
1
Fifth stage
Pediatric
Lec-3
.د
أوس
14/12/2015
CHRONIC DIARRHOEA
• chronic or persistent diarrhea is defined as an episode that lasts longer than 14 days.
• four principle pathophysiologic mechanisms: osmotic, secretory, dysmotility
associated, and inflammatory
1- Osmotic diarrhea is caused by a failure to absorb a luminal solute, resulting in secretion
of fluids and net water retention across an osmotic gradient(best exemplified by the
common disorder of lactose malabsorption) , either because of dissacharidase deficiencies
or because the absorptive capacity of the intestine for that sugar may be overwhelmed by
excessive consumption, eg, fructose and sorbitol. Such excessive intake may be seen in
young children drinking fruit juices
2- Secretory diarrhea occurs when there is a net secretion of electrolyte and fluid from the
intestine without compensatory absorption, Children with a pure secretory diarrhea will
therefore continue to experience diarrhea even while fasting. (Congenital chloride diarrhea)
3- Chronic diarrhea associated with intestinal dysmotility typically occurs in the setting of
intact absorptive abilities. Intestinal transit time is decreased, the time allowed for
absorption is minimized, and fluid is retained within the lumen(diarrhea-predominant
irritable bowel syndrome (IBS))
4- Inflammatory diarrhea (may encompass all of the pathophysiologic mechanisms) .
Inflammation with resultant injury to the intestine may lead to malabsorption of dietary
macronutrients which, in turn, creates a luminal osmotic gradient. Additionally, particular
infectious agents may induce secretion of fluid into the lumen, and blood in the gut may
alter intestinal motility. Diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and celiac
disease
AETIOLOGY
1- Enteric infections are by far the most frequent cause of chronic diarrhea, both in
developing and industrialized countries
2
2- Lactose intolerance or carbohydrate malabsorption may be caused by a brush-border
enzyme defect in lactase or other enzymes--More commonly, lactose intolerance is
secondary to lactase deficiency caused by intestinal mucosal damage.
3- Allergy to cow’s milk protein and other food proteins also may present during infancy
with chronic diarrhea
4- Chronic diarrhea may be the manifestation of maldigestion caused by exocrine
pancreatic disorders. In most patients with cystic fibrosis, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
results in steatorrhea and protein malabsorption
5- The most benign etiology of chronic diarrhea is nonspecific diarrhea that encompasses
functional diarrhea (or toddler’s diarrhea) in children younger than 4 yr of age and irritable
bowel syndrome in those 5 yr of age and older. The diseases fall under the umbrella of
functional disorders, in that in older children abdominal pain is often associated with
diarrhea alternating with constipation and growth and weight gain are normal
6- In older children and adolescents, inflammatory bowel diseases, including Crohn
disease, ulcerative colitis cause chronic diarrhea that is often associated with abdominal
pain, elevated inflammatory markers
7- Diarrhea may be the result from an excessive intake of fluid and carbohydrate(fruit
juice). If the child’s fluid intake were >150 mL/kg/24 hr, fluid intake should be reduced not
to exceed 90 mL/kg/24 hr
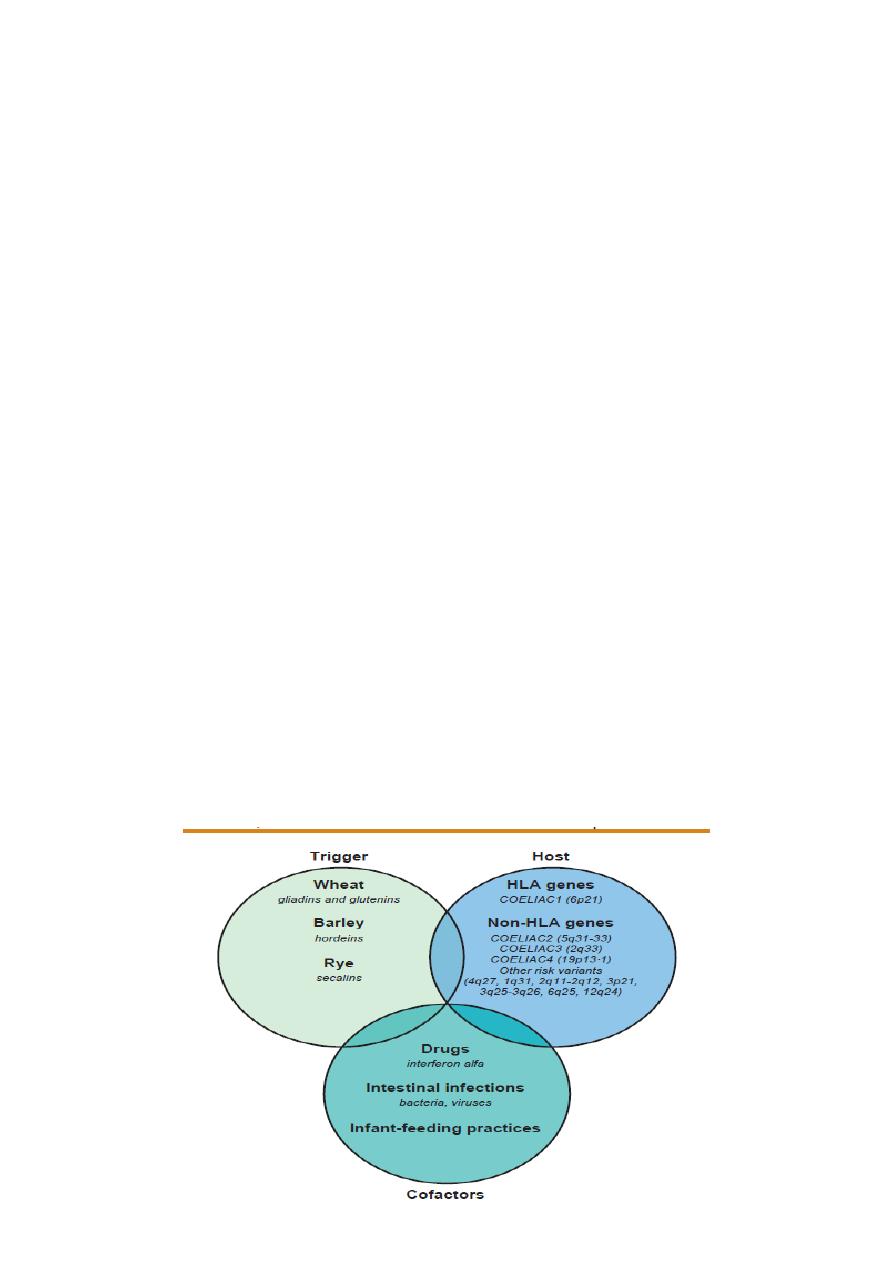
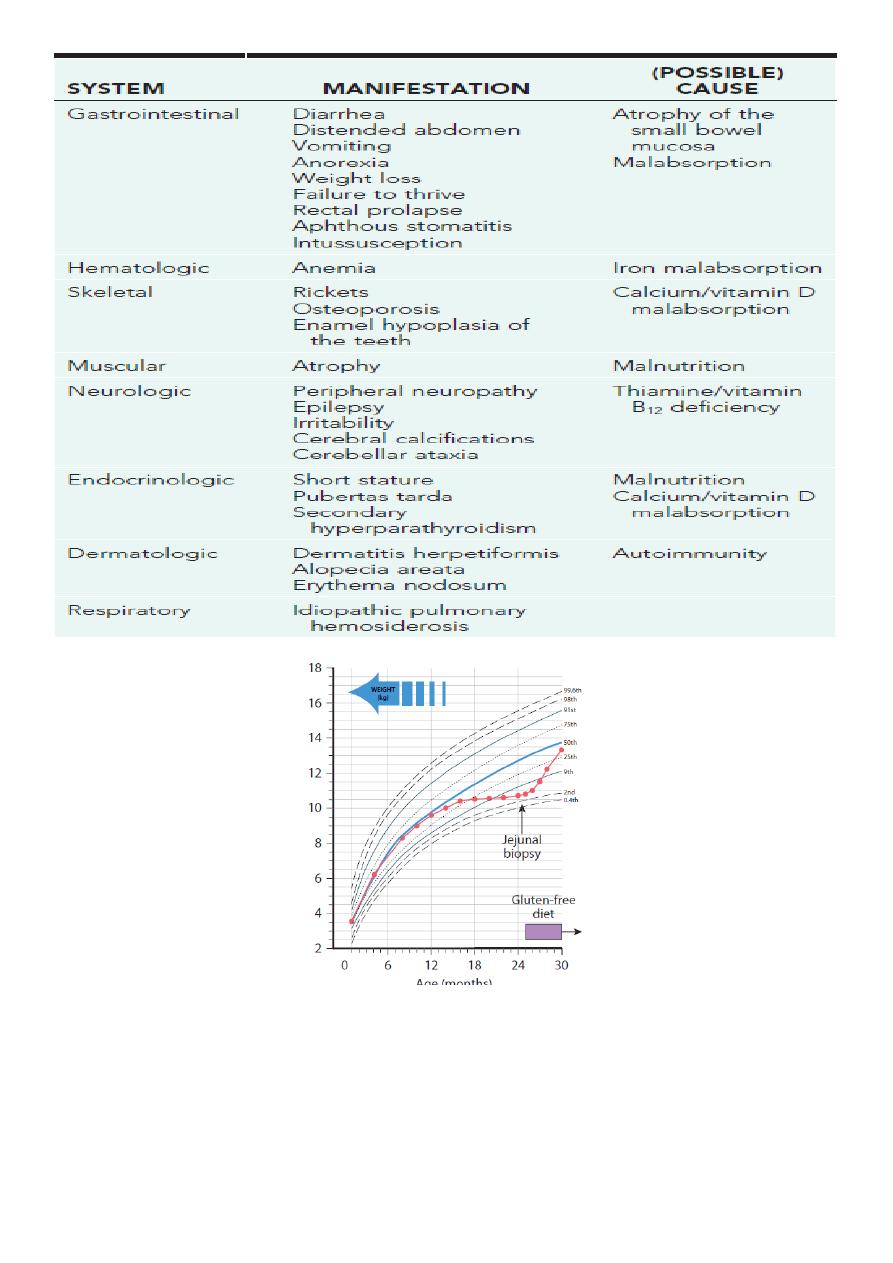
8- A reduction of intestinal absorptive surface is responsible for diarrhea in celiac disease, a
genetically determined permanent gluten intolerance that affects as many as 1 in 100
individuals, depending on geographic origin. In the genetically susceptible host, gliadin, the
major protein of gluten, reacts with the immune system to cause villous atrophy. The
reduction of functional absorptive surface area is reversible upon restriction of gluten from
the diet.
3
DIAGNOSIS
• The diagnosis of celiac disease is based on a combination of symptoms,antibodies,
HLA, and duodenal histology
TREATMENT
• The only treatment for celiac disease is lifelong strict adherence to a gluten-free diet
.This requires a wheat-, barley-, and rye-free diet
