By
Dr. Samir Al-Saffar
Professor of Surgery
Anatomy of Liver
Largest organ
Right upper quadrant
Having large right lobe
and smaller left lobe
Anatomy of Liver
Functional anatomy: “Couinaud”
Divided into 2 lobes along the line passing
between gall bladder fossa and middle
hepatic vein. “Cantil’s line”
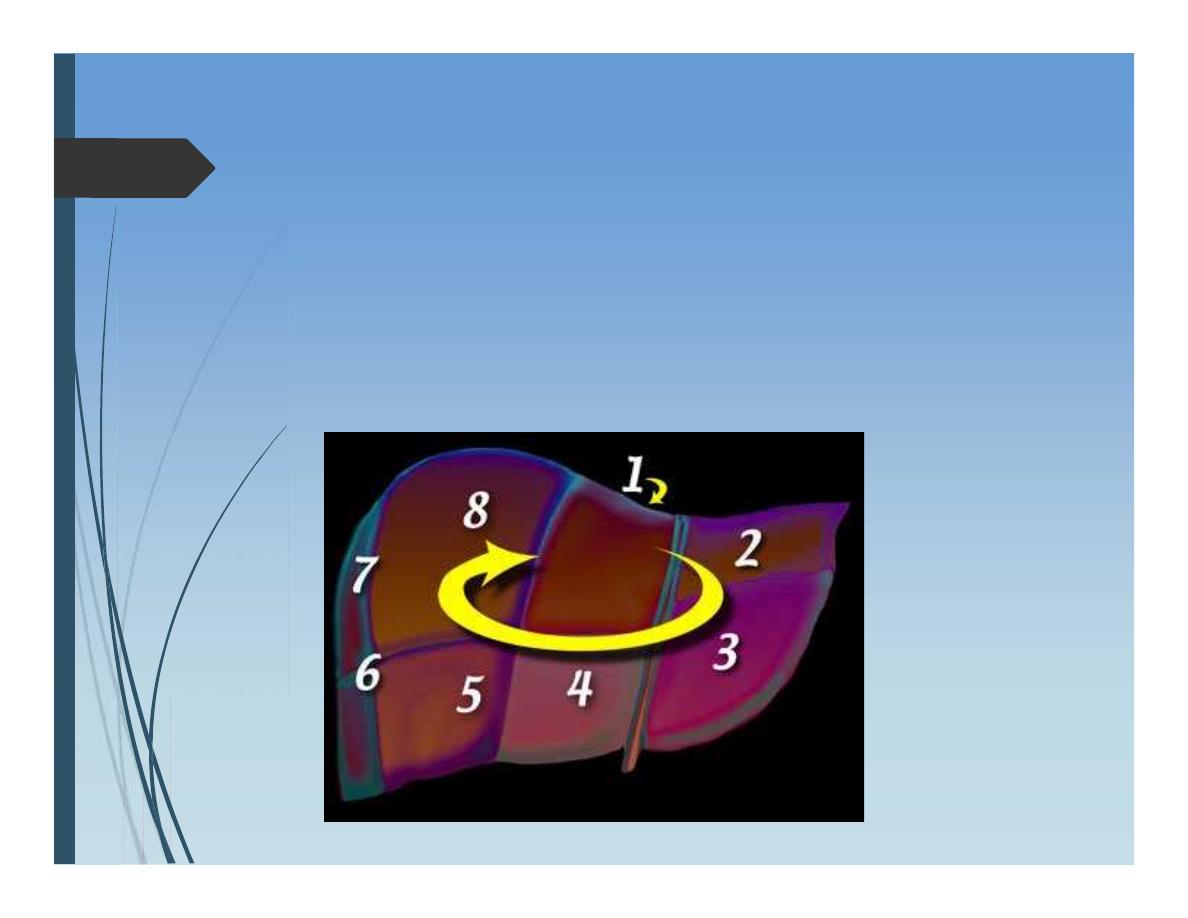
Anatomy of Liver
8 segements
I – IV -------functional left lobe
V – VIII -----Functional right lobe
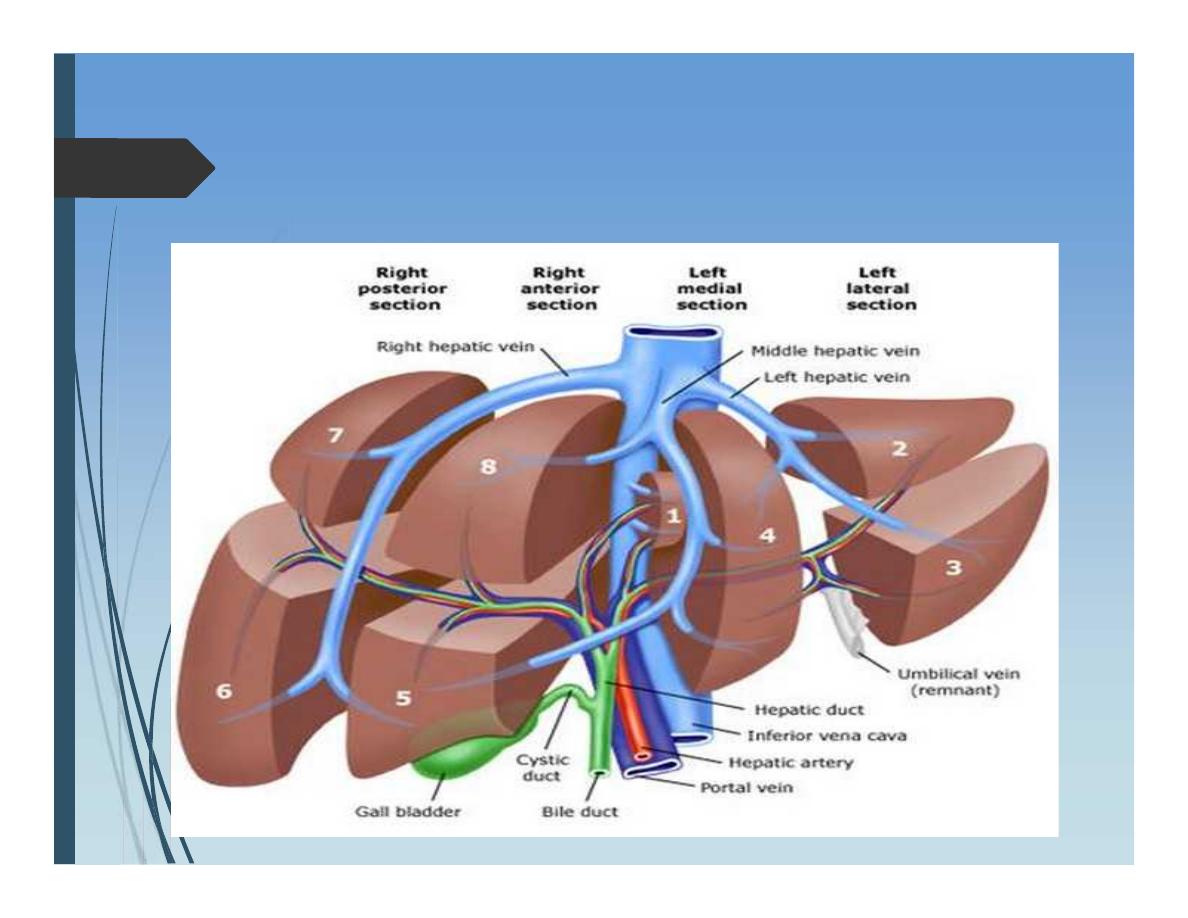
Anatomy of Liver
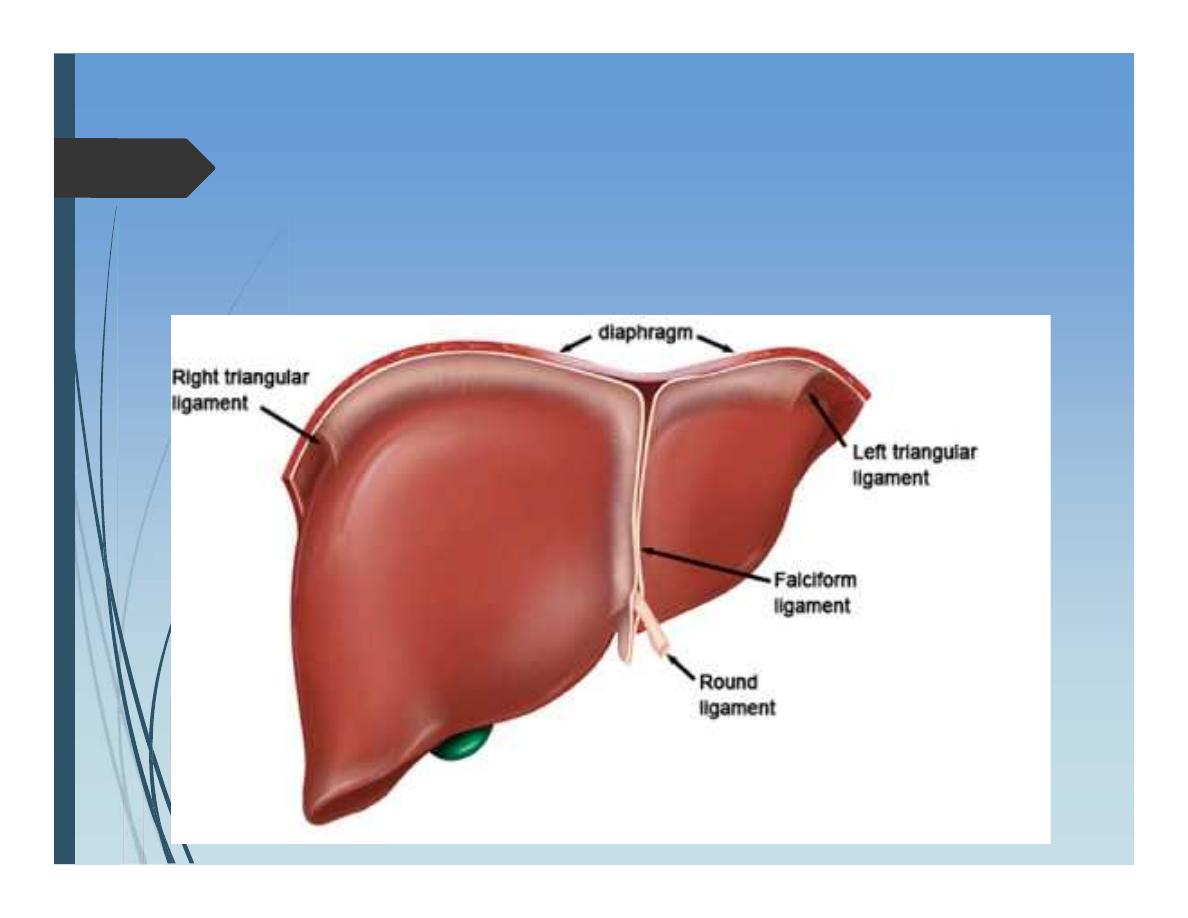
Ligaments that fix the liver in its place:
• Left triangular ligament
• Right triangular ligament
• Falciform ligament
• Lesser omentum (hepatoduodenal ligament)
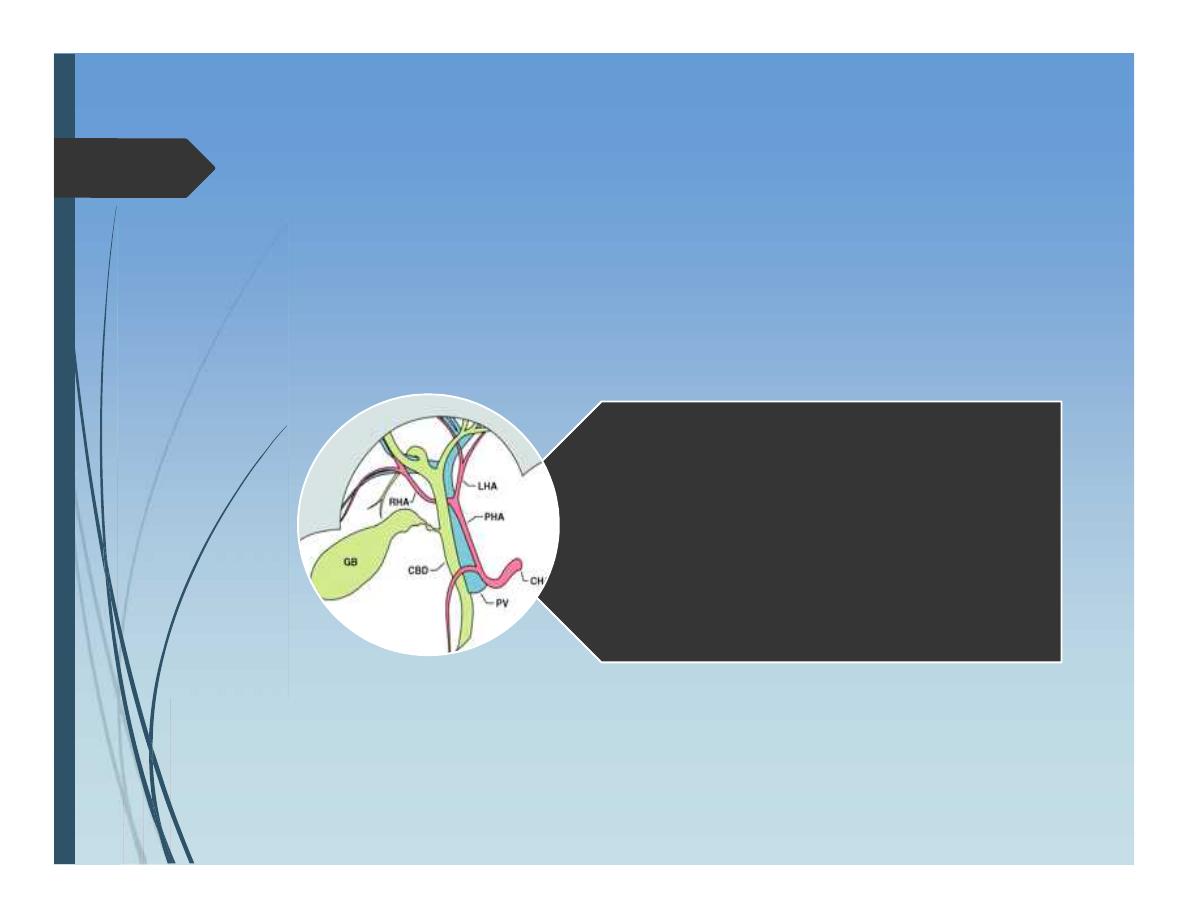
Anatomy of Liver
Hilum of liver:
•Bile duct
•Hepatic artery
•Portal vein
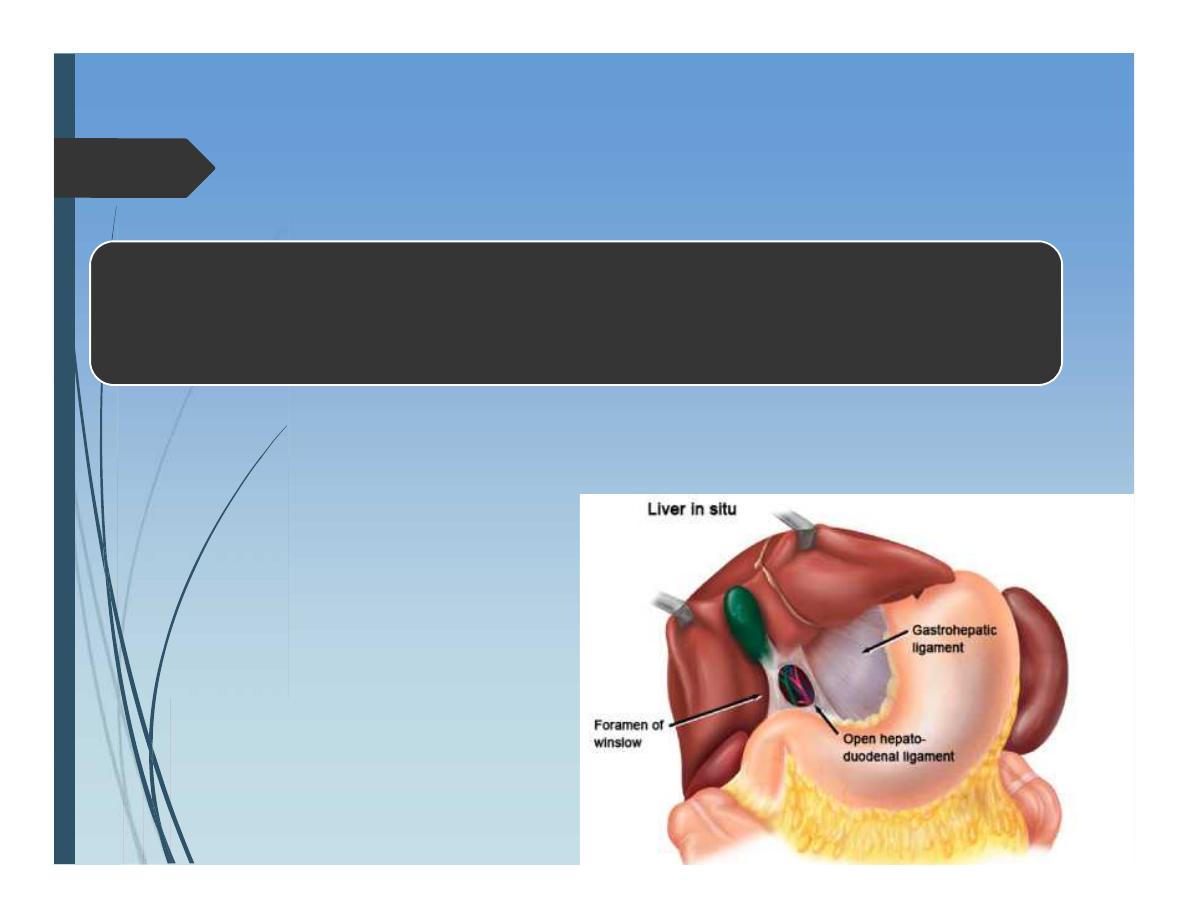
Anatomy of Liver
Foramen of Winslow:
•Anterior: CBD, HA, PV
•Posterior: IVC
•Upper: Liver
•Lower: duodenum
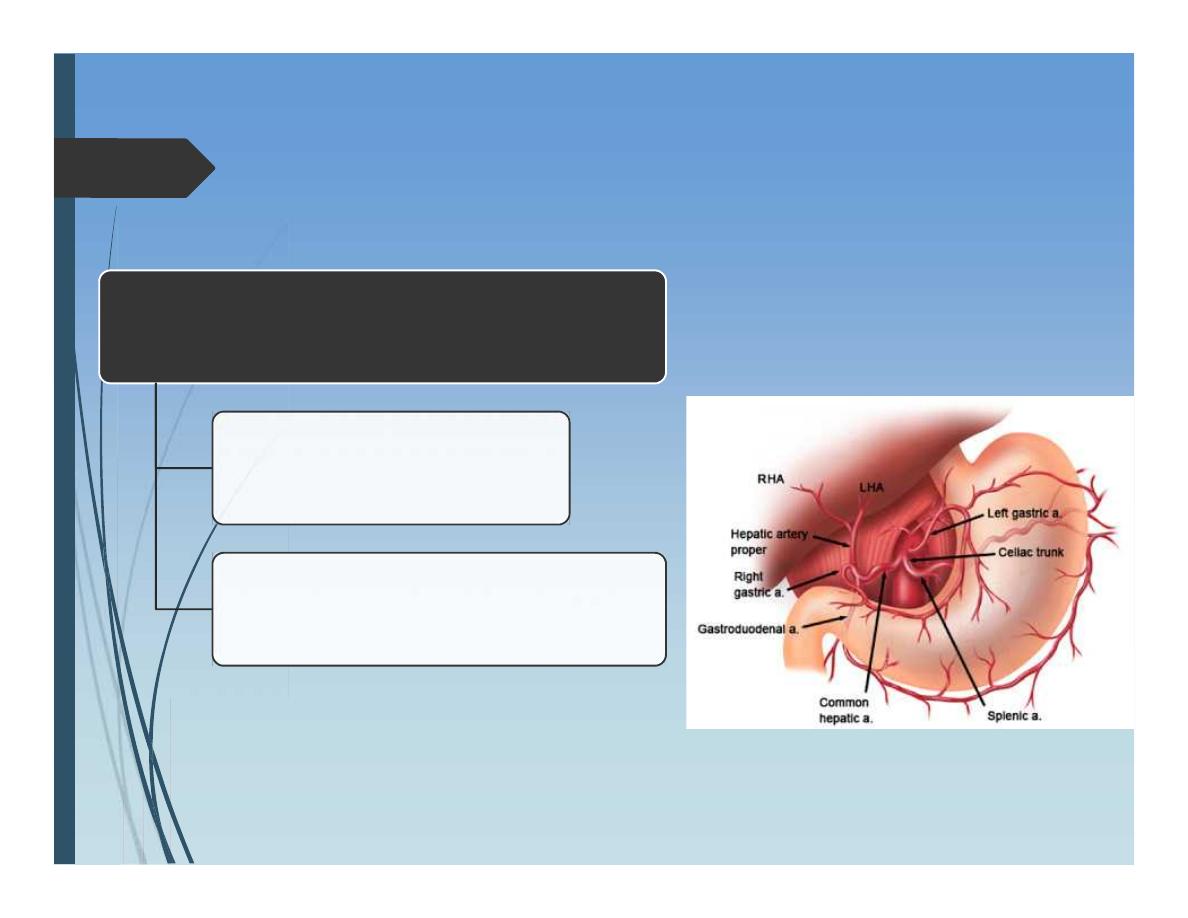
Anatomy of Liver
Liver Blood supply:
Portal vein 80%
Hepatic artery 20%
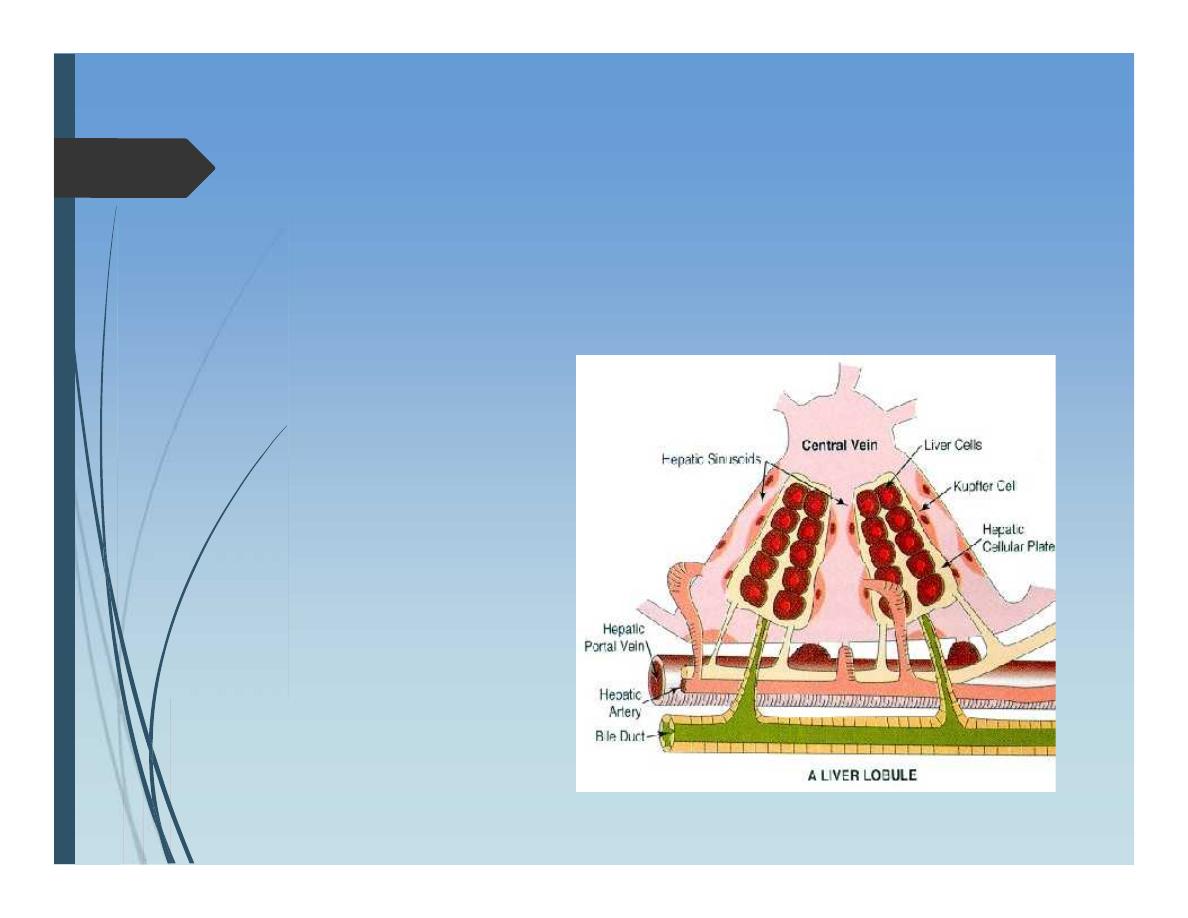
Internal anatomy of liver:
Liver Lobule:
Is the functional
Unit within liver
segments
Embryology
Foregut :
hepatocytes
Biliary passages
Septum transversum
Kupffer cells
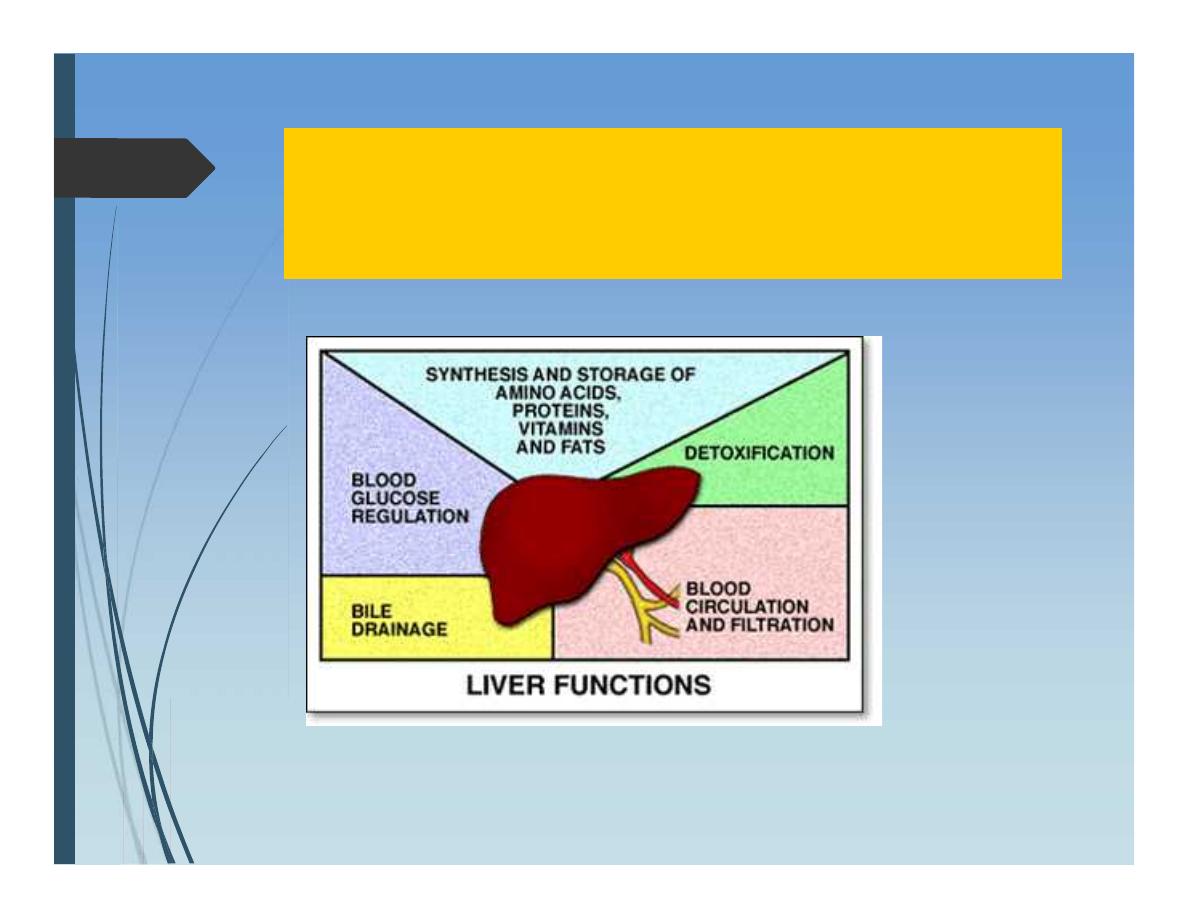
Liver Functions
Liver Functions
Metabolism of bilirubin
Formation of bile;
Water,
electrolytes,bile pigments,
bile salts, phospholipids
(lecithin), and cholesterol.
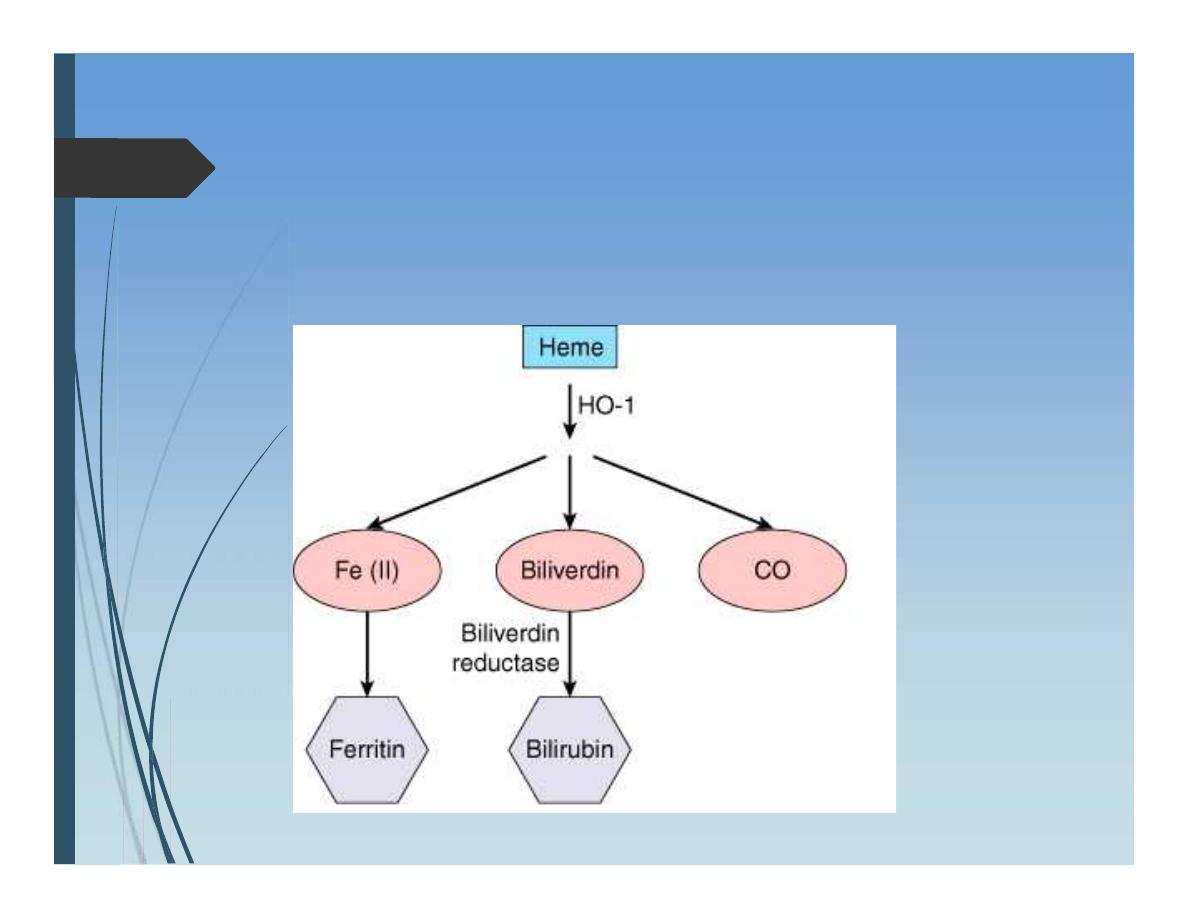
Metabolism of bilirubin
Investigations of liver
Liver Function tests:
USED TO
Detect presence of liver disease
Distinguish among different types of liver diseases
Gauge the extent of known liver damage
Follow the response of treatment
Tests for excretory function
Serum bilirubin
Urine bilirubin
Blood ammonia
Tests that indicate liver cell
injury
Serum enzymes :
AST
ALT
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Serum Enzymes – that reflect
cholestasis
Serum Alkaline phosphatase
5’Nucleotidase
Tests that measure
Biosynthetic function of liver
Serum Albumin
PT ,INR
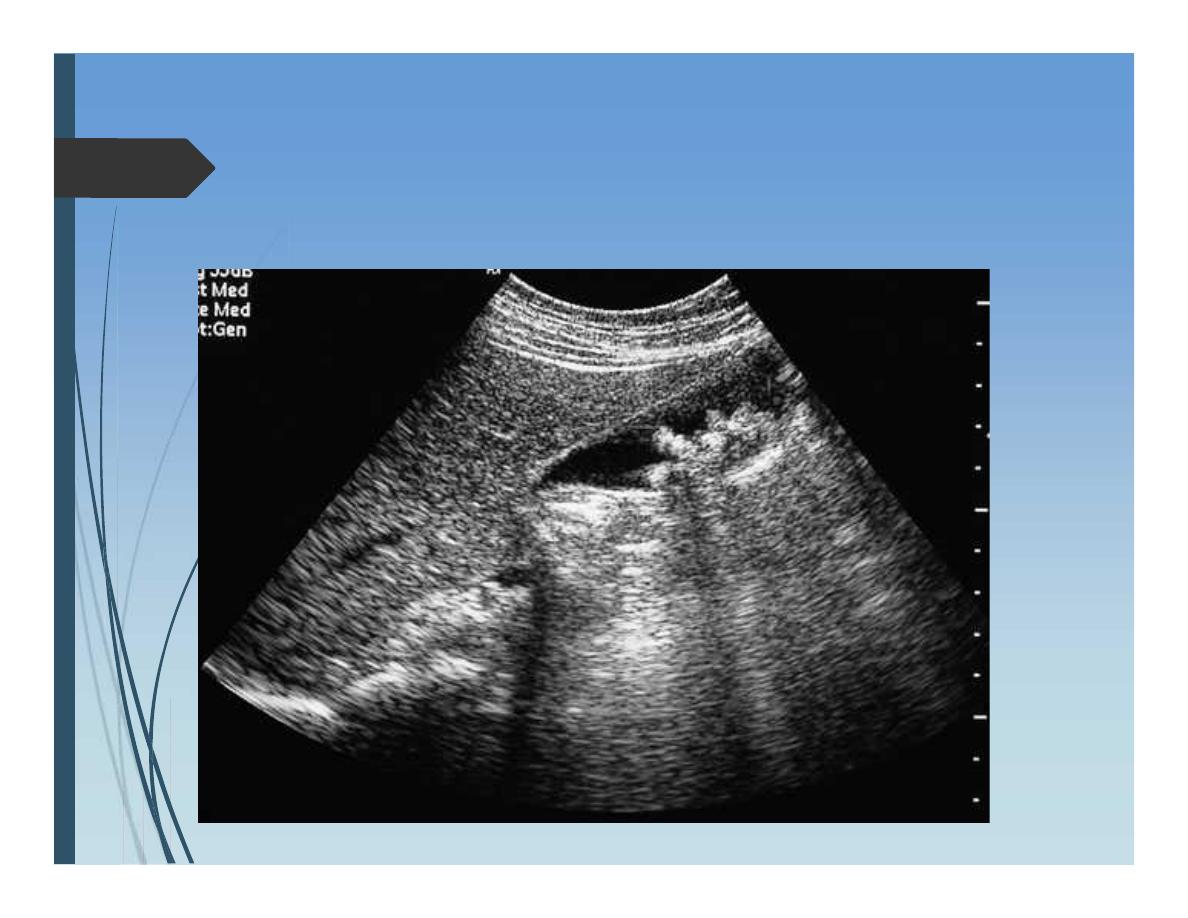
Imaging of liver
Ultrasound:
First line test
Useful for
Liver SOL
State of biliary passages
As a guide for needle liver biopsy or
catheterization
.
Doppler Ultrasound:
Blood flow
Vascularity of liver tumors
Computerized tomography
(CT scan)
Triple-phase spiral CT is the gold standard
imaging modality of liver.
Liver lesions down to 1cm
Its density can be measured
Vascularity of lesion---contrast
Magnetic resonance imaging
More or less similar to CT scan
Its advantages:
No radiation
No contrast of value in allergy to iodine
Magnetic resonance
cholangiopancreatography
”
MRCP
”:
Provide excellent quality imaging of billiary tracts non
invasively
.
Magnetic resonance angiography
”
MRA
“ :
Provide high quality images of portal veins and
hepatic arteries without the need for cannulation
.
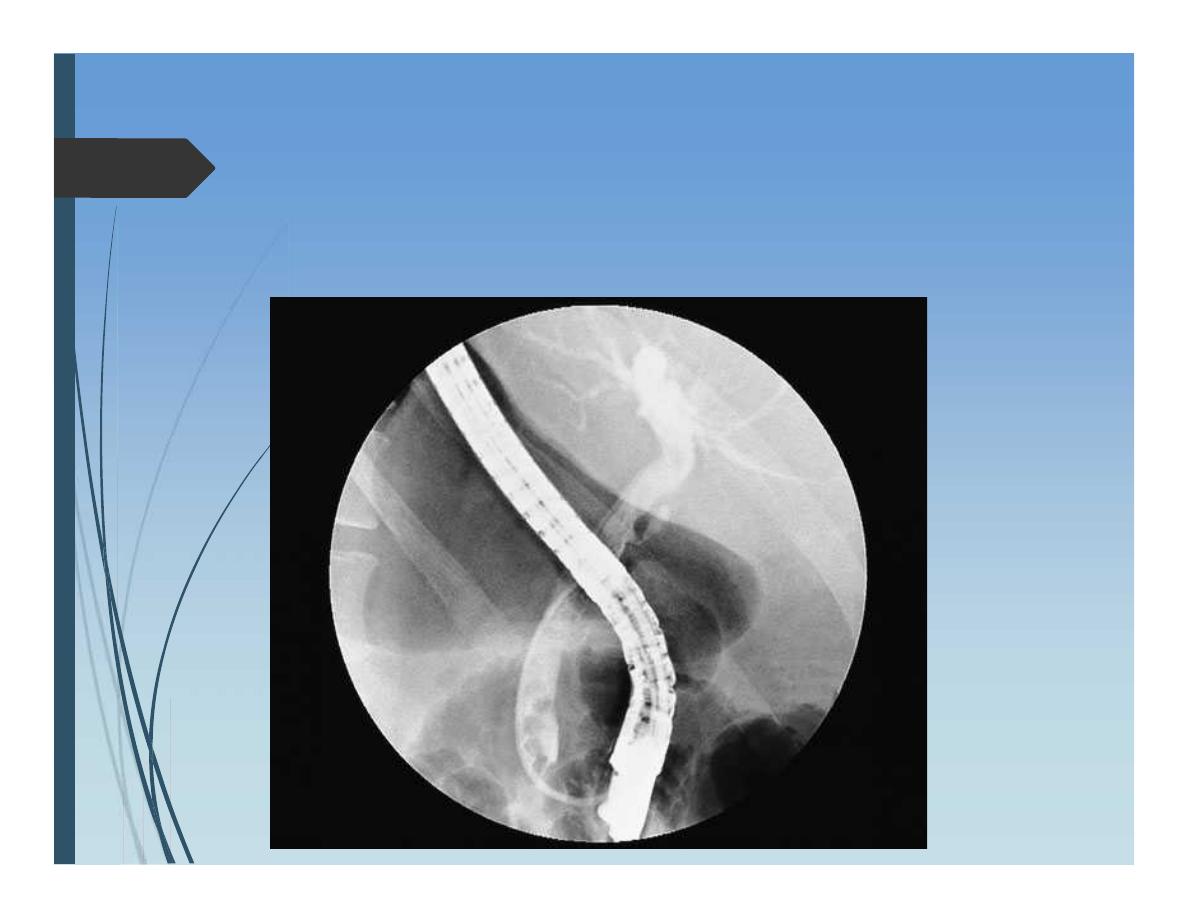
Endoscopic retrograde
cholangiopancreatography (
ERCP
)
Diagnosis
Therapeutic
Indications:
Obstructive jaundice ? Aetiology
An imaging suggested abnormality in biliary tracts
ERCP
Preparation:
Checking coagulation state; PT , INR
Informed consent:
Pancreatitis
Cholangitis
Bleeding
Perforation of duodenum
Prophylactic antibiotics
Therapeutic ERCP
Sphincterotomy and Stone retrieval from CBD
Balloon dilatation of strictures
Stenting (Endoprosthesis) of strictures of CBD.
Percutaneous transhepatic
cholangiography
Indications:
When Endoscopic cholangiography failed
When ERCP impossible
polya gastrectomy
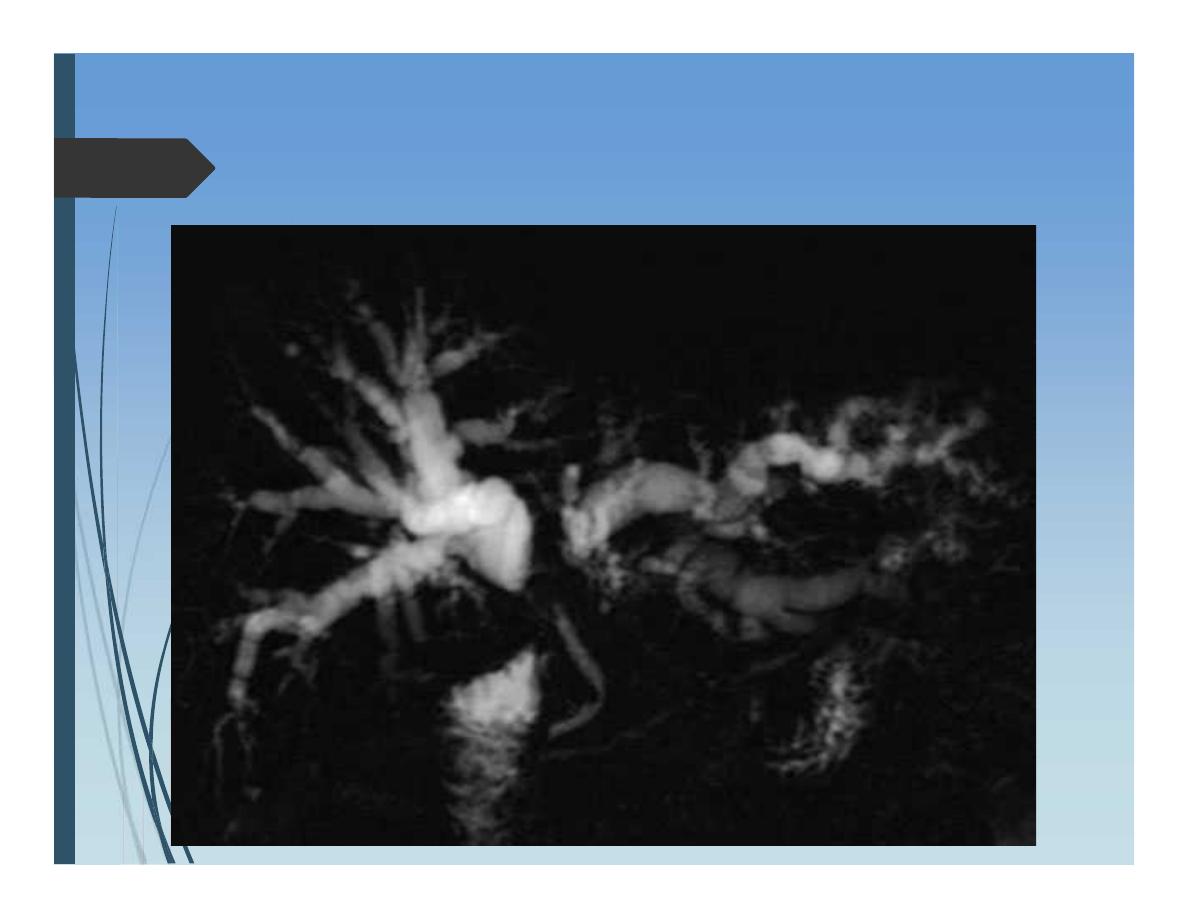
Selective Visceral angiography
Diagnosis
Clear anatomy of hepatic artery prior to liver resections
Therapy:
Embolization
arteriovenous malformation
Stop bleeding from liver
Chemoembolization for liver tumors
Nuclear medicine scanning
Technetium 99m labeled radionuclide:
Handled like bile and so its uptake and excretion can be
monitored in real time.
Useful in:
Bile leak
Bile obstruction
Laparoscopy and
laparoscopic ultrasound
Staging of liver tumors
Detection of small lesions not detected by other
imaging modalities
Peritoneal sedlings
Small superficial lesions
Help in detection of other additional lesions not
detected by CT or MRI
Flurodeoxyglucose-postron
emission tomography
Helpful for determing the nature of a mass lesion
detected by other imaging modalities
Blunt injuries:
Contusion, laceration, avulsion
Penetrating injuries:
Stab
Gunshot
Diagnosis of liver injury:
Clinical suspicion of liver injury
All lower chest and upper abdominal stab
wounds
should be suspect, especially if
considerable blood volume replacement
has been required.
Similarly
,
severe crushing injuries to the
lower chest or upper abdomen often
combine rib fractures, haemothorax and
damage to the spleen and/or liver
Tools may be of help in the diagnosis of liver
injury:
FAST
Peritoneal aspirate
Laparoscopy
Management of liver injury
General consideration:
Not usual
Serious
Think of associated injuries
Management of liver injury
General plan:
General resuscitation: ATLS
Penetrating injury :
emergency
laparotomy
Blunt injury
stable circulation after initial
resuscitation sent the patient for:
CT scan with oral and iv contrast
Management of liver injury
Blunt injury to liver
There is a place for conservative treatment
When to stop conservative treatment
Ongoing blood loss
Generalized peritonitis
Surgical approach to liver
trauma
Good and wide access (rooftop) incision
Stop blood inflow “Pringle manueuvre”
Suturing of tears
Excision of avulsed devitalized tissue
Repair of major vessel injury
Packing
Complications
Massive blood loss
Abscess ….. Subcapsular hematoma
Bile collection “Biloma:, Biliary fistula
Arteriovenous fistula
Arteriobiliary fistula
Hepatic artery aneurysm
Liver failure
Pyogenic liver abscess
Aetiology:
in the majority unknown
Possible causes:
Impaired biliary drainage
Hematogenous drug abuse, teeth
cleaning
Local spread diverticulitis
Immune compromised apportunistic
Pyogenic liver abscess
Infecting mo
Enteric organisms; Streptococcus faecalis,
Klebseilla, Proteus vulgaris , E coli,
Streptococus melleri
Opportunistic staph

Pyogenic liver abscess
Clinical features:
• Nonspecific
• Fever, malaise, anorexia
• Right upper quadrant
discomfort
• Jaundice occurs in up to one
third of affected patients
Diagnosis:
Lab investigations:
Leucocytosis,
an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate
an elevated alkaline phosphatase (AP) level
Blood cultures reveal the causative organism
in approximately 50% of cases
Diagnosis:
Ultrasound examination
reveals pyogenic abscesses as round or
oval hypoechoic lesions with well-defined
borders and a variable number of internal
echoes
CT scan
highly sensitive in the localization of
pyogenic liver abscesses
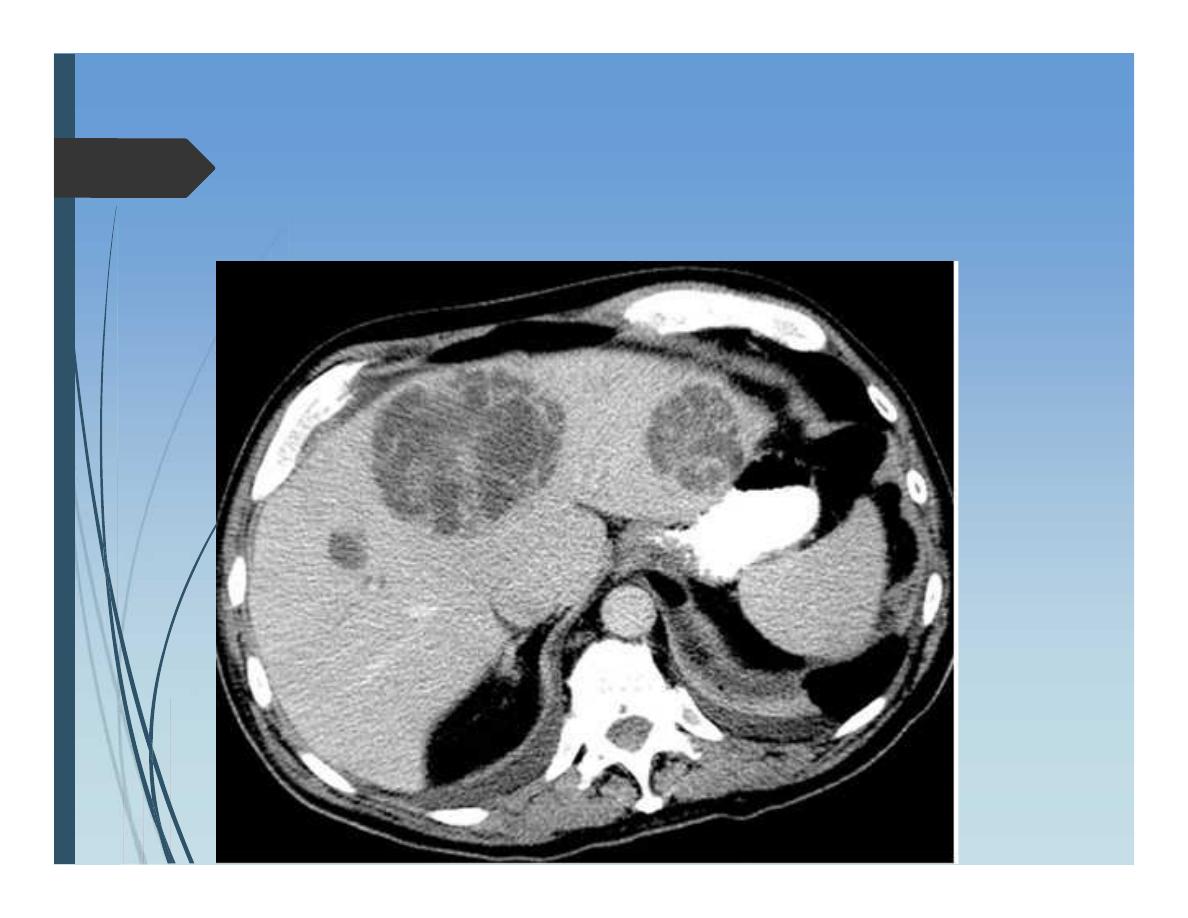
CT scan

Pyogenic liver abscess
Treatment:
•Antibiotics
•Percutaneous drainage
under ultrasound guide
Look for the source
Amoebic Liver Abscess
Causative:
Entamoeba histolytica
Clinical Features
History of dysentery
Travel to endemic area
Symptoms
Non specific
Diagnosis:
US
CT scan
Confirmation is by isolation of the
causative organism.
Treatment
Metronidazol 750mg t.i.d for 5 – 10
days
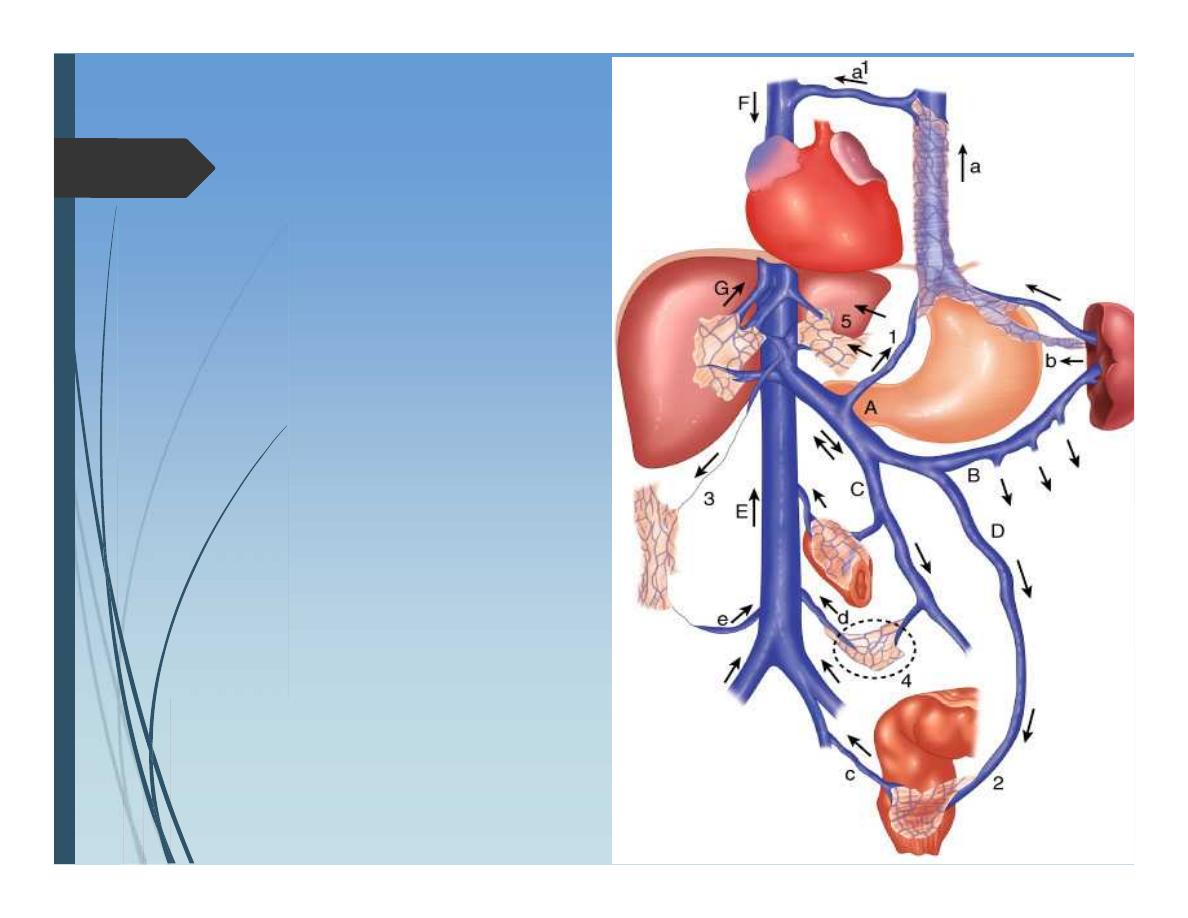
Portal Hypertension
Portal circulation:
Portal vein formed from
confluence of SMV and splenic
vein. Also a tributary from
coronary (left gastric) vein.
Portasystemic communications:
gastroesophagus junction
Anal canal
Retroperitoneum
Falciform ligament
Normal portal venous pressure is about 10 -15 mmHg.
Aetiology:
Liver cirrhosis
Extrahepatic portal vein occlusion
Intrahepatic veno-occlusive disease
Occlusion of main hepatic veins ( Budd-
Chairi syndrome)
Clinical presentaion:
Variceal bleeding
decompensated chronic liver disease
Encephalopathy
Ascitis
Diagnosis:
High portal venous pressure ( > 20mmHg )
Hepatic venography
Direct cannulation of portal vein
Oesophagoscopy; oesophagial varices
Doppler ultrasound and CT for patency of portal vein
Management of bleeding varices
General resuscitation:
Blood replacement
Coagulopathy:
Vit K iv
Fresh frozen plasma
Thrombocytopenia < 50*10^9/l
Urgent endoscopy:
Confirm dx
therapy
Measures to stop bleeding:
Drugs:
Vasopressin
Octreotide
Endoscopic:
Sclerotherapy ethanolamine oleate
Banding
Sengenstakin – Blackmore tube
Temporary control
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (
TIPS )
Complication :
perforation of liver capsule and fatal haemorrhage
Occlusion
Post shunt encephalopathy
Surgical shunts for variceal haemorrhage
Child’s grade A cirrhosis in whom the initial bleed has
been controlled by sclerotherapy
Types of shunts
Selective; splenorenal
Non-selective : porto-caval
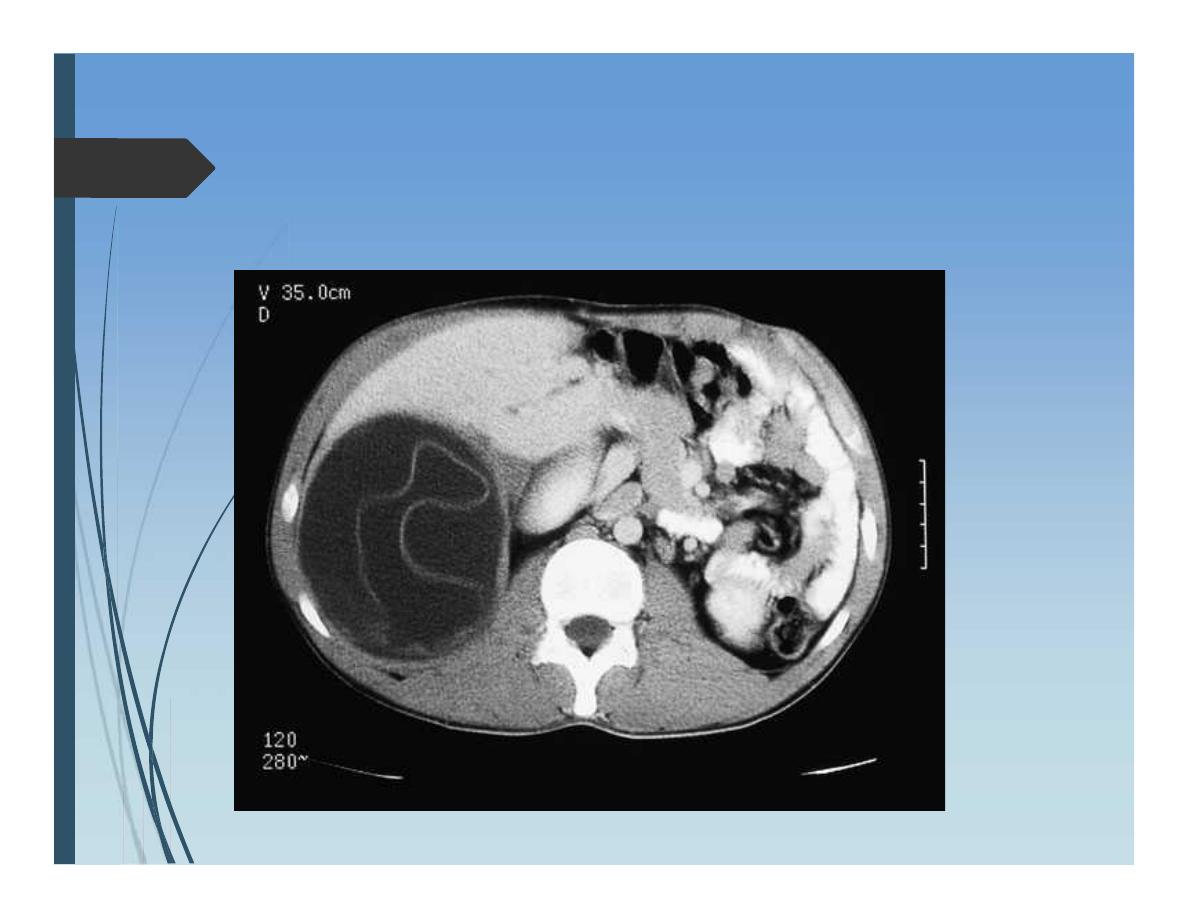
Hydatid Liver Disease
The causative tapeworm: Echinococcus granulosis
Liver is affected in 80% of cases, Lung 15%. And 5% rest
organs.
Hydatid Liver Disease
Clinical presentation:
Incidental finding on Ultrasound examination
Chronic right upper quadrant discomfort
Complications of cyst:
Rupture into peritoneum; features of
acute peritoneal irritation
Urticaria
Anaphylaxis
Hydatid Liver Disease
Rupture into biliary passages:
Jaundice and cholangitis
Rupture into pleura:
Empyema
Infection-----Liver abscess
Hydatid Liver Disease
Diagnosis
Ultrasound exam
Multilocular cyst
CT scan
Floating membrane within the cyst
Serological
ELISA for Antibody against hydatid antigen
Hydatid Liver Disease
Treatment:
Mainly surgical
Open
laparoscopic
Other methods
Drugs Albendazol
Percutaneous injection of hypertonic saline or Alcohol
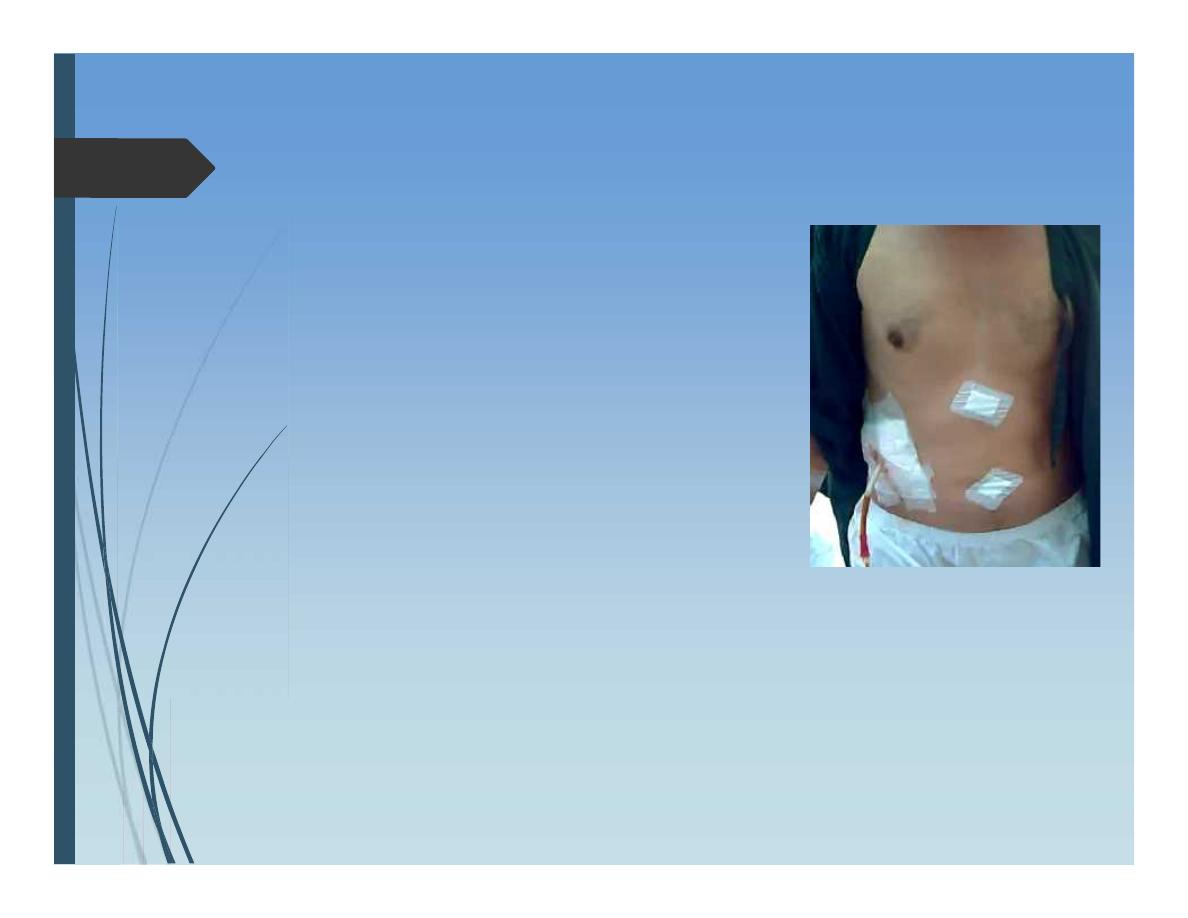
Hydatid Liver Disease
Surgical options:
Deroofing and evacuation of contents
liver resection
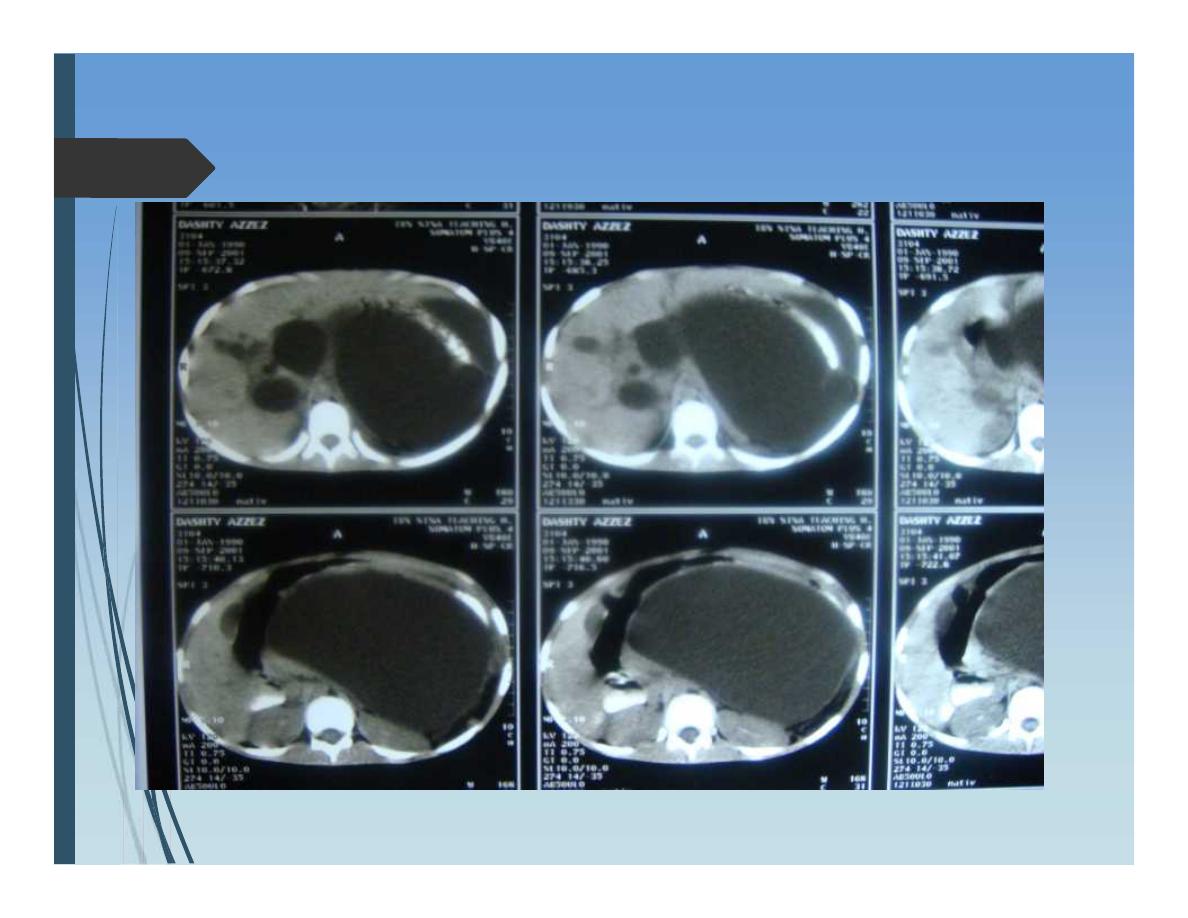
Liver tumors
Benign tumors:
Haemangiomas
Adenoma
Focal nodular hyperplasia
Liver tumors
Malignant:
Primary
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma
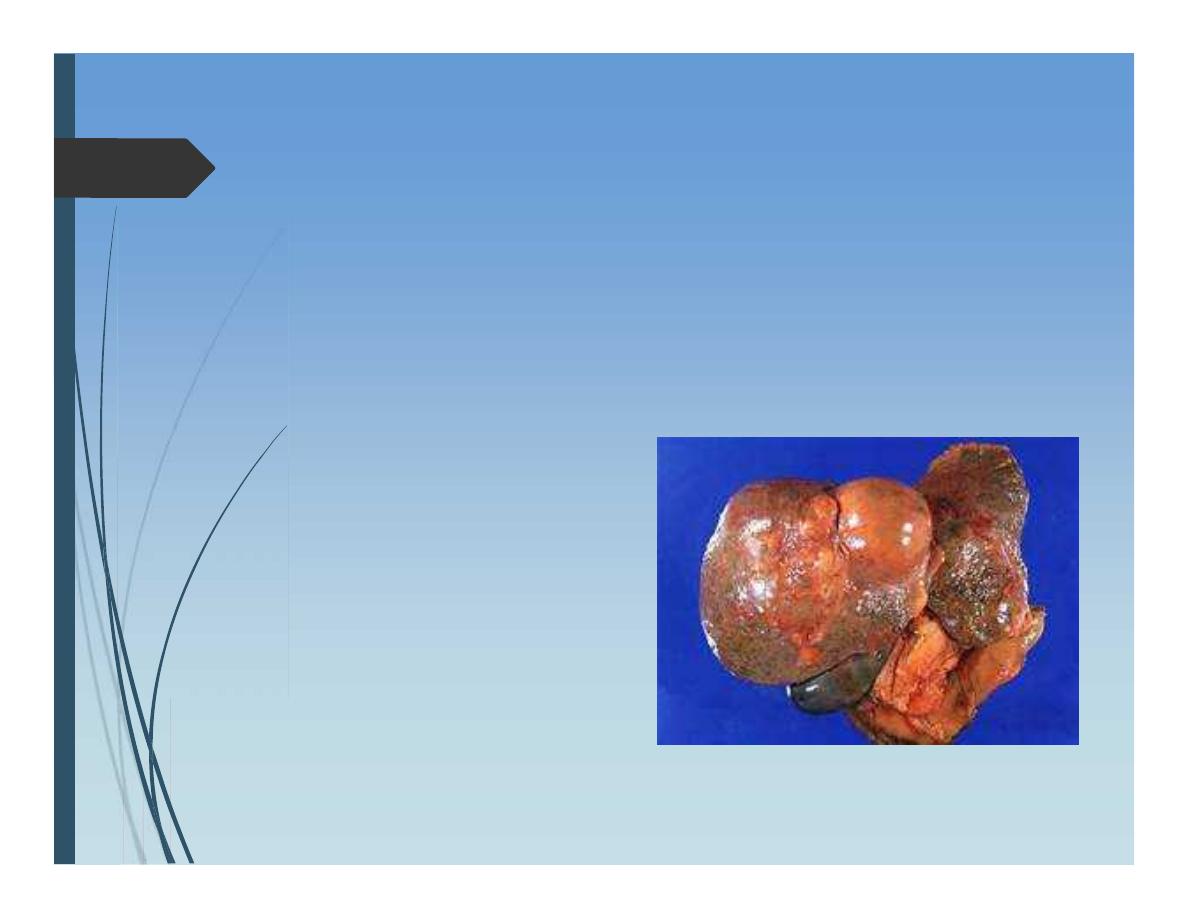
Liver tumors
Secondary metastesis
Metastatic colorectal cancer
Metastatic neuroendocrine cancer (carcinoid)
Other metastatic cancers
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Aetiology:
Association with chronic liver disease cirrhosis
HBV, HCV
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Presentation
Middle aged
Features of chronic liver disease
Anorexia and Weight loss
Hepatocellular carcinoma
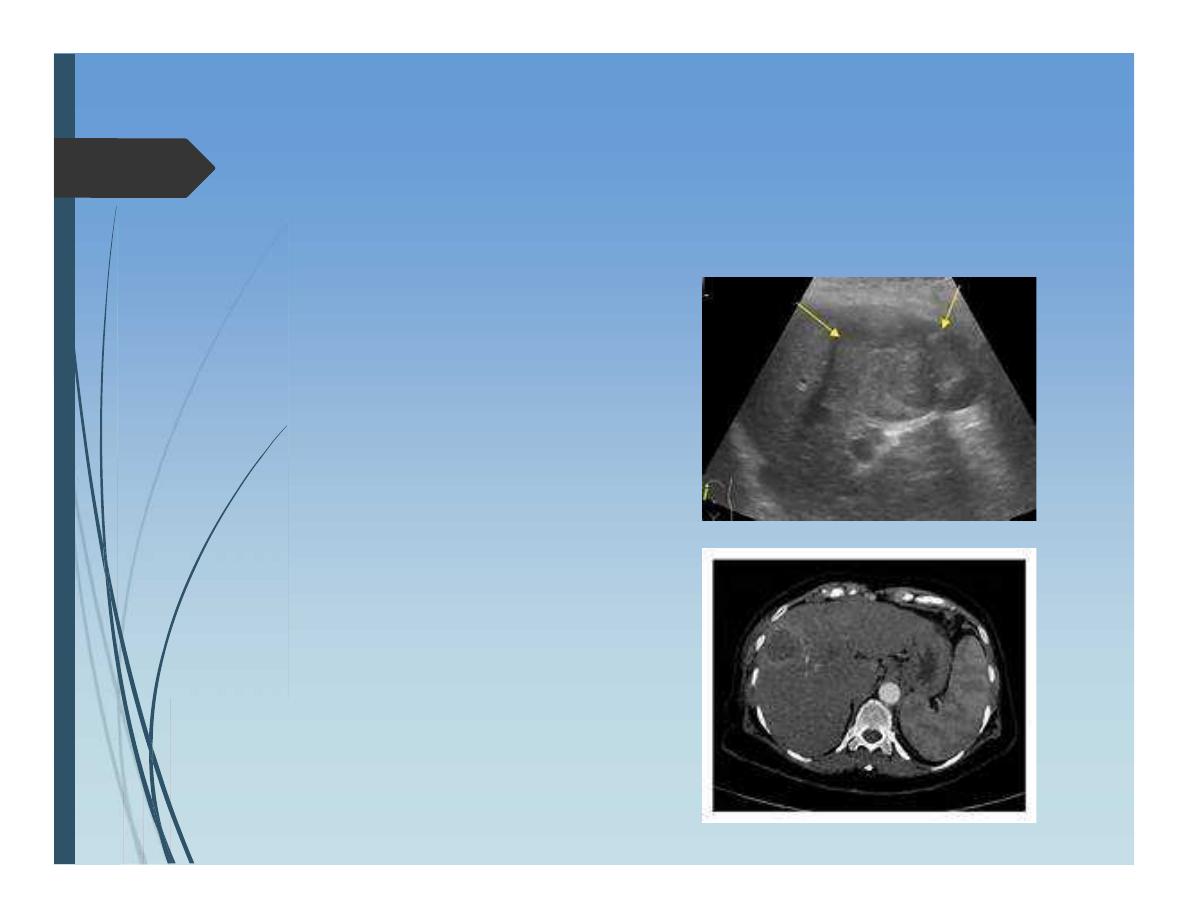
Diagnosis:
Ultrasound
CT scan
Alpha fetoprotein
For staging:
Chest scan
Bone scan
Laparoscopy
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Assessment of patient:
•General assessment
•Severity of underlying liver
disease “Child score”

Hepatocellular carcinoma
Treatment:
• Surgical resection
• Liver transplantation
Depend on:
• Staging of liver tumor
• Size and site of tumor
• Availability of organ transplantation
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Local Ablation techniques
Radiofrequency ablation
Ethanol ablation
Cryoablation
Microwave ablation
Regional liver therapies
Chemoembolization/embolization
Hepatic artery pump chemoperfusion
Palliative procedures

Hepatocellular carcinoma
Follow up:
• Chemotherapy ??
• Alpha fetoprotein as tumor marker
• Imaging

Cholangiocarcinoma
Elderly
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Site: confluence of right and left
hepatic ducts fibrous(Klatskin tumors)
Cholangiocarcinoma
Presentation:
Elderly patient with progressive painless jaundice
Cholangiocarcinoma
Diagnosis:
Ultrasound: dilated intrahepatic biliary passages but not
extrahepatic bile ducts.
Spiral CT scan little evidence of mass
Regional lymphadenopathy
Cholangiography: hilar stricture
Brush cytology + ve in 2/3rds

Cholangiocarcinoma
Treatment:
• Surgical resection:
• Radical resection of liver
parenchyma and the
affected bile ducts ---
potentially curative
• Local resection --- palliative

اﻟﻤﺤﺎﺿﺮة اﻟﺜﺎﻟﺜﺔ
Impaired liver function:
Depends on:
Severity of dysfunction
Rapidity; acute or chronic
Acute Liver Failure:
is defined by the presence of hepatic
encephalopathy occurring as the
consequence of severe liver damage
in a patient without a history of previous
liver disease or portal hypertension.
Acute Liver Failure:
Aetiology:
Viral Hepatitis, B, A, E, C,D
Drugs and toxins; halothane,
Overdose of Paracetamol
Mushroom poisoning
Acute Budd-Chiari syndrome
Wilson’s disease
Pregnancy –related
Indeterminate 20%
Acute Liver Failure:
Clinical presentation:
Jaundice
Cerebral edema “Hepatic encephalopathy”;
drowsiness, liver flap, confusion and finally coma
Acute Liver Failure:
Diagnosis:
Acute Liver Failure Laboratory Evaluation
Complete blood count
Complete metabolic panel
Arterial blood gas concentrations
ABO typing
Amylase and lipase levels
Acute hepatitis panel
Autoimmune marker levels
Ceruloplasmin level
Toxicology screening
Acetaminophen level
HIV screening
Pregnancy test (females)
Liver function tests
Bilirubin
Prothrombin time/international
normalized ratio
Alkaline phosphatase
AST, ALT
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Arterial serum ammonia level
Acute Liver Failure:
Treatment:
Supportive:
IV fluids electrolyte balance
Acid – base balance
Nutrition
Renal support hemofiltration
Antibiotics
Ventilation in coma
Mannitol for cerebral edema
Liver transplantation
Chronic liver disease
Clinical Features:
Lethargy and weakness
Jaundice
Hyperdynemic circulation:
High COP
Large pulse volume
Low blood pressure
Flushed extremities
Fever
Skin changes:
Spider naevi
Palmer erythema
White nails (leuconychia)
Endocrine abnormalites:
Hypogonadism
gynecomatsia
Hepatic encephalopathy
Portal hypertension
Flapping tremor of hands
Abdominal distension; Ascitis
Loss of muscle bulk and wasting
Child’s scoring
Group
A
B
C
Bilirubin mg/dl <2 2–3
>3
Albumin g/dl >3.5 3.0–3.5
<3.0
Encephalopathy None minimal advanced
Ascites
None Easily Controlled poorly
controlled
Nutrition
Excellent
Good
Wasting
Child class
Class A = 5–6 points
Class B = 7–9 points
Class C = 10–15 points

اﻟﻤﺤﺎﺿﺮة اﻟﺜﺎﻧﯿﺔ
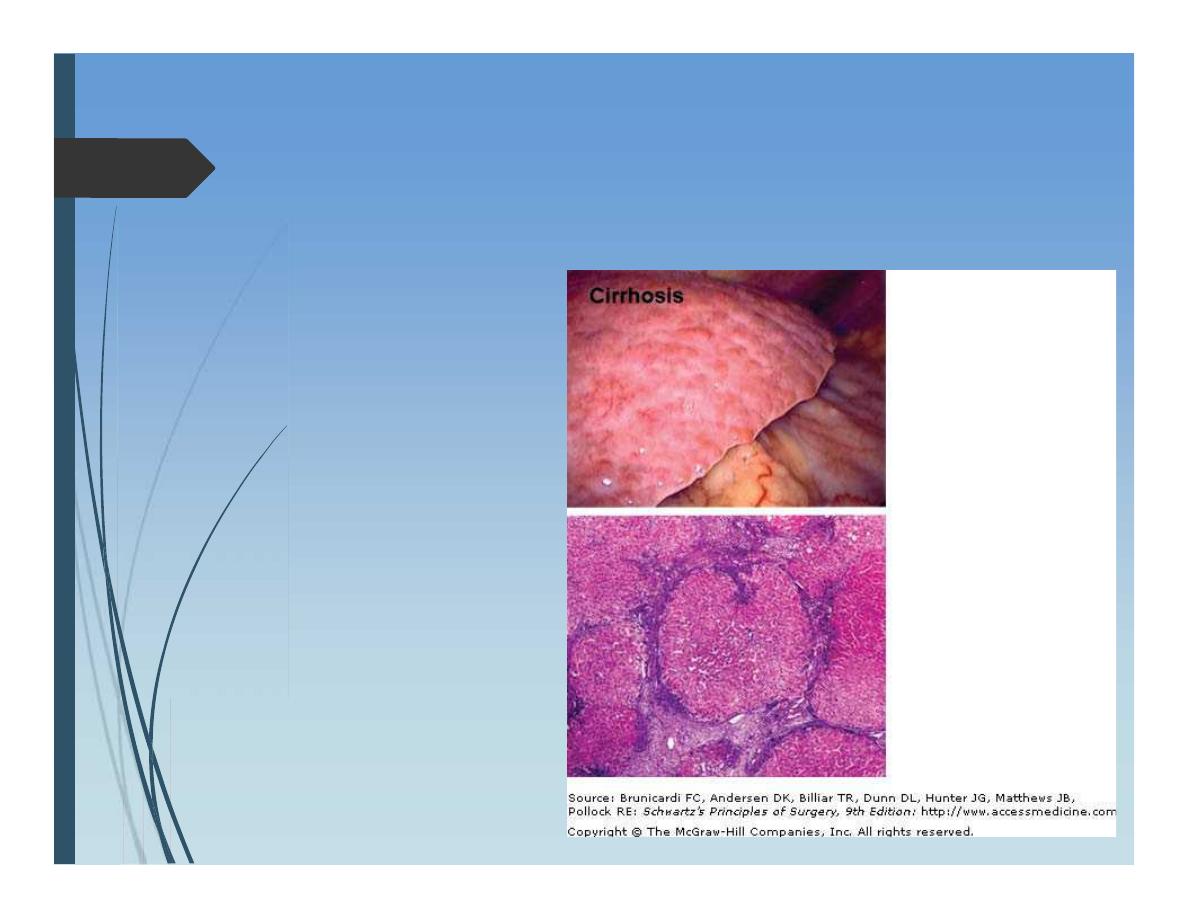
Liver cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is the consequence
of sustained wound healing
in response to chronic liver
injury.
Liver cirrhosis
Etiology of Cirrhosis
Viral hepatitis (hepatitis B, C, and D)
Cryptogenic
Alcohol abuse
Metabolic abnormalities
Iron overload (hemochromatosis)
Copper overload (Wilson's disease)
Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency
Glycogen storage disease (types IA, III, and IV)
Tyrosinemia
Galactosemia
Cholestatic liver disease
Hepatic vein outflow abnormalities
Budd-Chiari syndrome
Cardiac failure
Autoimmune hepatitis
Toxins and drugs