
1
4
th
stage
Surgery
Lec-7
Dr.Ahmed
1/1/2016
Peritoneum
is a single layer of flat mesothelial cells resting on a bed of loose connective tissue .
Divided to two part :
- parietal
- visceral
Innervations
parietal is sensitive and innervated by both somatic and visceral afferent nerves.
insensitive .
Generalised septic peritonitis
Aetiology :m.o like E-coli ,aerobic and unaerobic strep. , bacteroids ,staph and pneumococci.
Source of infection
1- Local spread:
- infected organ: appendicitis
- leaking organ: perforated PU, anastamotic leak, extravasated urine.
2- Direct entry:operation
3- Blood spread:septicemia
4- Primary peritonitis :child,female,unknown .str. And pneumococci.
Pathology
Fate depends on
1. Virulance of m.o
2. Effect of treatment
3. Resistance of the body

2
Factors predispose to generalized peritonitis
1. High virulance m.o
2. Sudden perforation of viscous
3. Persistnt source of infection
4. Stimulation of peristalsis by e,ating,enema
5. Rough handling of localized collection during surgery
6. Immune suppretion (AIDS,STROID,D.M)
7. children ,elderly
Clinical picture
Examination
s ,rebound T.
Investigations
3
Treatment :
- Preoperative :
- NG suction
- I.V. Fluid
- Antibiotics
- Analgesia
-Urinary catheter
- Surgery
UGA
Mid line or paramedian
Pus send for C/S
Dealing with the pathology(appendix,D.U)
Peritoneal toilet
Drainage
-Post operative care
Continue antibiotics
I.V fluid
NG suction
Chart for assessment
Prevent septicemia
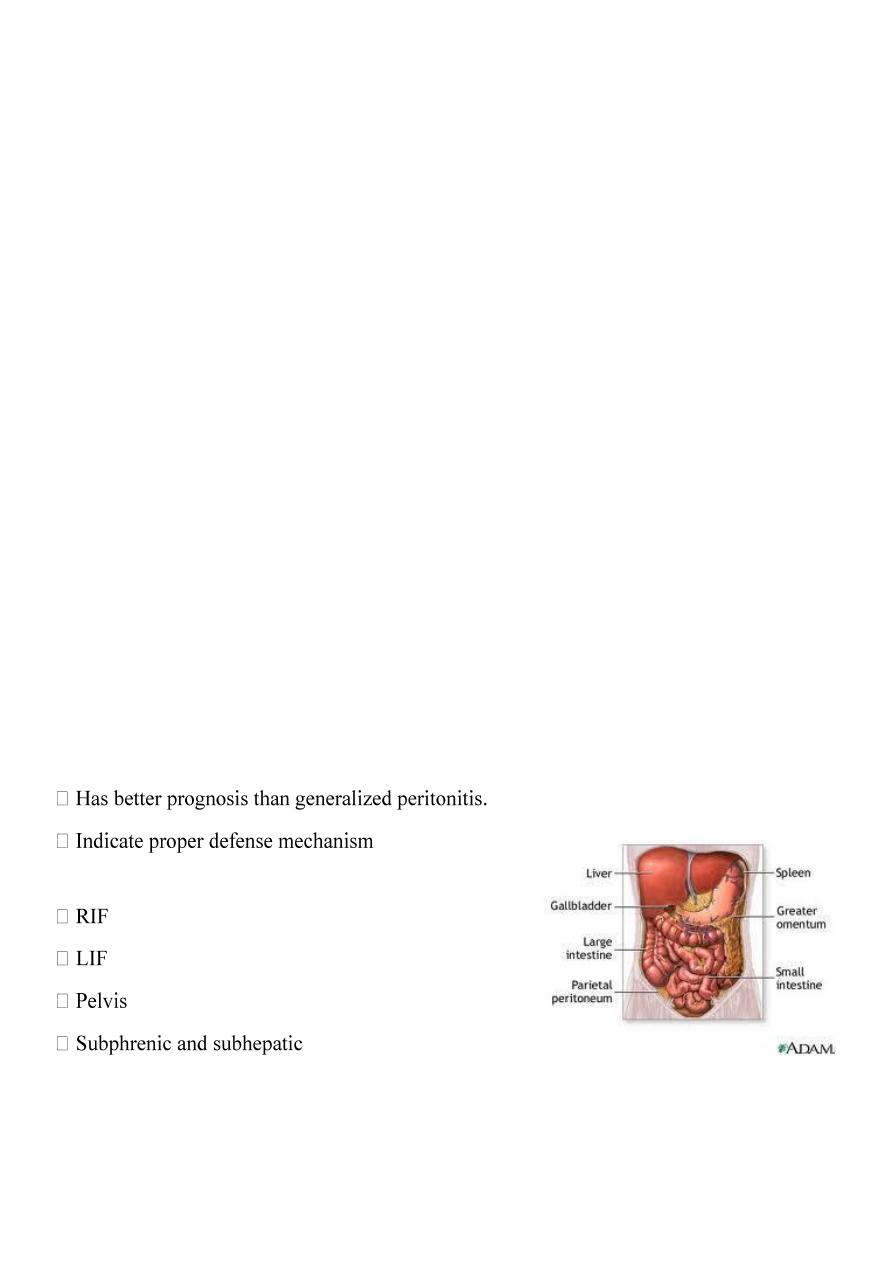
Localized intraperitoneal abscess
Common sites of collection

4
Iliac abscess
Clinical picture
Investigation
Treatment :
the cause
_ drainage should be done extraperitonealy through muscle cut incision.
_ percutaneous drainage under U/S or CT guide is preferable .
_ appendisectomy (interval)12 weeks
Pelvic abscess
Collection of pus in the recto-vesical pouch or Doglas pouch.
Causes:
- Acute appendicitis
- localization of resolving diffuse peritonitis
- pelvic inflammatary disease in female
Clinical picture
1. Hectic temp.
2. Deep pelvic pain
3. Diarrhea due to irritation of the rectum
4. Burning micturition ,friquency due to bladder irritation.
5. Suprapubic mass.
6. Rectal examination fullness ,tenderness in front of rectum

5
7. If neglected may rupture to rectum or vagina
Treatment
in rectum =trans – rectal
- vaginal through the post fornix
Subphrenic abscess
Further divided to subhepatic and suprahepatic , the falciform ligament divide it
to RT and LT.
Sub- phrenic space :
1- Right supra hepatic space :between R. leaf of diaph. And the sup. And ant.
Surface of the liver. Medially falciform ligament.
2- Right infrahepatic (hepato renal pouch of Morison):
above and ifront:the liver and GB
below and behind: upper pole of kidney ,lower part of RT suprarenal gland,
2
nd
part of the duodenum.
3- RT extra peritoneal space: between bare area of liver and the diaphragm.
4- Lt suprahepatic space:between diaph. Above and the stomach , spleen
below.
5- LT ant. Infrahepatic space :liver above ,stomach and lesser omentum below
and behind.
6- LT post. Infrahepatic: liver above ,stomach anteriorly, pancrease
posteriorly.
7- LT extra peritoneal space :around the upper part of the left kidney
Aetiology :
Residual pus collection from generalized peritonitis.

6
Perforated viscous.
Lymphatic spread from chest infection.
Post operative collection(bile, blood).
Clinical picture :
Eigastric Pain may referred to shoulder.
Hectic temp.
Tachycardia .
Anorexia, vomiting, sweating and wasting.
Persistent hicough
Examination :
Inspection : diminished chest wall movement with respiration and rarely
bulging upper abdomen.
Palpation :- tenderness below costal margin.
- rigidity on upper abdomen
- downward displacement of the liver and upward displacement of apex
beat.
Percussion :
- dullness of the pleural effusion
- resonance in the gas of abscess
- dullness of the liver and the pus of the abscess
Auscultation : impaired air entry over the lung base .
Investigations :
1- WBC count
2- CXR shows:
- thickened elevated diaph.
- pleural effusion
- air under diaph.(gas forming)
3- U/S
4- CT

7
Treatment :
If conservetive treatment failed ,
Drainage by aspiration extraperitoneal or extrapleural better.
1- 1-post. Extraperitoneal by excision of 12
th
rib +drain
2- ant. Extraperitoneal by incision subcostal.
3- aspiration under CT or U/S guide .
4- open drainage .
TB peritonitis
Secondary to primary focus that reach the peritoneum :
1- direct spread from L .N. ,salpingitis ,enteritis.
2- blood spread from pulmonary TB
3- lymphatic spread from pleura to bowel.
Pathology :
1- Acute type: the peritoneum studded with tubercles, straw color exudates.
2- Caseous :also tubercles ,multiple collections, cold abscess , sinus.
3- Ascetic type:(commonest)also tubercles , straw color fluid ,thickened
greater omentum,fibrous.
4- Encysted type(localized ascetic type).
5- Adhesive type: adhesions leads to I. O.
Clinical picture :
Children,young adult
Abdominal pain ,distention,vomiting.
High fever, anorexia, night sweating
Palpable swelling,ascitis.
Tenderness ,guarding may be.
Mass of rolled omentum above umbalicus.
PV. May reveal pelvic mass.

8
Investigation :
1. CBP and ESR
2. Tuberculin test Positive.
3. CXR
4. U/S
5. Ascetic fluid aspiration
6. Diagnostic laparoscopy, biopsy
7. Exploration laparotomy
Treatment :
Medical anti TB like INH, Rifadin
Surgery for Intestinal obstruction
Ascitis
Pathological accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity. It can be diagnosed
clinically when >1500 cc
Causes :
1. General causes:-liver ,cardiac, renal and nutritional disease
2. Local:- TB peritonitis, malignancy,chylous ascitis or pancreatic ascitis
3. Rare :- Meig’s syndrom(ovarian fibroma) , pseudomyxoma peritoni
Peritoneal tumor
Carcinoma peritonea:
pathology
- implantation from stomach, colon,overy.
- peritoneal nodules, bloody fluid
Treatment :
Radioactive gold intraperitonealy

9
Pseudomyxoma peritoni :
Causes :-
rupture of pseudomucinous cyst of the overy
rupture of mucocele or mucoid carcinoma of the appendix
Pathology :-
Abdomen full with jelly like material,
Clinically : abdomen distended with multiple masses
Treatment :
- laparatomy and removal of the material and the primary pathlogy.
- liable for recurence.
Mesothelioma :
- Primary neoplasm of the peritoneum .
- either present with ascitis or abdominal mass.
Mesenteric cyst
Collection of fluid between 2 layers of small bowel mesentry , 2 type:
1- False mesenteric cyst: - no epithelial lining like blood cyst due to trauma or
caseating L N (cold abscess)
2- True cyst:
- chylolymphatic cyst
- enterogenous cyst
- teratomatous dermoid cyst
- hydatid cyst
Clinical picture :
- Abdominal mass,pain,vomiting,dyspepsia
- The site near the umbalicus
- Moved in one direction
- Dull on percussion
Treatment : excision

11
Mesenteric lymphadenitis
Commonest cause of acute abdominal pain in children
Causes : unknown, viral following respiratory tract infection
Clinical picture :
- Affect children
- Upper abdominal pain and localized to RT side
- Pain colicky ,nausea, vomiting, anorexia and fever.
On examination :
- Guarding
- Tenderness
- PR tenderness positive
- Shifting tenderness
Treatment :
conservative and in doubtful cases appendicectomy
The retroperitoneum
Bounded by post. Perit. Anteriorly and spine and post. Abdominal muscles
posteriorly.
Superiorly the 12
th
rib and the diaphragm and inferiorly the pelvis
Retroperitoneal tumors
1- Renal ,adrenal gland tumors and L N
2- Retroperitoneal sarcoma
presented with mass (abdominal),pain,uretric obstruction and hadronephrosis.
Dx : CT,MRI,u/s.
Treated by surgery , radiotherapy as pallative .
3- Retroperitoneal lipoma
