surgical treatment:operative treatment of the underlying condition e.g. closure of perforated ulcer or appendicectomy.
peritoneal lavage.
Non-surgical (conservative): indicated for conditions like pancreatitis, spontaneous peritonitis provided that the diagnosis made with certainty.