بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
CEREBRAL PALSY
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
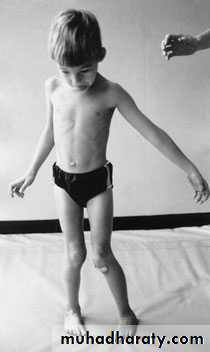
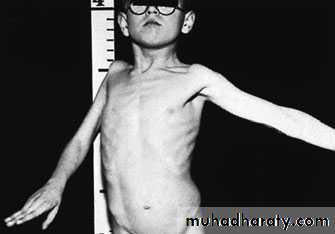
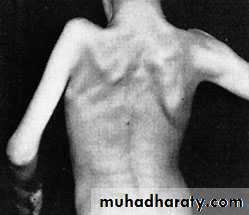
a group of disorders that result from non-progressive brain damage during early development and are characterized by abnormalities of movement and posture
causal factors are
maternal toxaemia,prematurity,
perinatal anoxia,
kernicterus and postnatal brain infections
birth injury, though often blamed, is a distinctly unusual cause.
Classification
Spasticity , is the commonest muscle movement disorderand is associated with damage to the pyramidal
system in the CNS.
Hypotonia , is usually a phase, lasting several years
during early childhood before the features of spasticity
become obvious
Athetosis. manifests as continuous, involuntary,
writhing movements which may be exacerbated
when the child is frightened. It is caused by damage
to the extrapyramidal systems of the CNS.
.
Dystonia, There is a more generalized increase in muscle tone and abnormal positions induced by activity.
• Ataxia. appears in the form of muscular incoordination during voluntary movements. It is usually due to cerebellar damage.
Mixed palsy, appears as a combination of spasticity and athetosis
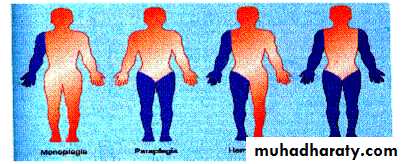
TOPOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION
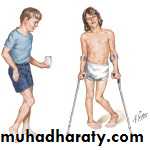
Hemiplegia is the commonest. This usually appears as a spastic palsy on one side of the body.Diplegia
involves both sides of the body, with thelower limbs always most severely affected
Total body involvement
describes a general and often more severe disorder affecting all four limbsMonoplegia
occasionally appears in an upper limb
Diagnosis in infancy
A history of prenatal toxaemia,haemorrhage,
premature birth,
difficult labour,
foetal distress or
kernicterus should arouse suspicion
Early symptoms
include difficulty in sucking andswallowing, with dribbling at the mouth. The mother
may notice that the baby feels stiff or wriggles awkwardly.
Diagnosis in later childhood
Most children presenting to the orthopaedic surgeon have already had the diagnosis made.Occasionally, for example with a mild hemiplegia or a symmetrical mild diplegia, the diagnosis has not been made and the child is simply referred for advice about their gait or their tendency to trip and fall
Tests for diagnosis in children over 1 year
The primitive neck-righting reflex,• asymmetrical and symmetrical tonic neck reflexes,
• the Moro reflex and the extensor thrustresponse should all have disappeared at 1 year of age.
.
Children who retain more than two primitive reflexes
after that age,cannot sit unsupported by 4 years and
cannot walk unaided by 8 years are unlikely ever towalk independently
Ideally the child should be reviewed by a multidisciplinary
team so that speech, hearing, visual acuity,intelligence and motivation can also be assessed.
Management
Medical treatmentBaclofen, acts by inhibiting reflex activity
Dantrolene. produces weakness without much
reduction in spasticity
Analgesic medication , for the reduction ofpain associated with musculoskeletal problems
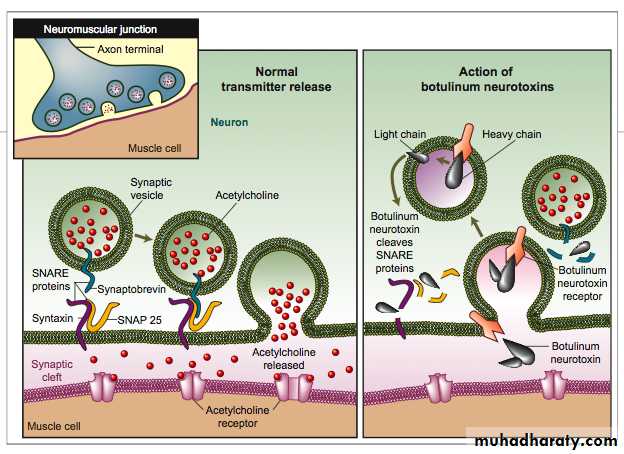
Botulinum toxin, This potent neurotoxin is produced
by Clostridium botulinum; it acts by blocking acetyl
choline release at the neuromuscular junction. The
preparation is injected into the ‘spastic’ muscle
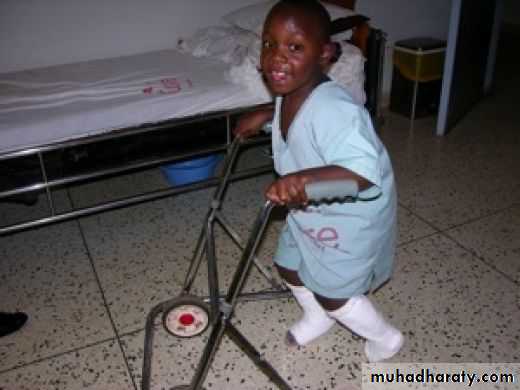
Physical therapy
Manipulation and serial casting
Operative treatment
The indications for surgery are:(1) a spastic deformity which cannot be controlled by conservative measures;
(2) fixed deformity that interferes with function; and
(3) secondary complications such as bony deformities, dislocation of the hip and joint instability.
Surgery
SplintageDeformity
Lengthen tendo Achillis
and transfer
lateral half of tibialis
anterior to cuboid
Spring-loaded
dorsiflexion
Bracing in
eversion and
dorsiflexion
Equinus
Equino varus
Foot
Hamstring release
Long caliperflexion
Knee
Obturator
neurectomy
Adductor muscle
release
Adduction
Hip –
Release elbow flexor
Flexion
ElbowLengthen or release
wrist flexors;
may
need fusion or
carpectomy
splint
Flexion wrist
Wrist
Lenghten or release flexor
flexion
Fingers –POLIOMYELITIS
Poliomyelitis is an acute infectious viral disease,Spread by the oropharyngeal route, that passes through several distinct phases.
Clinical features
Poliomyelitis typically passes through several clinical phases,from an acute illness resembling meningitis to
paralysis, then
slow recovery or convalescence
and finally the long period of residual paralysis.
The disease strikes at any age but most commonly in children
The acute illness
Early symptoms are
fever and
Headache.
in about one-third of cases the patient gives a history of a minor illness with sore throat, mild headache and slight pyrexia 5–7 days before
Paralysis
Soon muscle weakness appears; it reaches apeak in the course of 2–3 days and may give rise to difficulty with breathing and swallowing.
Recovery and convalescence
A return of muscle poweris most noticeable within the first 6 months, but there
may be continuing improvement for up to 2 years.
Post polio syndrome
Treatment
Depending on the stage .Stage of onset.
Greatest paralysis.
Recovery.
Residual deformity.
Early treatment
.During the acute phase the patient is isolated and kept at complete rest, with symptomatic treatment for pain and muscle spasm. Active movement is avoided but gentle passive stretching helps to prevent contractures.
Late treatment
Passively correctible deformityResidual paralysis
Fixed deformity
Flail joint
Shortening
Vascular dysfunction Sensation is intact but the paralyzed limb is often cold and blue
operative treatment
Two main group of operationsArthrodesis of joints.
Muscle or tendon transfers.