1
Fifth stage
Medicine
Lec-16
د.خالد نافع
1/5/2016
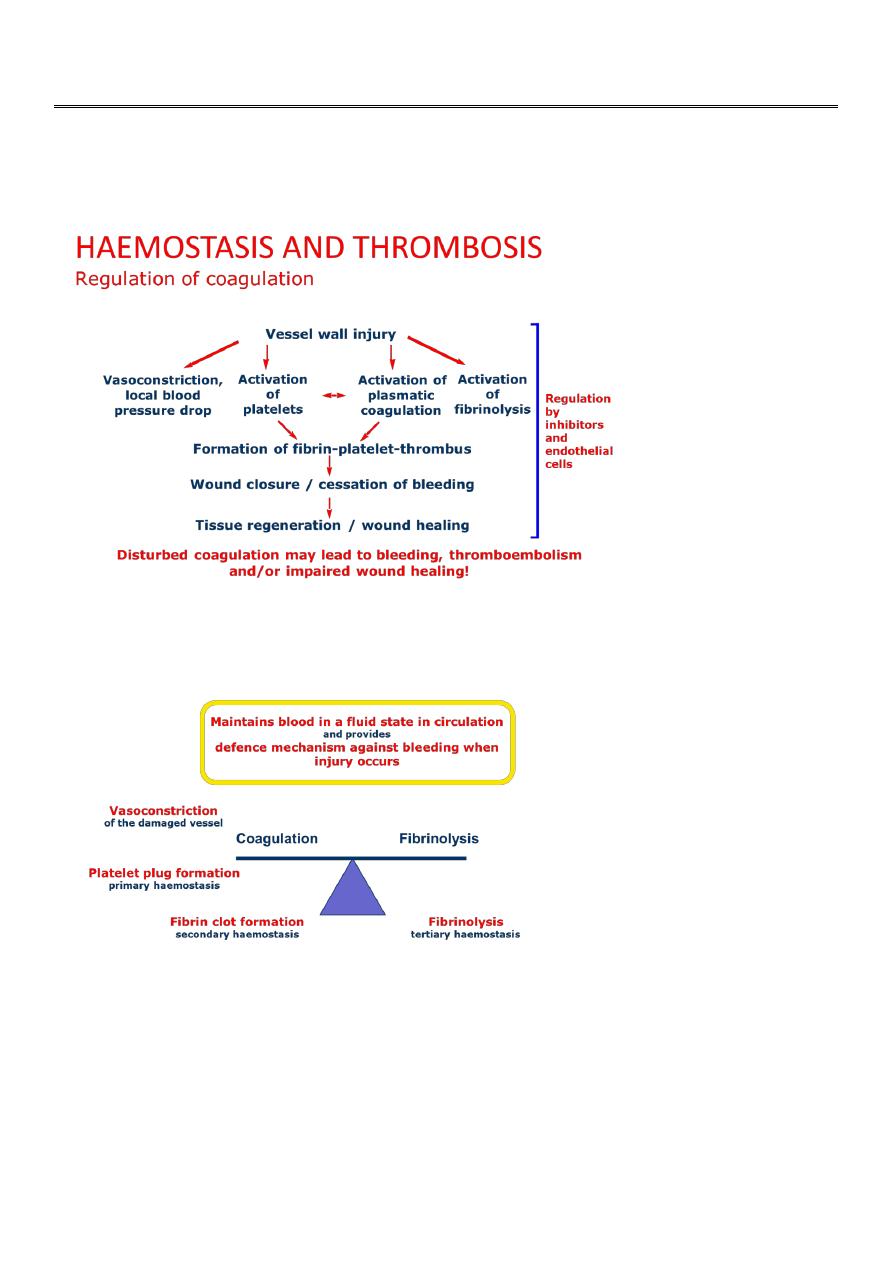
HAEMOSTASIS AND THROMBOSIS
What is haemostasis?
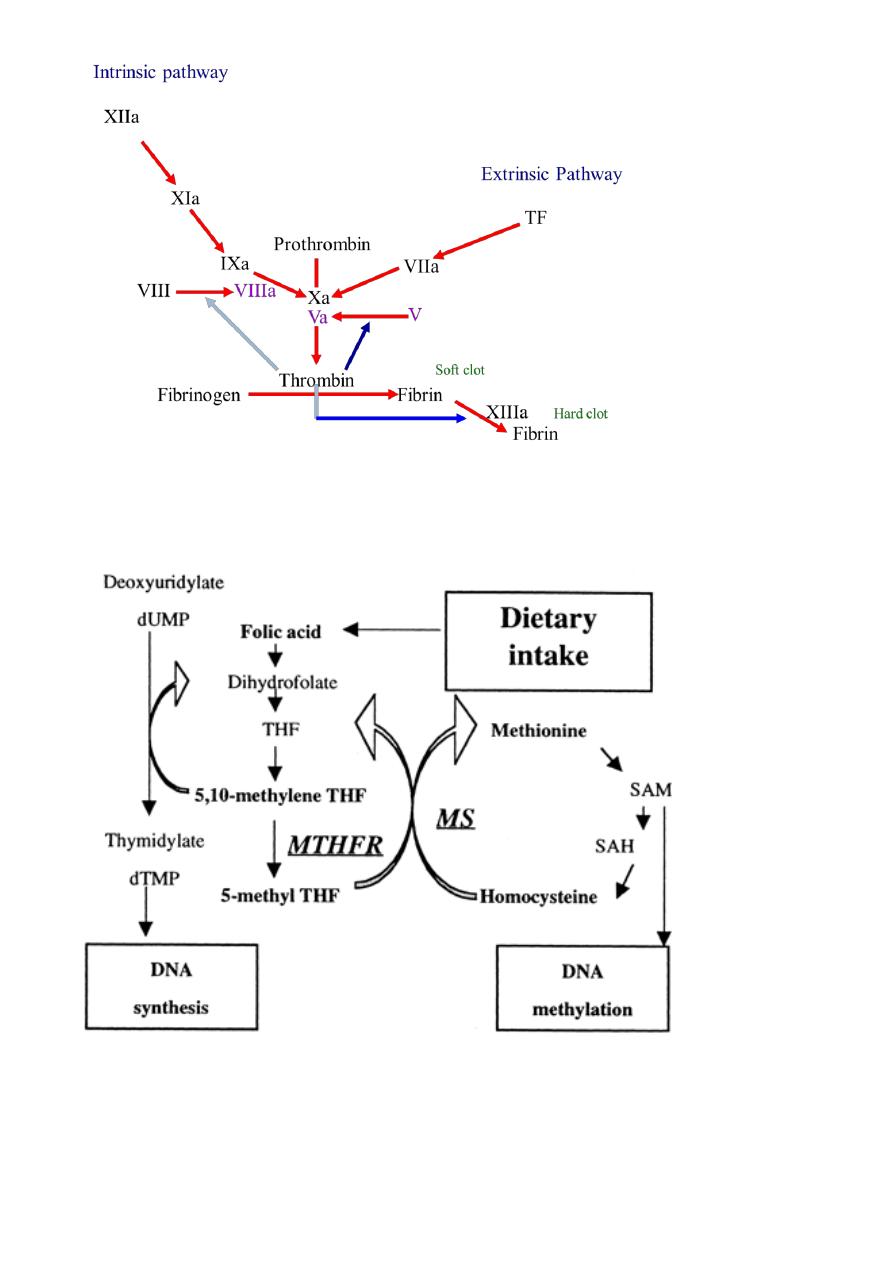
What is the function of thrombin?
Activates platelets
Activates FVIII and FV
Activates FXIII necessary for the formation of fully stabilized fibrin clots/plugs
Activates FXI (feed-back loop leading to more thrombin formation via FIX)
Activates TAFI (thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor)
Necessary for haemostasis
2
Summary
o Initiation
TF complexes with FVIIa, which activates FX to FXa
FXa generates small amount of thrombin on surface of TF-bearing
cells with FVa as co-enzyme
FVIIa also activates FIX to FIXa
o Amplification
Thrombin activates platelets
Thrombin cleaves FVIII from vWF and FVIII is activated to FVIIIa
Thrombin activates FXI and FV
o Propagation
FIXa-FVIIIa complex generates FXa on the surface of activated platelets
This FXa generates a huge thrombin burst
Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin
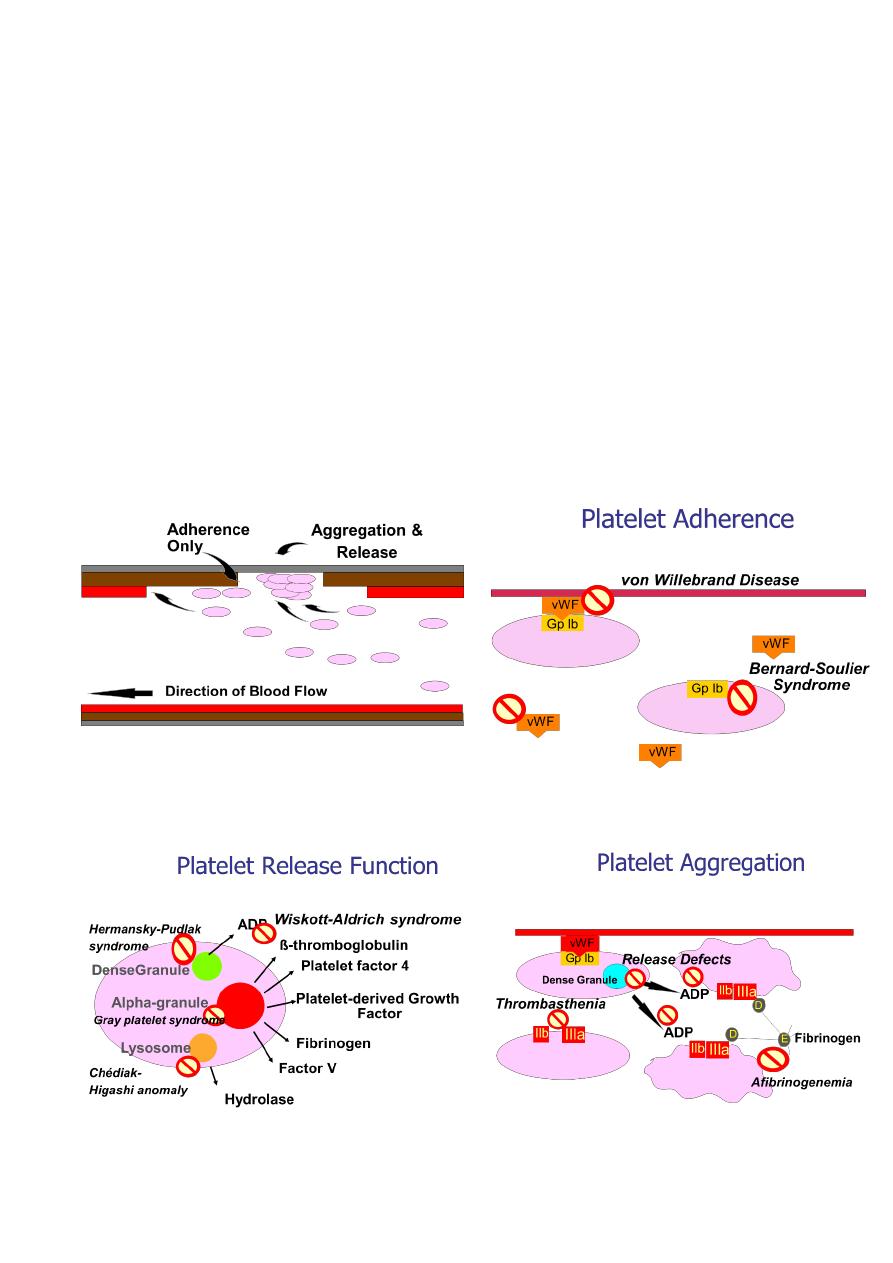
Platelet Function
3
Antithrombotic Properties of the Endothelium
Anti-platelet properties
Healthy endothelium does not bind platelets
Produce PGI-2 (prostacyclin) and NO (Nitric Oxide), which inhibit platelet binding
Produce ADP-ase which counters the platelet aggregating effects of ADP
Anticoagulant properties
Produce Heparin-like proteoglycans which activate anti-thrombin
Produce Thrombomodulin which make a complex with thrombin (TM.T complex ) and
activates protein C ,a
Produce tPA which activates fibrinolysis by activating plasminogen to plasmin
Prothrombotic Properties of the Endothelium
Synthesis of von Willebrand factor
Release of tissue factor
Production of plasminogen activator inhibitors (PAI)
Membrane phospholipids bind and facilitate activation of clotting factors via Ca++
bridges
Virchow’s Triad
Pathogenesis of a Thrombus
Endothelial injury
Abnormal blood flow
Hypercoagulability
Genetic
acquired
4
Folate and Homocysteine Metabolic Pathways
