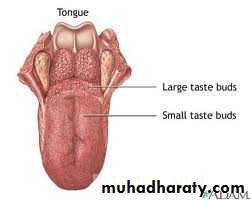
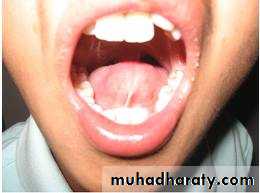
Tongue
Anomalies of the tongue
AglossiaTongue tie.
Bifid
Lingual thyroid
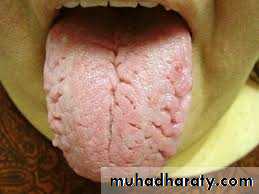
Congenical fissured tongue
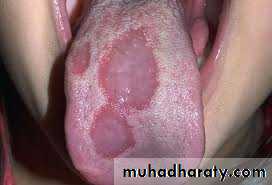
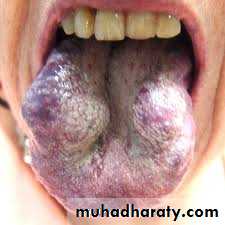
Geographic tongue
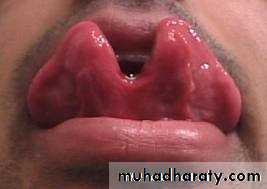
Macroglossia
Congenital causes of macroglossia
Cavernous haemangioma
A-V fistulaeLymphangioma
Neurofibromatosis
Aquired causes
- Muscular hypertrophy
- Amyloidosis
- Acromegaly
- Diffuse carcinoma ,sarcoma
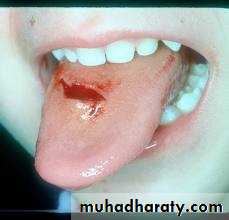
TONGUE INJURIES
Mechanism of injury :Tongue biting (epileptic fit )
Fracture jaw
C/F: bleeding ,if unconscious may be sever
Rx : arrest bleeding (pressure )
Suturing UGA
Haematoma may need tracheostomy
Inflammation of tongue
1- Acute :superficial (red, painful) or deep due to streptococcal infection or angioneurotic edema may need tracheostomy2- Chronic :
Due to irritation by smoking, denture ,sharp tooth.(erythroplakia then leukoplakia)
Treatment
Stop irritationWash with antiseptic
Excisional biopsy
Diathermy coagulation
3. Tuberculer glossitis
4 . Syphilitic glossitis at any stage of the disease 1ry ,2ry and 3ry.5. Candida glossitis (oral thrush)
6. Apthus ulcer
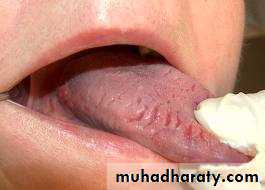
Tongue ulcer
1- Traumatic e.g. denture2- Inflammatory :
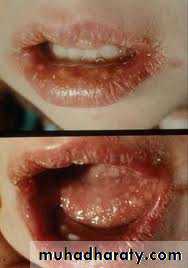
Acute : apthus painful 2 weeks spontaneous healing,lichin planus ,herpetic.
Chronic : tubercular ulcer (undermined edge +submandibular L.N
Treatment: anti TB +antiseptic wash +anesthetic jelly.
Syphilitic ulcer.
Chronic superficial glossitis.
3- Neoplastic :Scc (commonest),lymphoma.
The lip
Common lesions1- Herpis simplex infection :
- Fever
- Trauma
2- Malignant :carcinoma
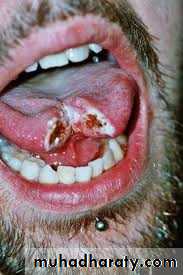
Carcinoma of the lip
Commonly in the lower lip away from the contact with the upper lip.Only 5%in the upper lip .
Spread
Laterally rather than deeply.
If uncontrolled it can spread to ant. Triangle of neck and invade the mandible.
L .n. metastasis late.
Treatment
Both surgery and radiotherapy are highly effective with cure rate 90%Up to one third of the lip can be removed with primary suture
Larger tumor needs facial flap.