
1
Fifth stage
Medicine
Lec-5
د . منوع
1/1/2014
LIPID-LOWERING DRUGS
Objectives
Describe the groups of lipid lowering drugs
Describe the mode of action
Their indication
The clinical use
Indications
To prevent cardiovascular disease in all those at high risk of atherosclerosis,include
Those who already have atherosclerotic disease
Diabetics aged over 40 years.
Abnormal lipid concentration
Other risk factors
( smoking ,blood pressure, impaired glucose tolerance, male sex,
age, premature menopause ,ethnicity, obesity, triglyceride concentration, and a
family history of premature cardiovascular disease).
Those with a 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease of 20 %
or more stand to benefit
from drug treatment.
Lowering the concentration of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and raising high-
density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol slows the progression of atherosclerosis.
Lipid-regulating drug treatment must be combined with
Advice on diet and lifestyle measures ,
Lowering of raised blood pressure .
Management of diabetes.
For preventing cardiovascular disease events in those at high risk
A target total cholesterol concentration of less than 4 mmol/litre
( or a reduction of
25 %
if that produces a lower concentration )and
A target LDL-cholesterol concentration of less than 2 mmol/litre
( or a reduction of
30 %
if that produces a lower concentration).

2
Classification
STATINS (HMG CoA) reductase inhibitors
(Atorvastatin ,Fluvastatin ,Pravastatin ,Rosuvastatin ,And Simvastatin)
Competitively inhibit 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a (HMG COA) reductase, an
enzyme involved in cholesterol synthesis in the liver.
More effective than other lipid-regulating drugs at lowering LDL-Cholesterol
concentration but they are less effective than the fibrates in reducing triglyceride
concentration.
However, statins reduce cardiovascular disease events and total mortality irrespective
of the initial cholesterol concentration.
Indications
All patients with coronary heart disease
( history of angina or acute myocardial
infarction ,)occlusive arterial disease
( peripheral vascular disease, non-haemorrhagic
stroke, or transient ischaemic attacks).
For all patients over 40 years with diabetes mellitus
Prevention of cardiovascular disease in asymptomatic individuals at increased risk (10-
year cardiovascular disease risk of 20 %
or more)
Caution
History of liver disease or with a high alcohol intake
( should be avoided in active liver
disease).
Liver-function tests should be carried out before and within 1–3 months of starting
treatment and thereafter at intervals of 6 months for 1 year
Hypothyroidism should be managed adequately before starting treatment with a
statin .
Caution if there is risk for myopathy or rhabdomyolysis
Avoided in porphyria

3
Contraindication
Active liver disease (or persistently abnormal liver function tests),
In pregnancy (adequate contraception required during treatment and for 1 month
afterwards)
Breast-feeding
Side effects
Reversible myositis is a rare but significant side-effect.
Headache
Altered liver-function tests ( rarely, hepatitis)
Paraesthesia
Gastro-intestinal effects (abdominal pain, flatulence, constipation, diarrhoea ,nausea
and vomiting).
Rash and hypersensitivity reactions (including angioedema and anaphylaxis) rarely
ATORVASTATIN (LIPITOR)
Primary hypercholesterolaemia and combined hyperlipidaemia ,10 mg once daily ;
increased at intervals of at least 4 weeks to max .80 mg once daily
Familial hypercholesterolaemia, initially 10 mg daily, increased at intervals of at least 4
weeks to 40 mg once daily; if necessary, further increased to max 80 mg once daily (or
40 mg once daily combined with anion-exchange resin in heterozygous familial
hypercholesterolaemia)
Prevention of cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes ,10 mg once daily
FLUVASTATINE
( LESCOL(
Hypercholesterolaemia or combined hyperlipidaemia, initially 20–40 mg daily in the
evening, adjusted at intervals of at least 4 weeks; up to 80 mg daily
Prevention of progression of coronary atherosclerosis, 40 mg daily in the evening
Following percutaneous coronary intervention, 80 mg daily
ROSUVASTATINE
( CRESTOR(
Initially 5–10 mg once daily increased if necessary at intervals of at least 4 weeks to 20 mg
once daily, increased after further 4 weeks to 40 mg daily
( only in severe
hypercholesterolaemia with high cardiovascular risk and under specialist supervision)
Elderly initially 5 mg once daily

4
Patient of asian origin, initially 5 mg once daily increased if necessary to max .20 mg
daily
SIMVASTATINE
( ZOCOR(
Primary hypercholesterolaemia, combined hyperlipidaemia ,10–20 mg daily at night,
adjusted at intervals of at least 4 weeks; usual range 10–80 mg once daily at night
Homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia ,40 mg daily at night or 80 mg daily in 3
divided doses (with largest dose at night)
Prevention of cardiovascular events, initially 20–40 mg once daily at night, adjusted at
intervals of at least 4 weeks ;max .80 mg once daily at night
FIBRATES
Bezafibrate ,Ciprofibrate ,Fenofibrate ,and Gemfibrozil
Act mainly by decreasing serum triglycerides; they have variable effects on LDL-
cholesterol .
Although a fibrate may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease events in those with
low HDL-cholesterol or with raised triglycerides, a statin should be used first .
Fibrates may be considered first-line therapy in those whose serum-triglyceride
concentration is greater than 10 mmol/litre.
Caution
Fibrates can cause a myositis-like syndrome, especially if renal function is impaired .
Combination of a fibrate with a statin increases the risk of muscle effects (especially
rhabdomyolysis) -gemfibrozil and statins should not be used concomitantly.
Monitoring of liver function and creatinine kinase should be considered
Contraindication
Severe hepatic impairment
Renal impairment
Hypoalbuminaemia
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Gall bladder disease
Nephrotic syndrome
Pregnancy

5
Breast-feeding
Side effects
Gastro-intestinal disturbances
Rash, pruritus
less commonly
headache, fatigue, dizziness, insomnia
rarely
Gallstones ,hepatomegaly, cholestasis, hypoglycaemia, impotence, anaemia,
leucopenia ,thrombocytopenia, increased risk of bleeding, alopecia, photosensitivity
reactions, raised serum creatinine (unrelated to renal impairment), and myotoxicity
Bezafibrate
( bezalip)
200 mg 3 times daily
fenofibrate
200 mg 1 capsule daily
Gemfibrazole
(
lopid
(
300
mg cap
600mg
tab (0.9 – 1.2 gm/day)
Indications
Hyperlipidaemias of types IIa ,II b ,III, IV and V in patients who have not responded
adequately to diet and other appropriate measures
Side effects
Gastro-intestinal disturbances
Headache ,fatigue, vertigo
Eczema ,rash
less commonly
Atrial fibrillation
Rarely
pancreatitis ,appendicitis, disturbances in liver functin, dizziness, paraesthesia,
sexual dysfunction, thrombocytopenia, anaemia, leucopenia, eosinophilia, bone-
marrow suppression, myalgia, myopathy, myasthenia, myositis, blurred vision ,
exfoliative dermatitis, alopecia, and photosensitivity

6
Anion-exchange resins
Cholestyramine
, Colestipol
Act by binding bile acids, preventing their reabsorption; this promotes hepatic
conversion of cholesterol into bile acids; the resultant increased LDL-receptor activity
of liver cells increases the clearance of LDL-cholesterol from the plasma
Thus effectively reduce LDL-cholesterol but can aggravate hypertriglyceridaemia.
Caution
Interfere with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins; supplements of vitamins A, D and K
may be required when treatment is prolonged .
Side effects
Gastro-intestinal side-effects predominate. Constipation is common ,diarrhoea ,
nausea, vomiting, and gastro-intestinal discomfort .
Hypertriglyceridaemia may be aggravated .
Increased bleeding tendency has been reported due to hypoprothrombinaemia
associated with vitamin K deficiency.
Cholestyramine
(4 g/sachet )
Hyperlipidaemias ,particularly type IIa, in patients who have not responded adequately
to diet and other appropriate measures
Pruritus associated with partial biliary obstruction and primary biliary cirrhosis
Diarrhoeal disorders
Dose
Lipid reduction 12–24 g daily in water, in single or up to 4 divided doses; up to 36 g
daily
Ezetimibe
Inhibits the intestinal absorption of cholesterol .
Ezetrol
(10 mg once daily)
Indications
Adjunct to dietary manipulation in patients with primary hypercholesterolaemia in
combination with a statin or alone
In homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia in combination with a statin

7
Caution
Hepatic impairment (avoid if moderate or severe(
Pregnancy
If ezetimibe is used in combination with a statin, there is an increased risk of
rhabdomyolysis
Side effect
Gastro-intestinal disturbances
Headache ,fatigue, myalgia
Rarely
Arthralgia ,hypersensitivity reactions including rash and angioedema, hepatitis
Very rarely
Pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, thrombocytopenia, raised creatine kinase,
myopathy, and rhabdomyolysis
NICOTINIC ACID ( VIT B3)
Reduce perepherral fatty acid release
lowers both cholesterol and triglyceride
increases HDL-cholesterol.
Indicated as adjunct to statin in dyslipidaemia or used alone if statin not tolerated
Dose Initially 100–200 mg 3 times daily, gradually increased over 2–4 weeks to 1–2 g 3
times daily
Cautions
Unstable angina, acute myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, gout ,peptic ulceration\,
hepatic impairment, renal impairment, pregnancy
Contra-indications
Arterial bleeding; active peptic ulcer disease; breast-feeding
Side-effects
Vasodilatation, flushing, itching, rashes, urticaria, erythema ;heartburn, epigastric pain,
nausea, diarrhoea, headache, malaise, dry eyes ;rarely angioedema, bronchospasm,
anaphylaxis
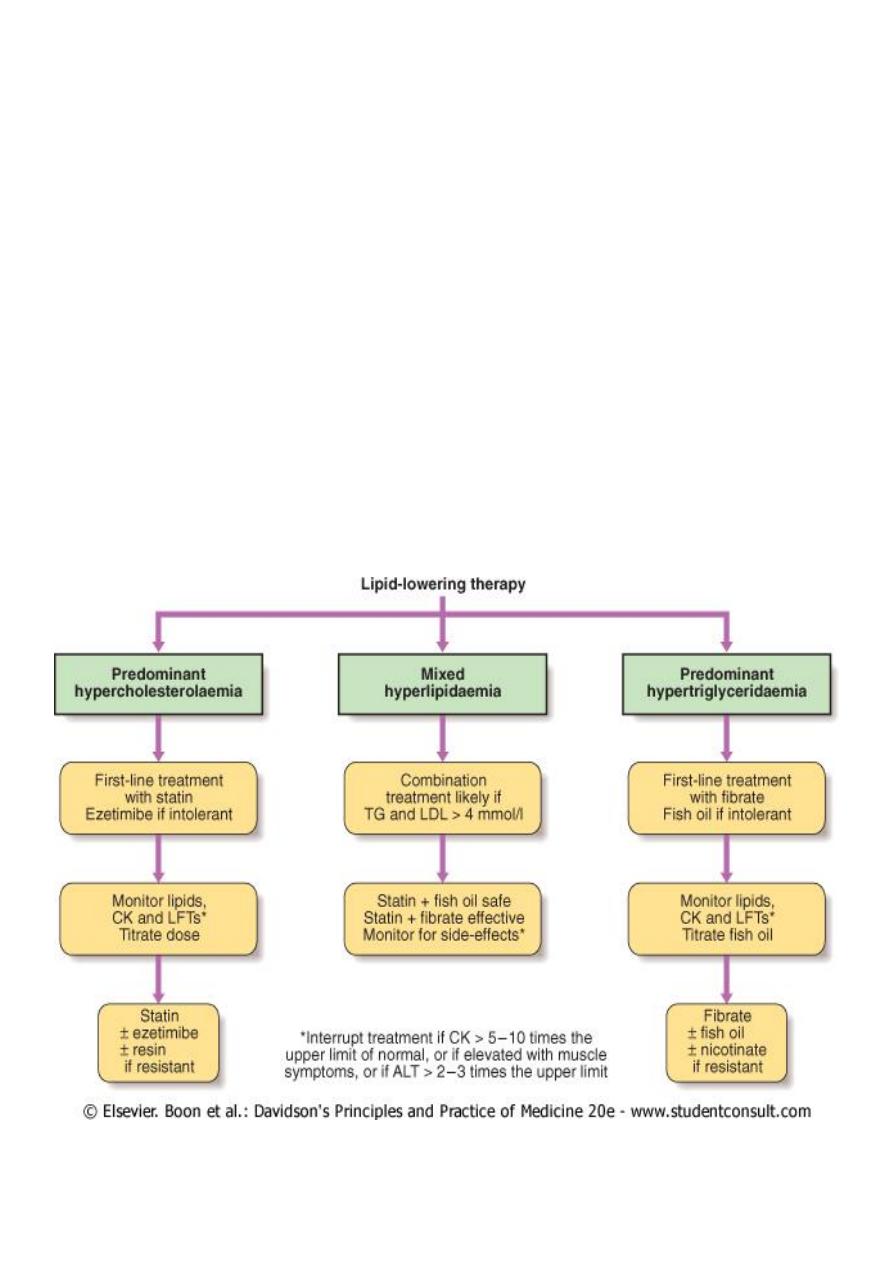
8
Omega-3 fatty acid compounds
Omega-3 fatty acid compounds may be used to reduce triglycerides, as an alternative
to a fibrate and in addition to a statin, in patients with combined (mixed)
hyperlipidaemia not adequately controlled with a statin alone .
A triglyceride concentration exceeding 10 mmol/litre is associated with acute
pancreatitis and lowering the concentration reduces this risk .
caution
haemorrhagic disorders, anticoagulant treatment (bleeding time increased) hepatic
impairment. pregnancy
Side effects
Gastro-intestinal disturbances
Less commonly taste disturbances, dizziness, and hypersensitivity reactions
Rarely hepatic disorders, headache, hyperglycaemia, acne, and rash
